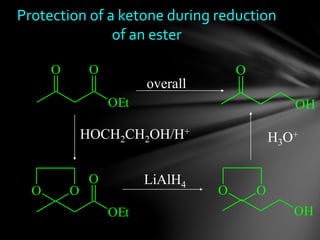
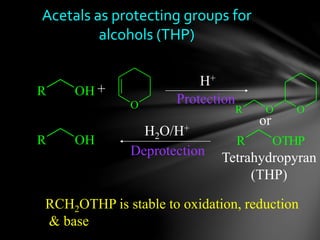
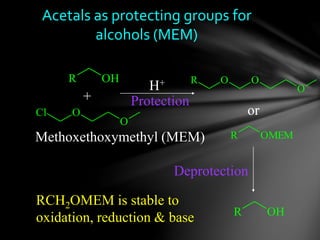
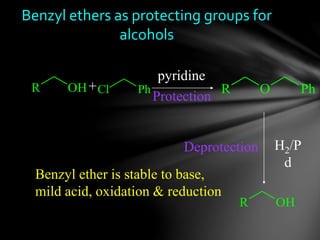
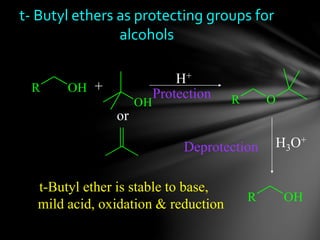
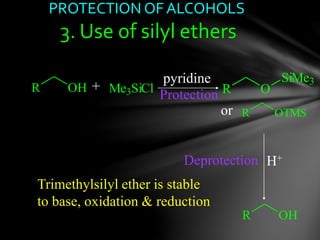
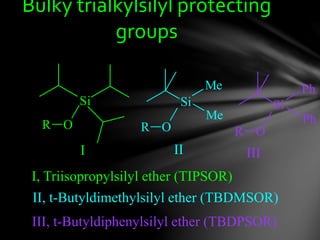
The document discusses protecting groups, focusing on protecting alcohols. It defines protecting groups as functional groups that are stable to reaction conditions but can be easily removed to regenerate the original functional group. The document outlines criteria for protecting groups and then discusses various methods for protecting alcohols, including using acetals, ethers, and silyl ethers. It provides examples of specific protecting groups like THP, MEM, benzyl ethers, and trialkylsilyl ethers.