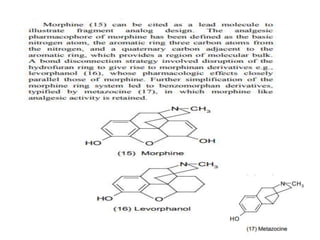
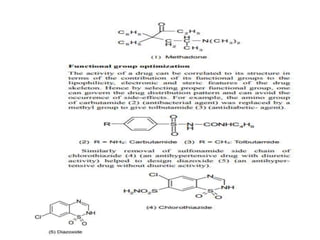
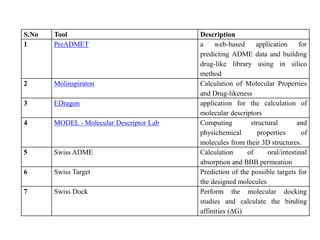
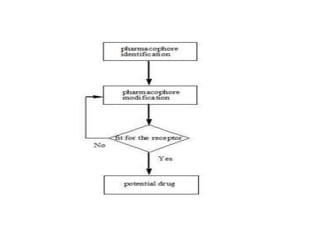
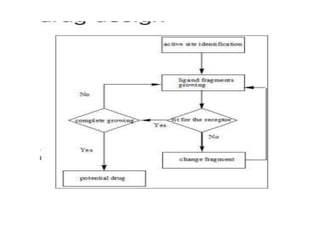
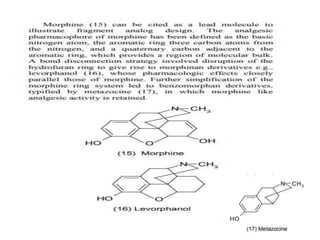
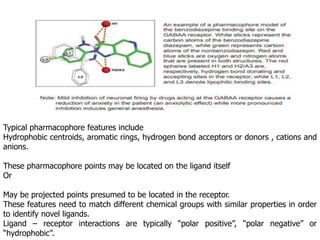
The document discusses lead identification and optimization in drug design. It describes the general drug discovery process which includes target validation, assay development, high-throughput screening, hit to lead identification, and lead optimization stages. Lead optimization is one of the most important steps and involves modifying lead compounds to improve potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic parameters. Structure-based and ligand-based drug design approaches are used, along with in silico tools to predict properties like toxicity and ensure drug-likeness. Key steps in structure-based design include identifying the binding site and growing fragments in an iterative process until an optimized lead is obtained.