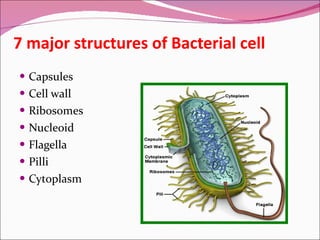
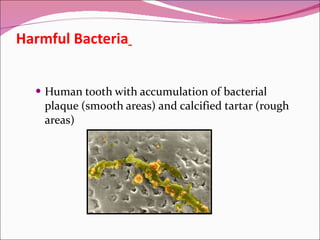
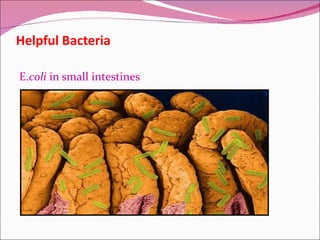
The document discusses microorganisms, specifically bacteria. It notes that bacteria are microscopic organisms found almost everywhere. It then describes the Kingdom of Monera, where bacteria belong. Bacteria are prokaryotes, meaning they lack nuclei and organelles. The structures of bacterial cells are also outlined, including the cell wall, ribosomes, flagella, and cytoplasm. The document discusses both harmful bacteria that can cause disease and helpful bacteria that decompose waste, produce antibiotics, and aid digestion.