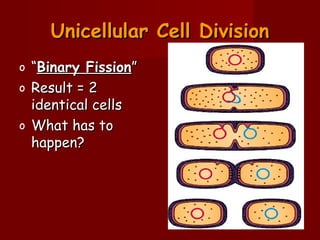
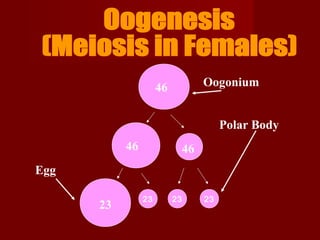
Cells need to divide for three main reasons: growth and repair of tissues, reproduction, and replacement of dying cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis, which produces identical body cells, and meiosis, which creates gametes for sexual reproduction. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and its DNA is replicated, and the M phase where the cell divides through mitosis or meiosis. Strict controls regulate the cell cycle to ensure cells only divide as needed. Cancer occurs when cells lose their ability to regulate division.