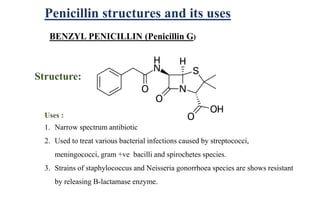
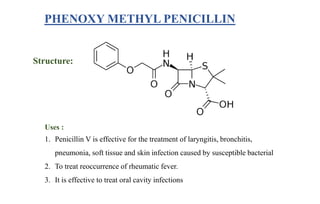
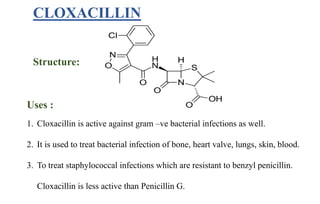
The document discusses penicillins, which are beta-lactam antibiotics. It describes how penicillin is produced by Penicillium fungi and was discovered by Alexander Fleming. It went on to explain that penicillin is used to treat bacterial infections by killing the bacteria. Finally, it provides the structures and uses of various penicillins including penicillin G, phenoxymethyl penicillin, amoxicillin, cloxacillin, and ampicillin; outlining their antibiotic properties and the types of infections each can be used to treat.