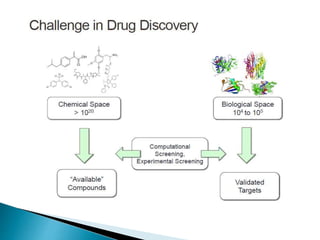
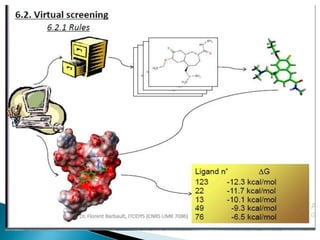
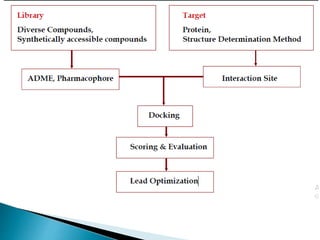
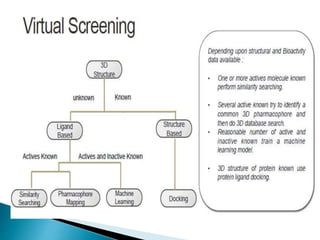
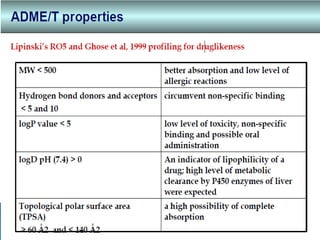
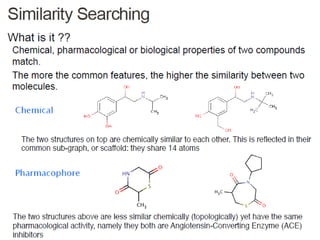
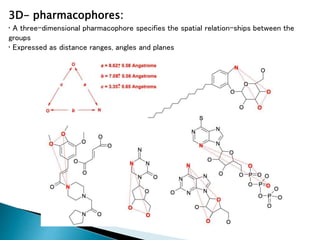
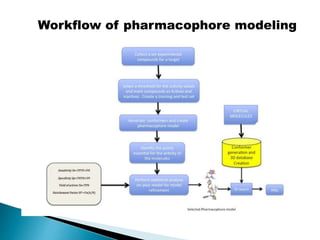
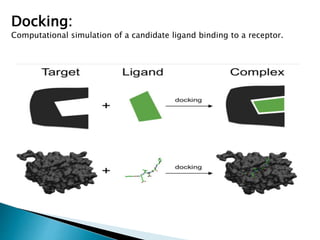
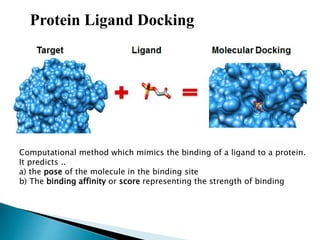
Virtual screening uses computer-based methods to identify potential drug candidates by assessing how well compounds interact with biological targets like proteins. It has advantages over laboratory experiments in being lower cost, allowing investigation of compounds that have not been synthesized, and enabling screening of a much larger number of potential compounds. Common virtual screening methods include similarity searching based on molecular fingerprints, pharmacophore searching to identify common chemical features among active molecules, and docking to computationally simulate ligand binding and predict binding affinity.