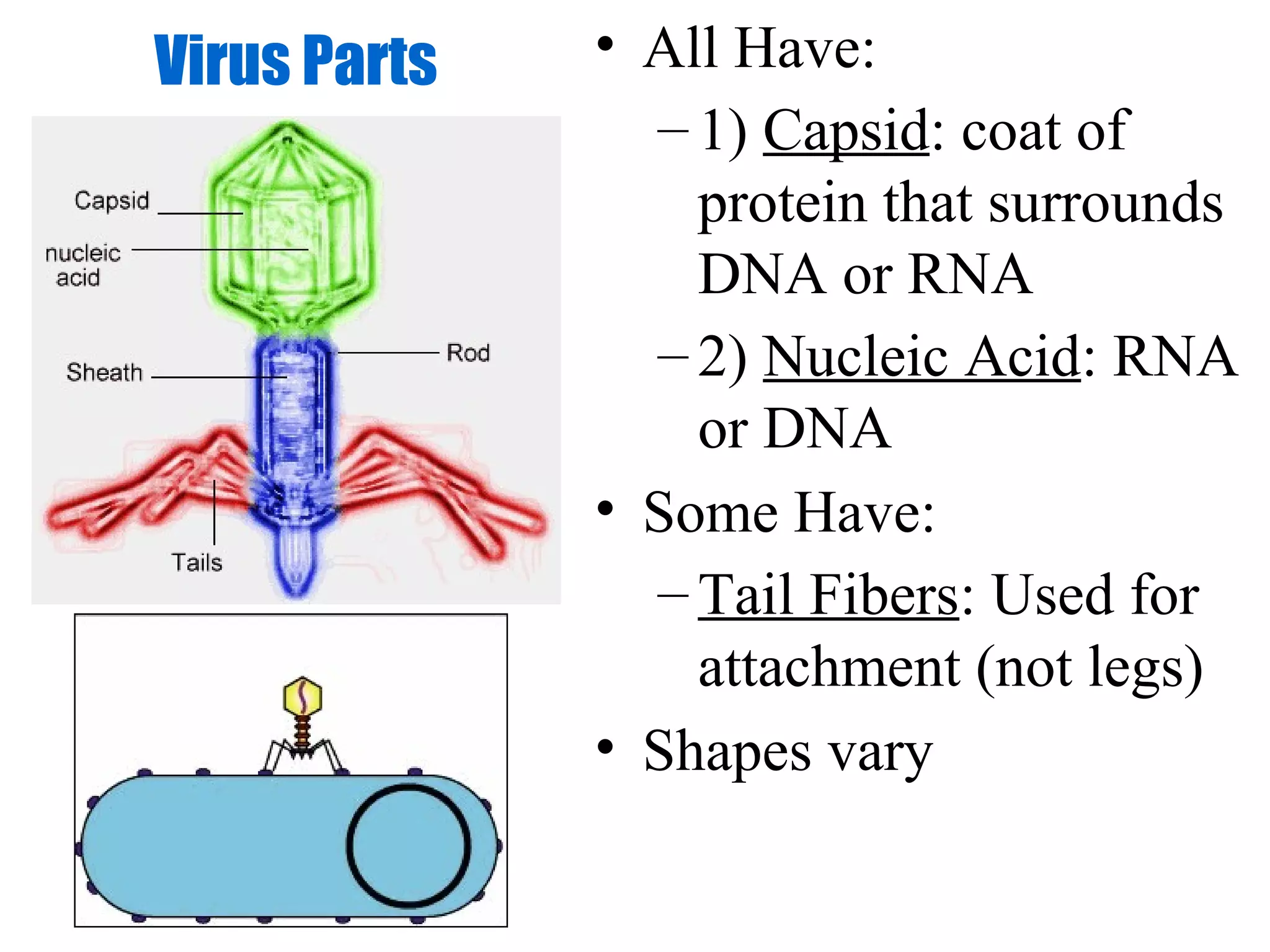
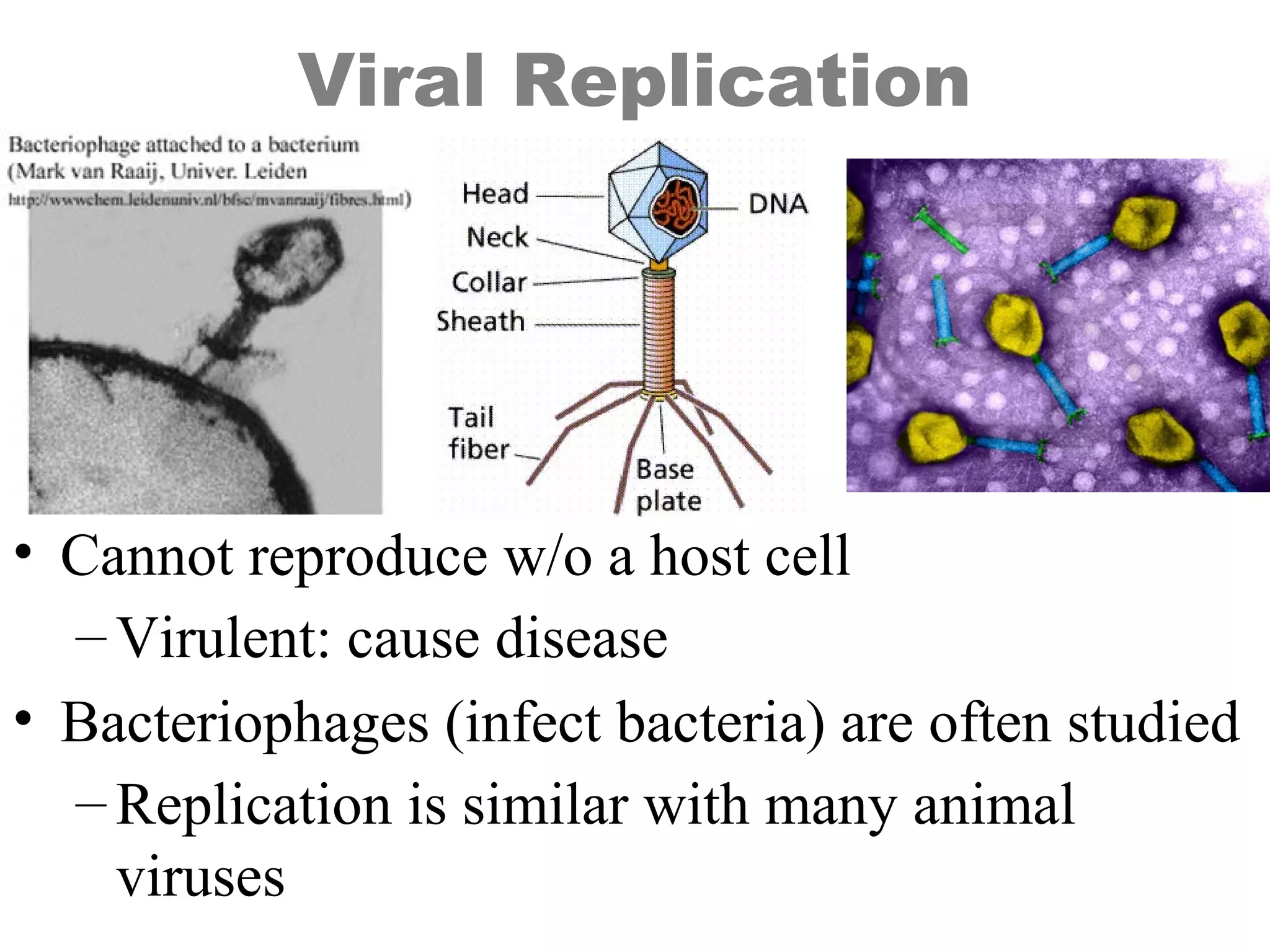
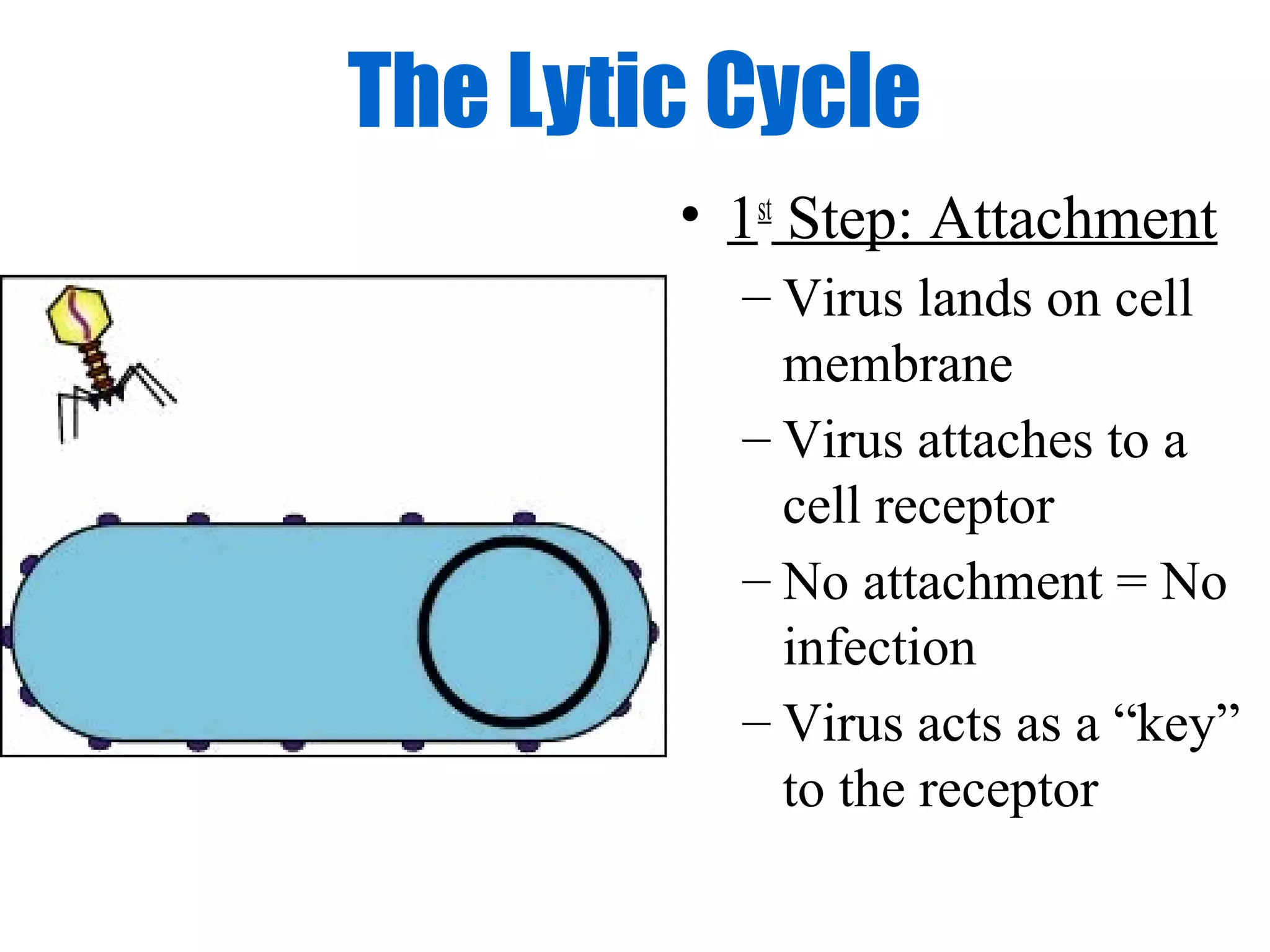
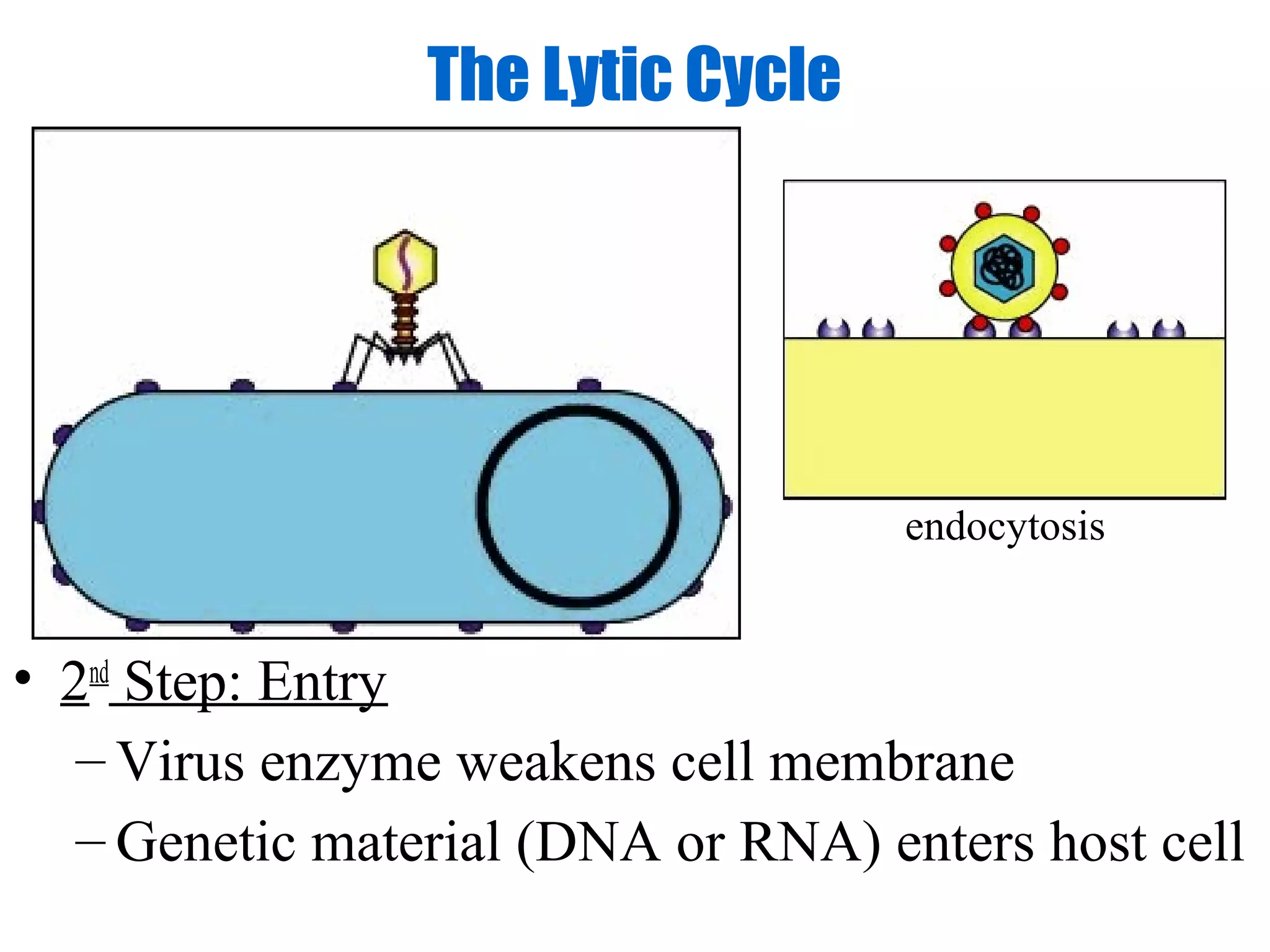
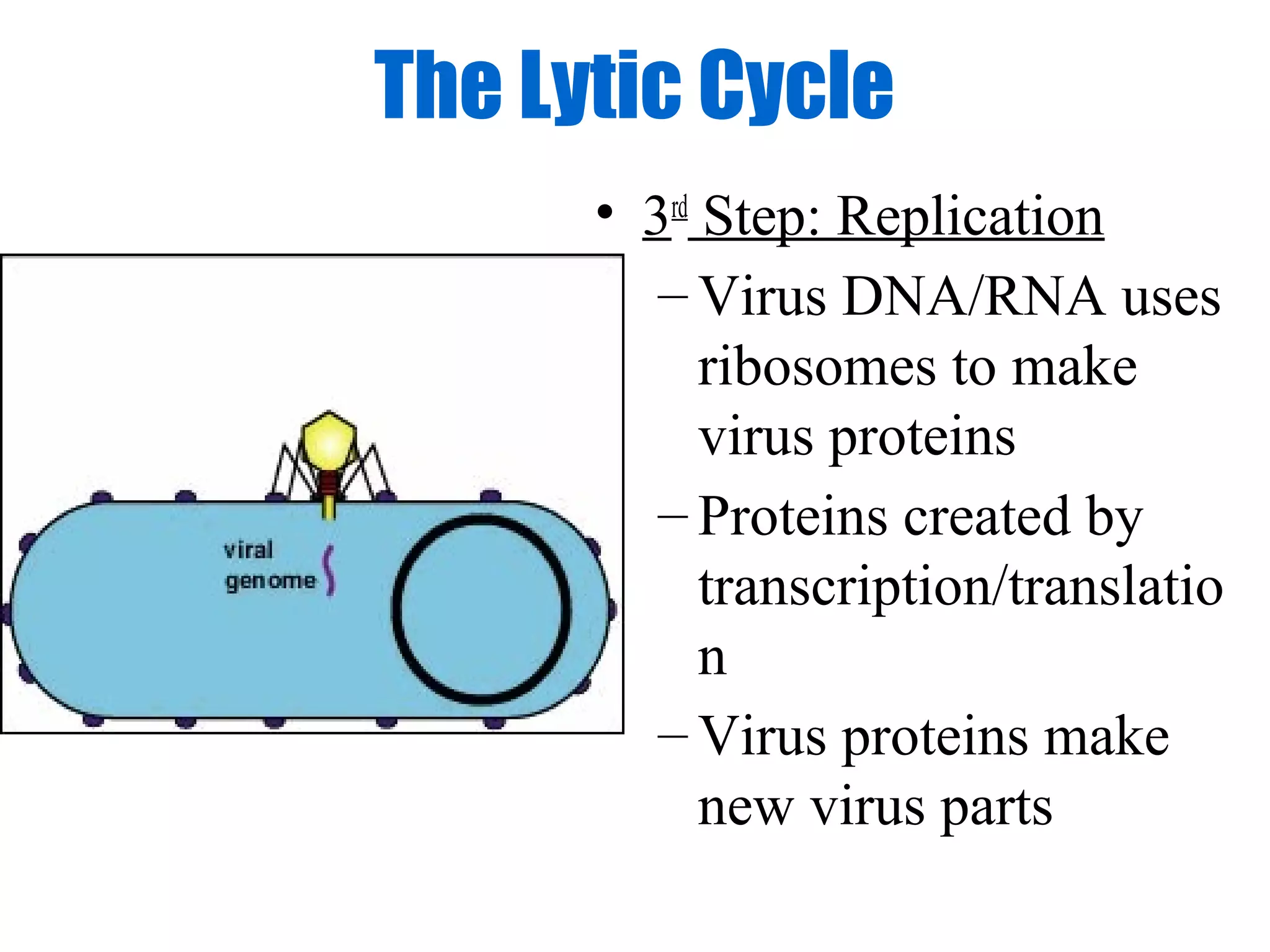
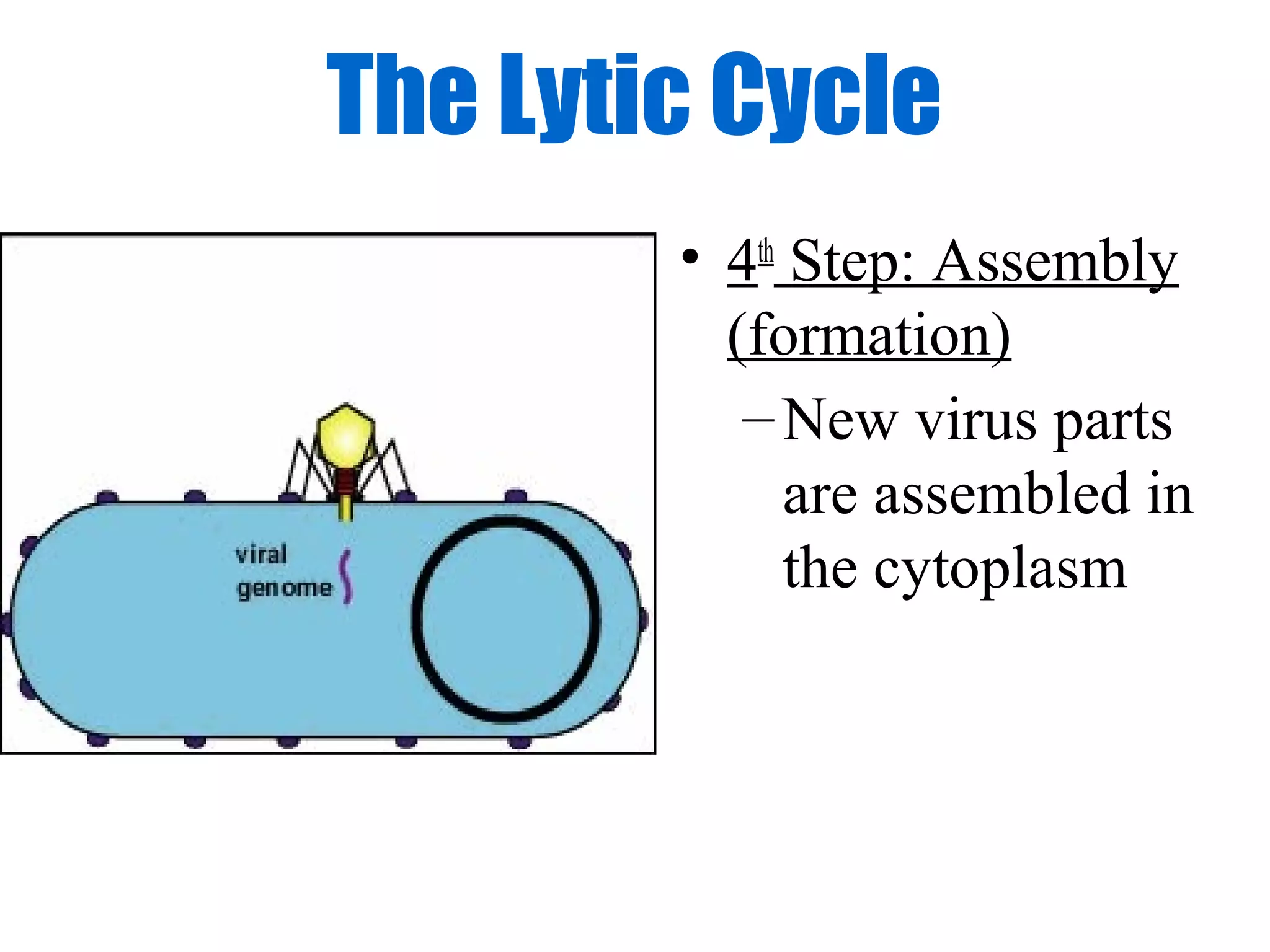
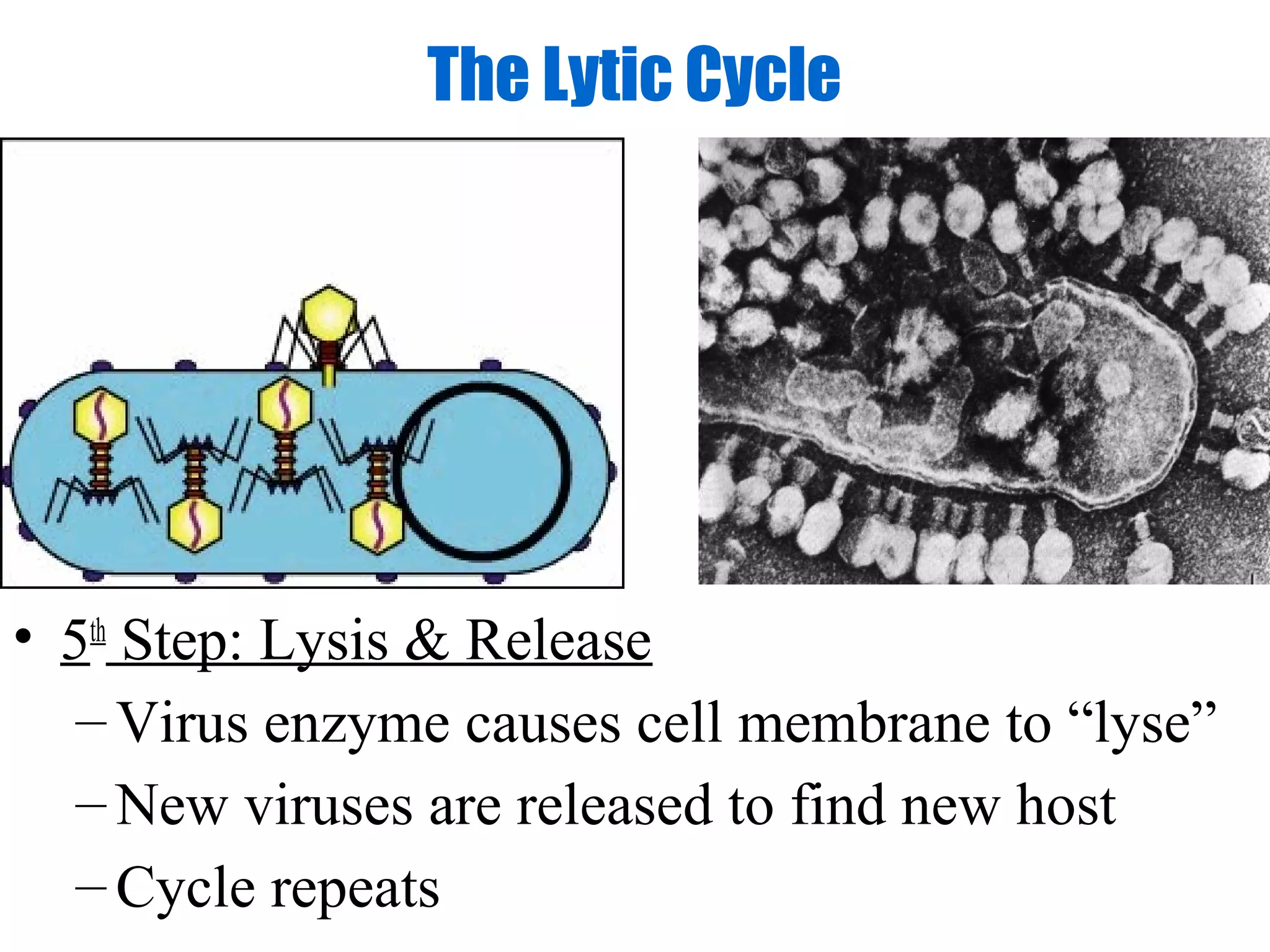
Viruses are intracellular parasites composed of nucleic acid and protein that can only reproduce inside host cells. They enter the host cell and use the cell's machinery to produce new virus particles, which causes the host cell to rupture and release the new viruses to then infect other cells. The viral replication cycle involves the virus attaching to and entering the host cell, producing new viral components using the host cell, assembling new virus particles, and then causing the host cell to burst open, releasing the new viruses.