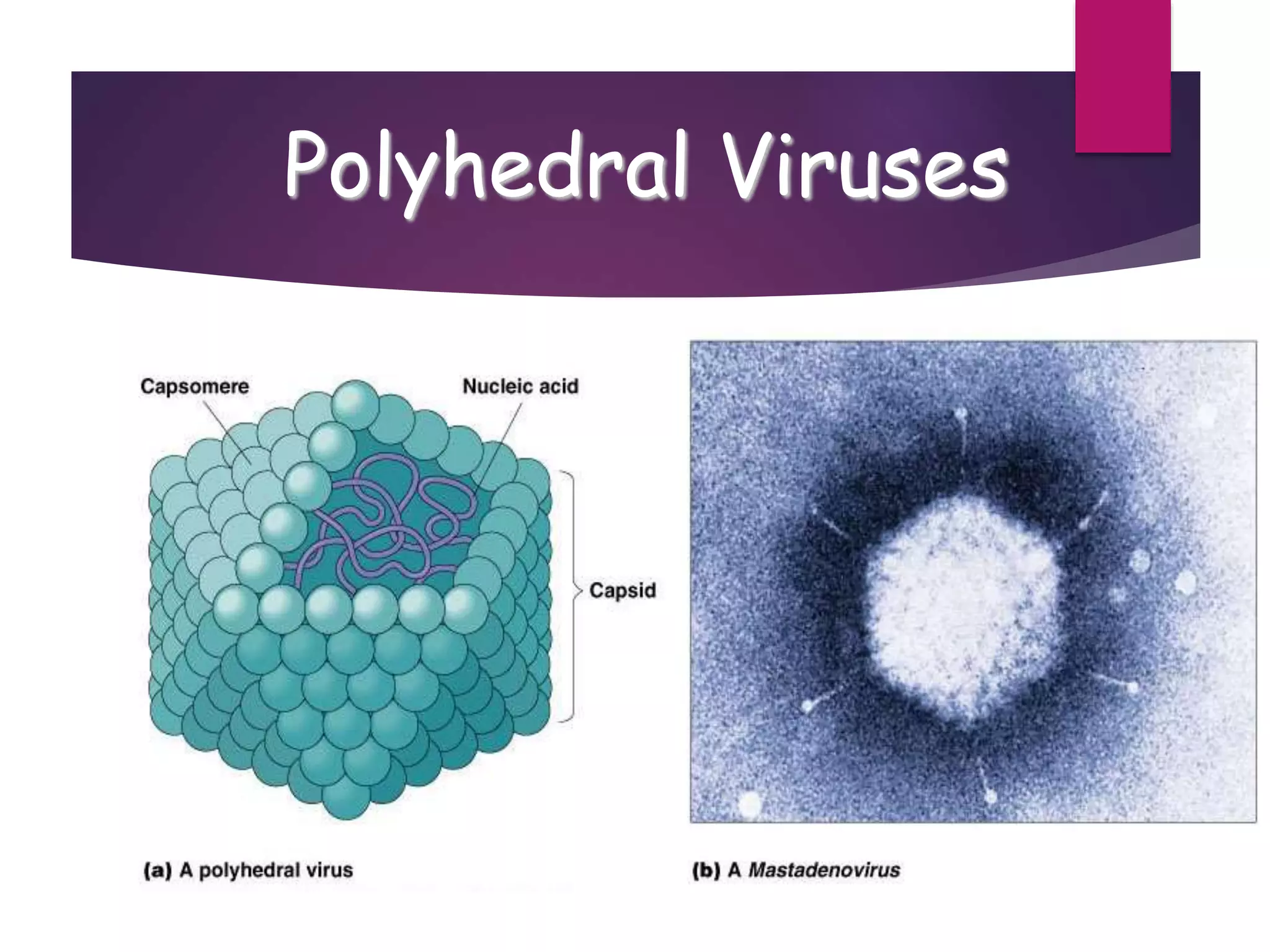
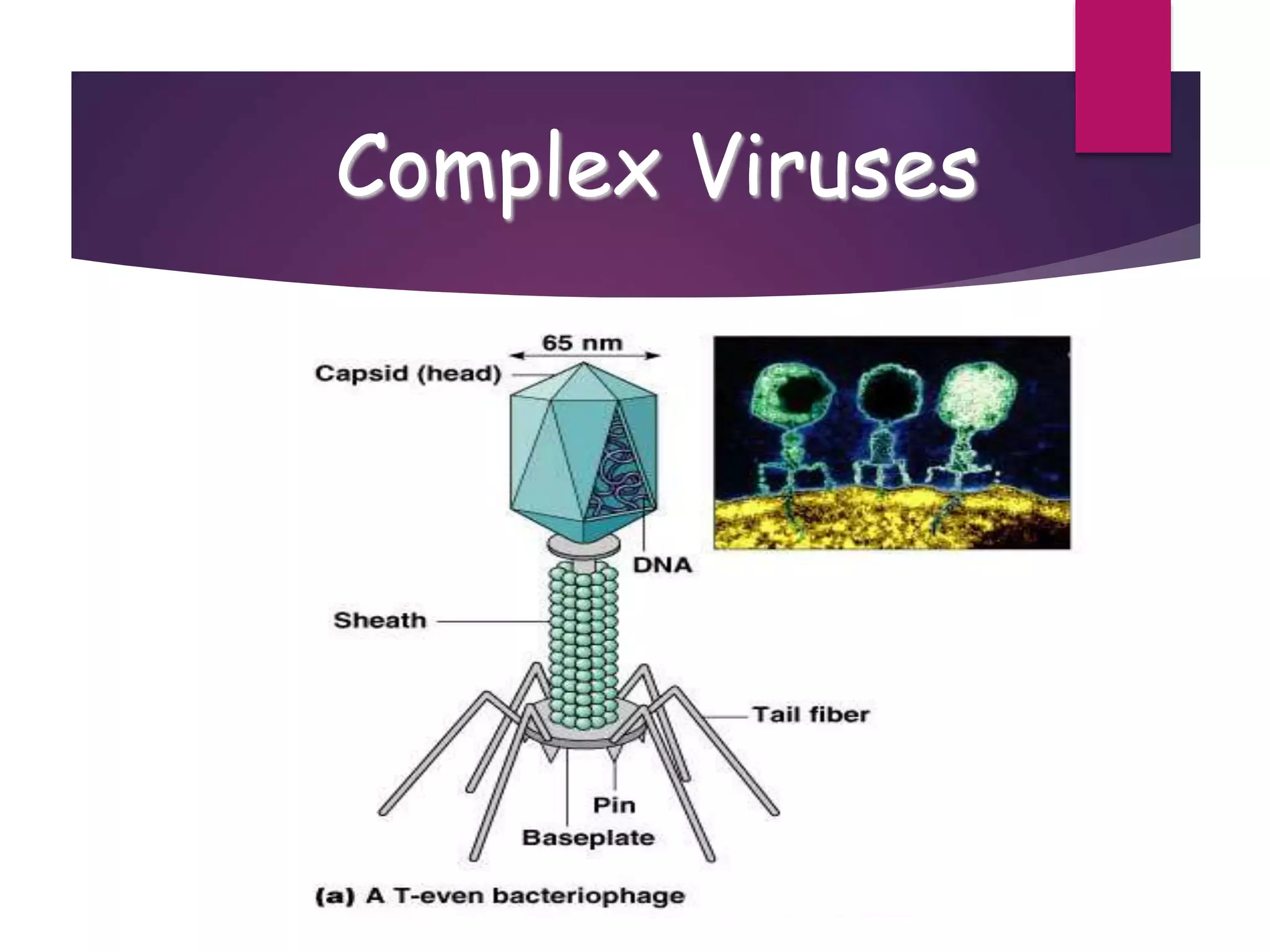
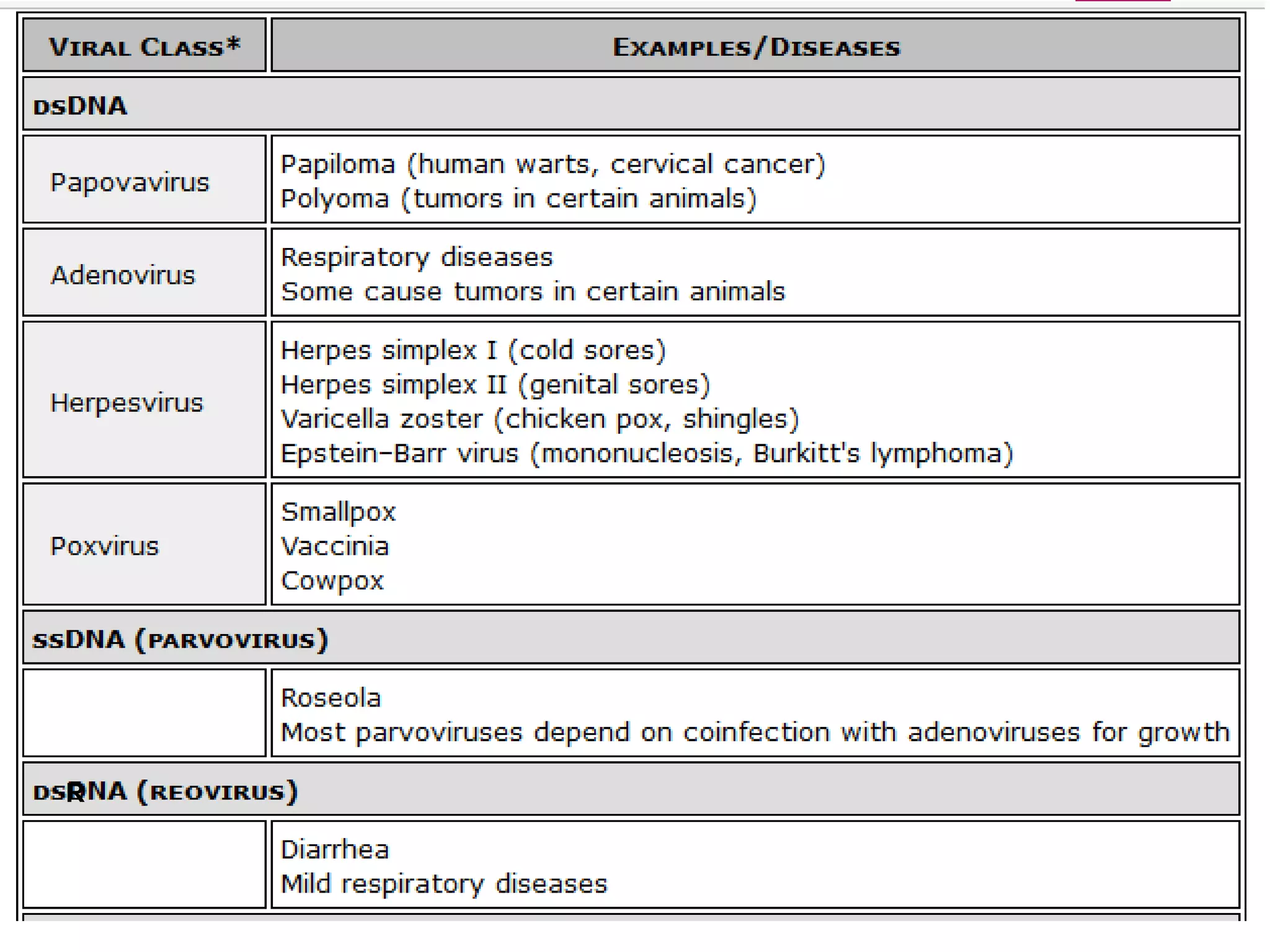
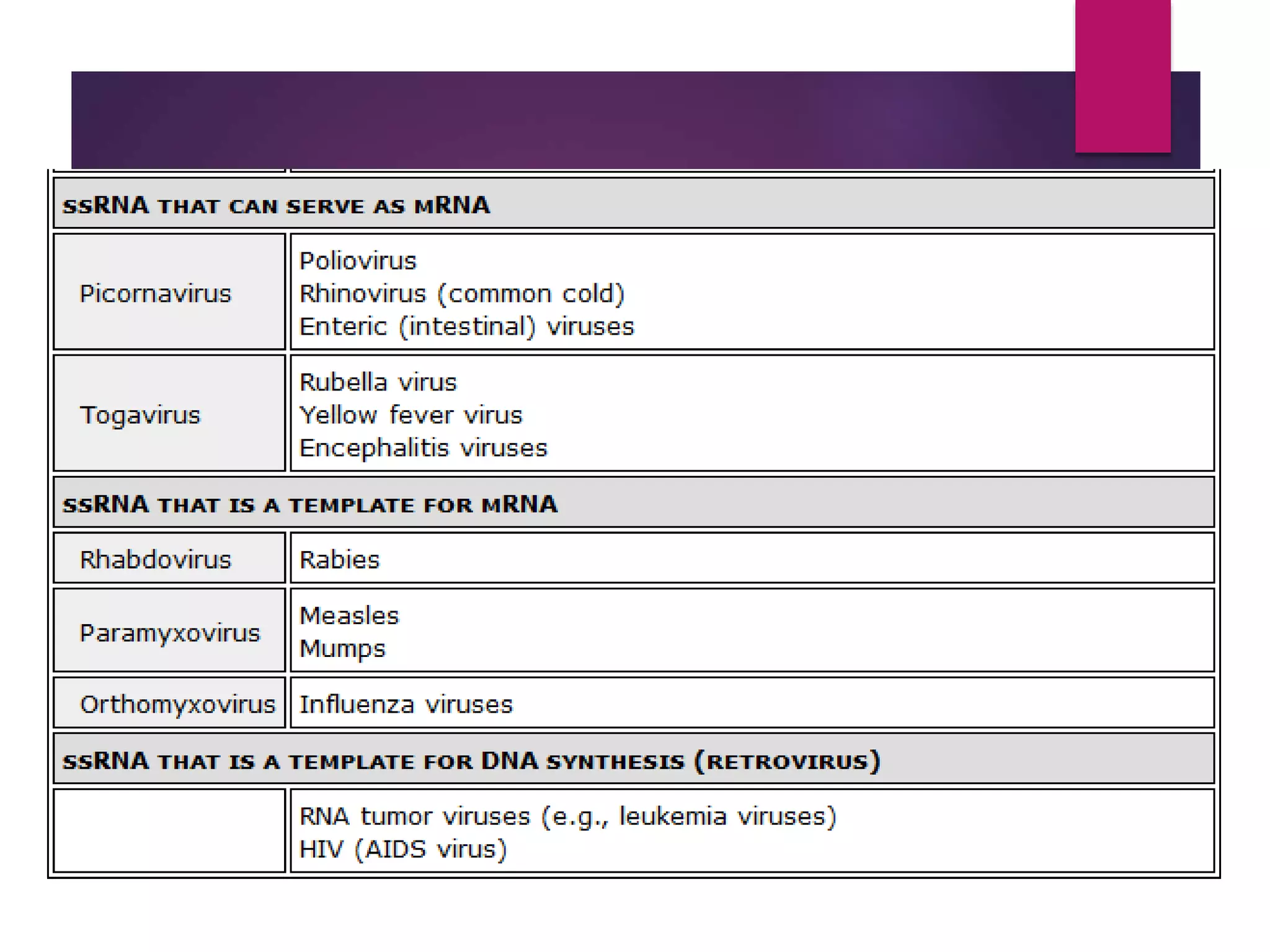
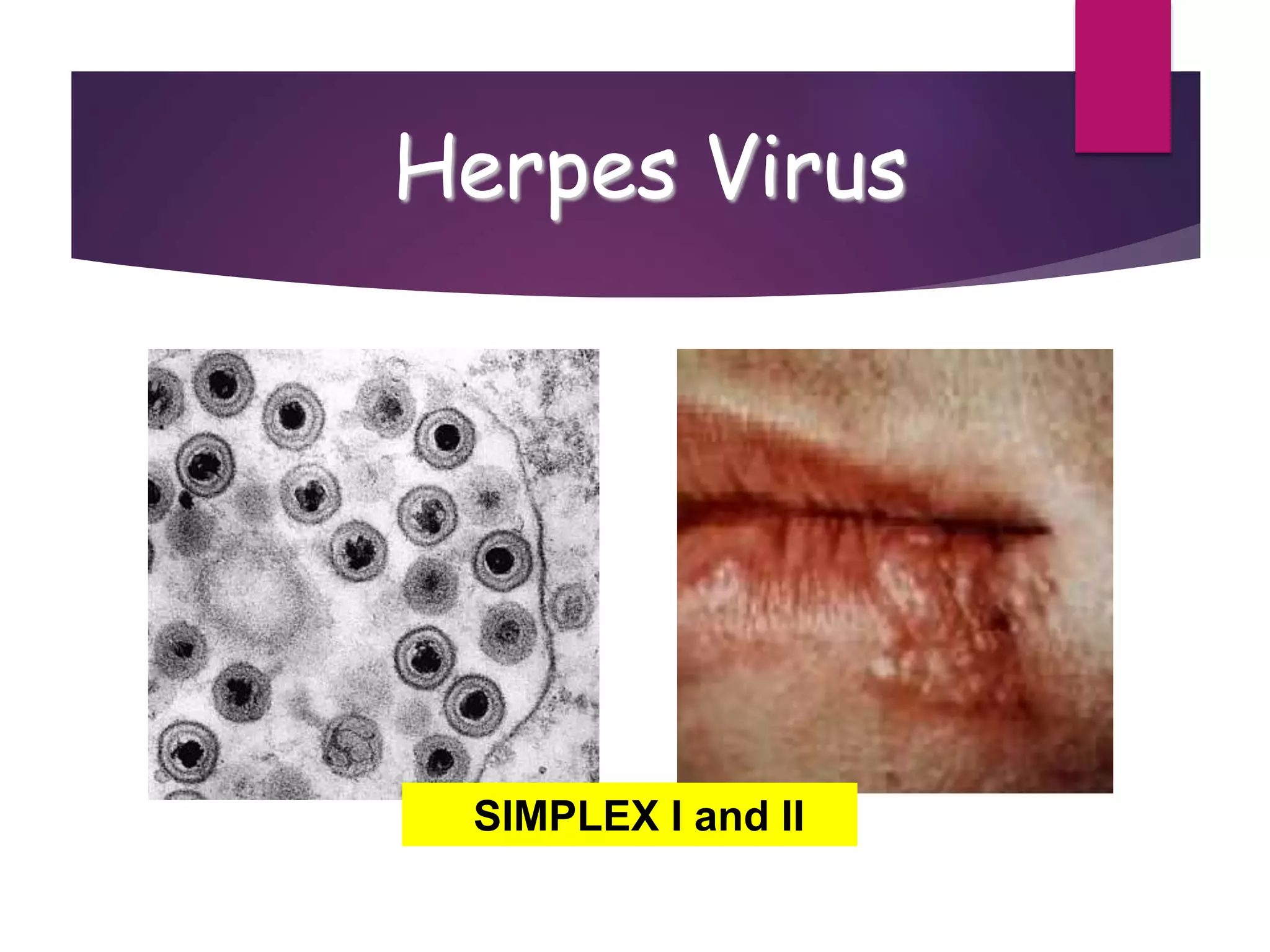
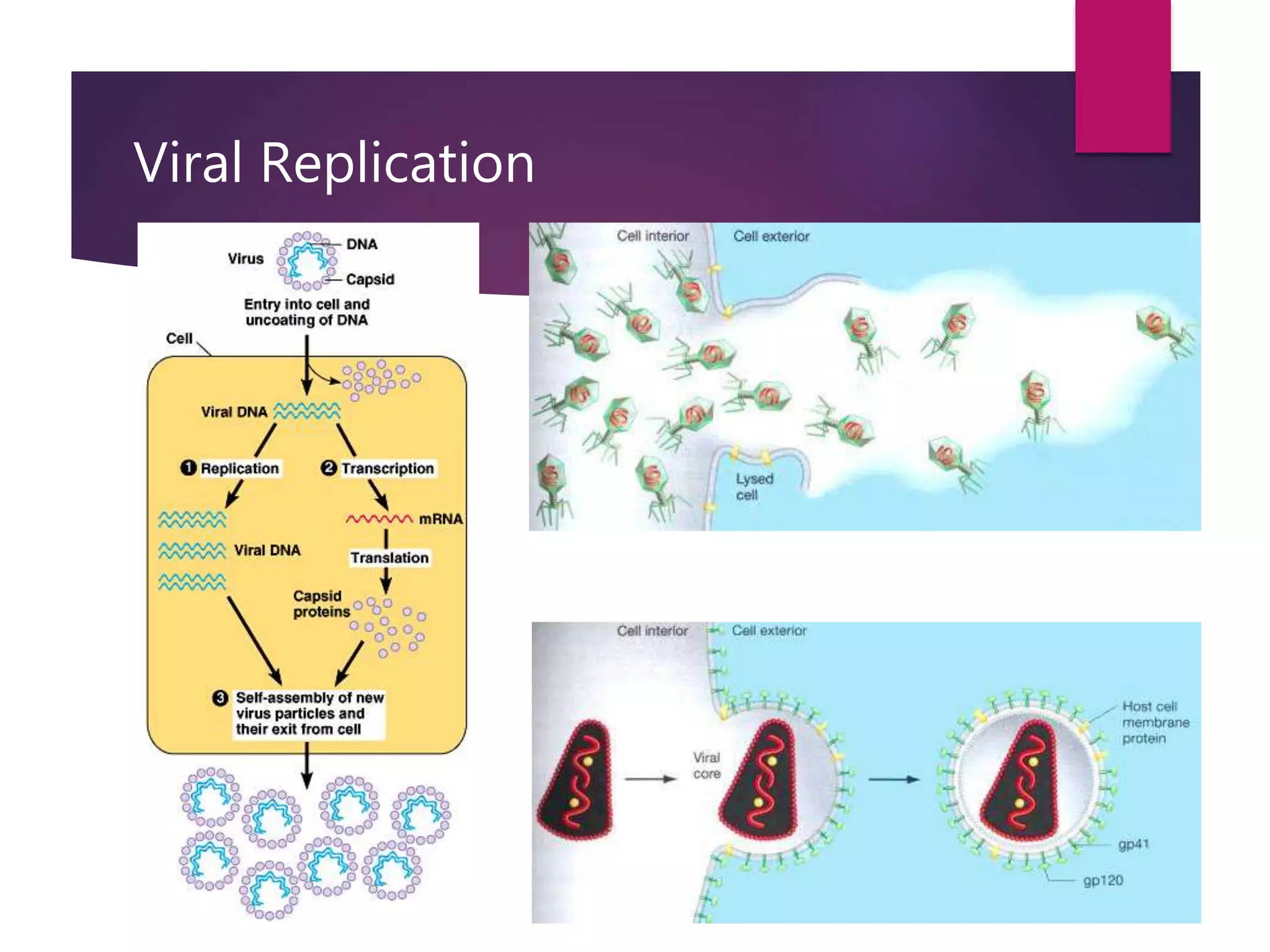
1) Viruses are non-living infectious particles that contain genetic material and a protein coat called a capsid. 2) Viruses can only replicate inside a host cell by injecting their genetic material and using the host cell's machinery. 3) Viruses exist in two states - as active viruses when infecting a host cell, or dormant virions when not in contact with a host.