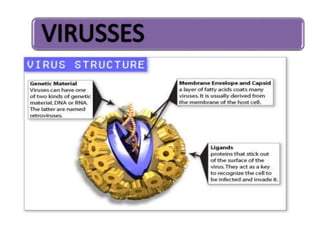
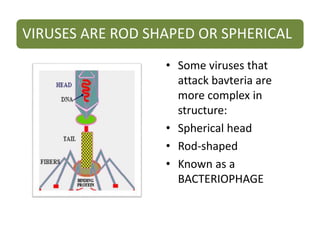
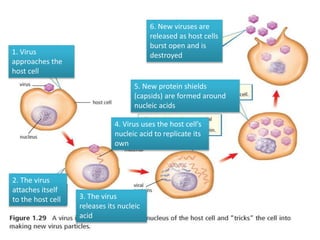
Viruses are the smallest microorganisms that can only replicate inside host cells. They consist of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites and are not considered living organisms as they cannot reproduce, grow, or metabolize on their own. The virus reproduction process involves the virus attaching to and entering a host cell, releasing its nucleic acid, using the host cell to produce more virus nucleic acid and proteins, assembling new virus particles, and bursting out to infect more cells. Common viral diseases include influenza, mumps, chickenpox, smallpox, polio, rabies, German measles, and viral meningitis.