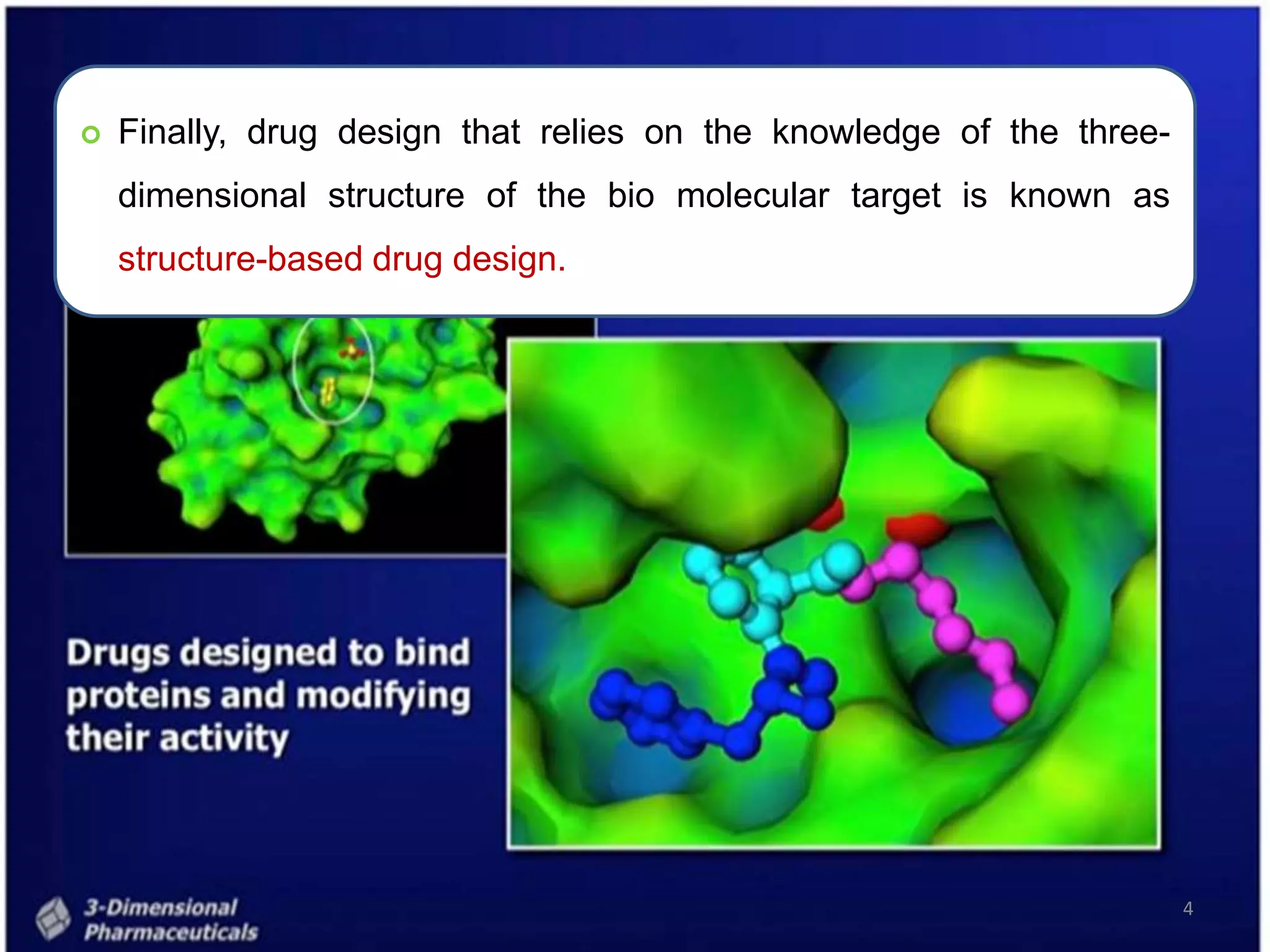
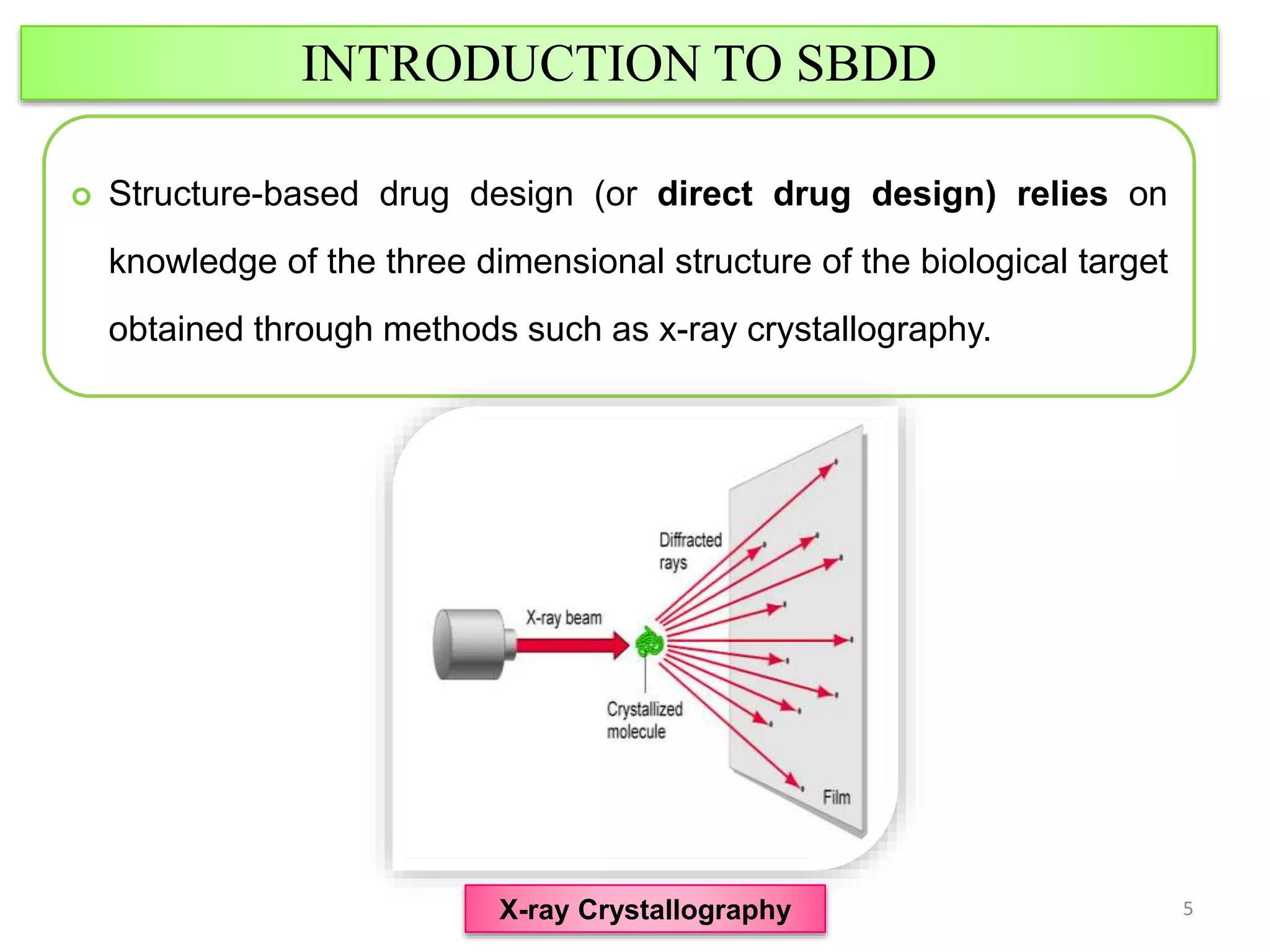
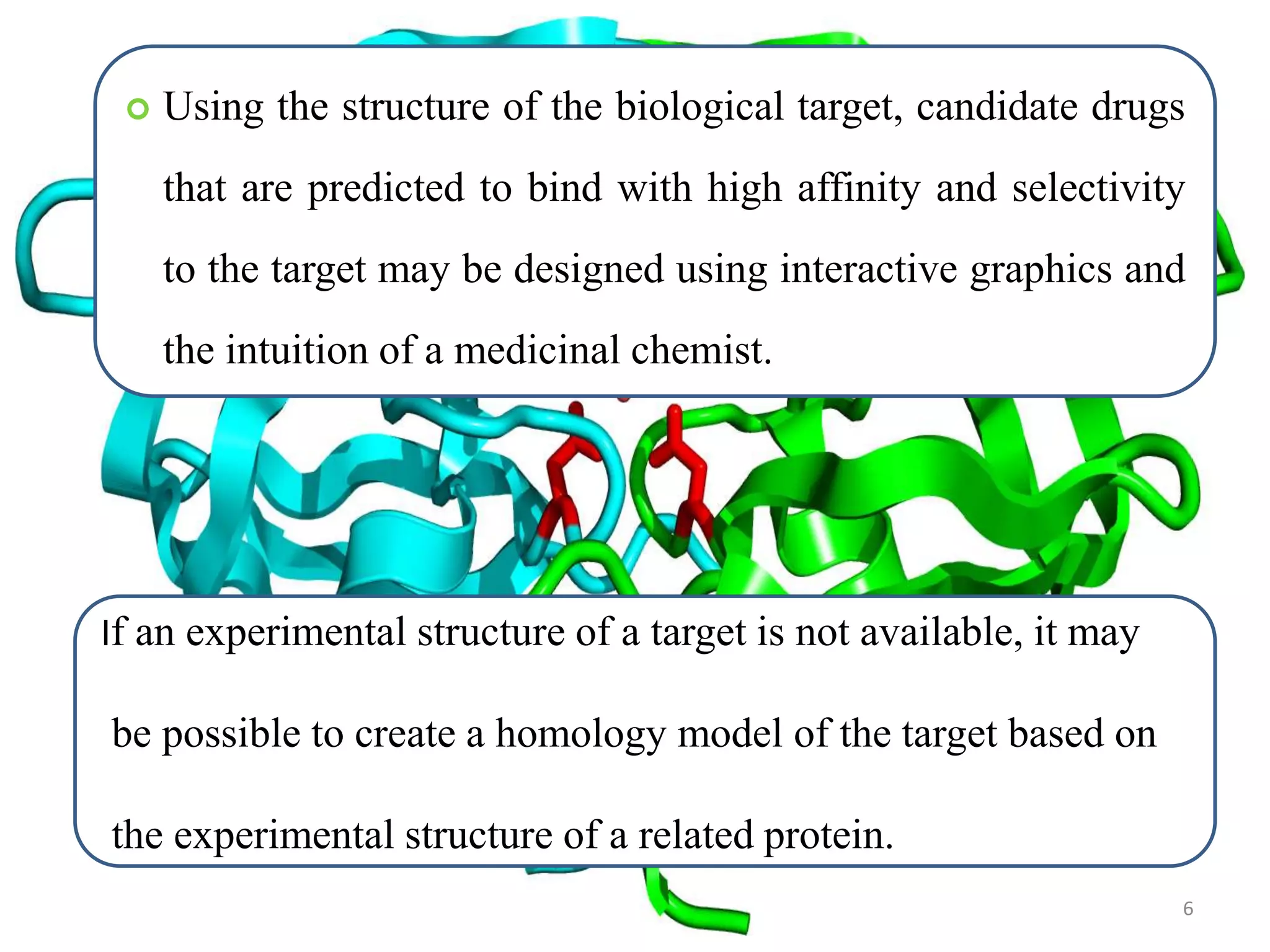
1. Structure-based drug design relies on knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biological target obtained through methods such as x-ray crystallography. Candidate drugs that are predicted to bind with high affinity and selectivity to the target can be designed.
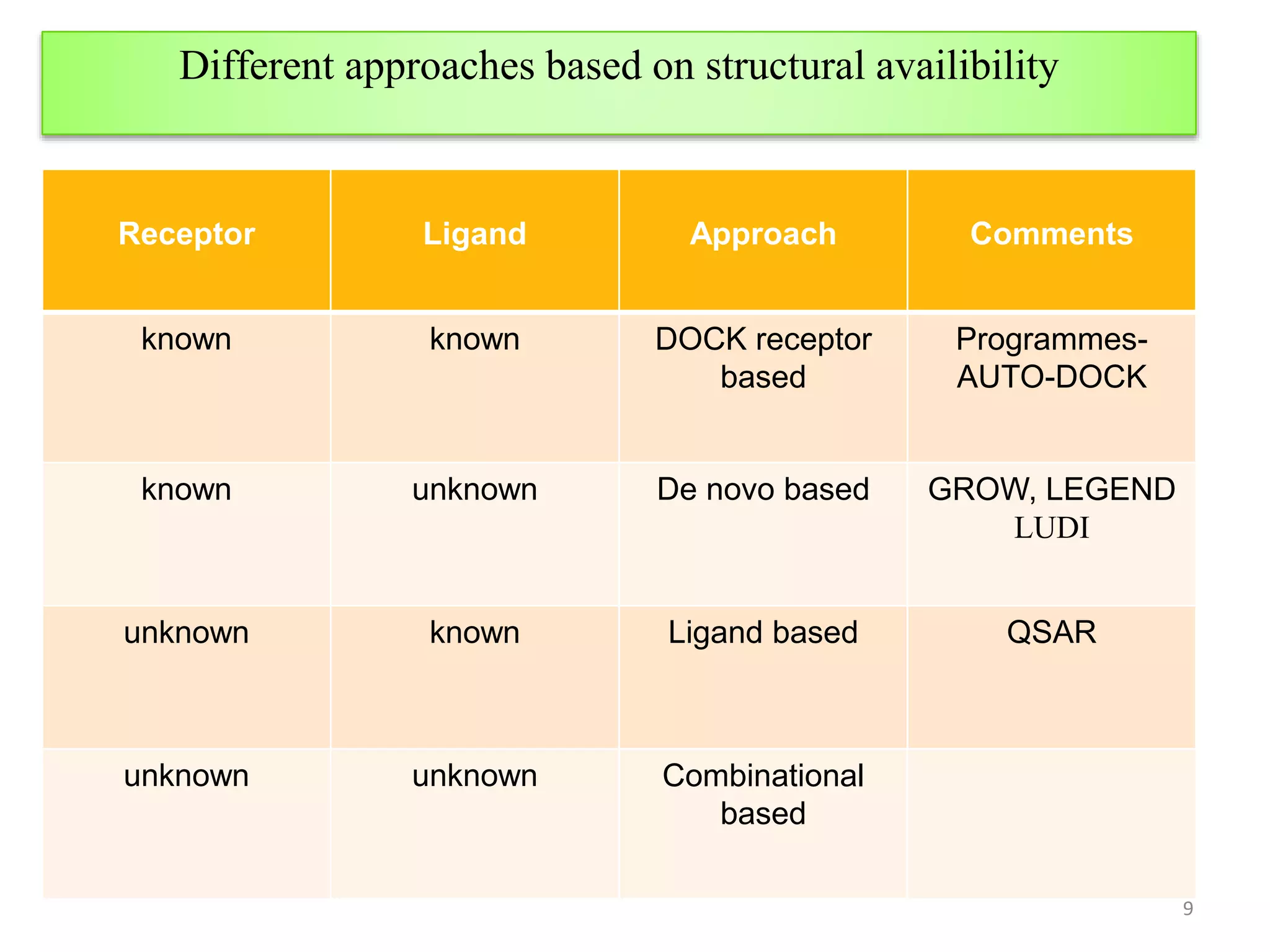
2. Structure-based drug design approaches include receptor-based drug design, which involves "building" ligands within the constraints of the binding pocket, and ligand-based drug design.
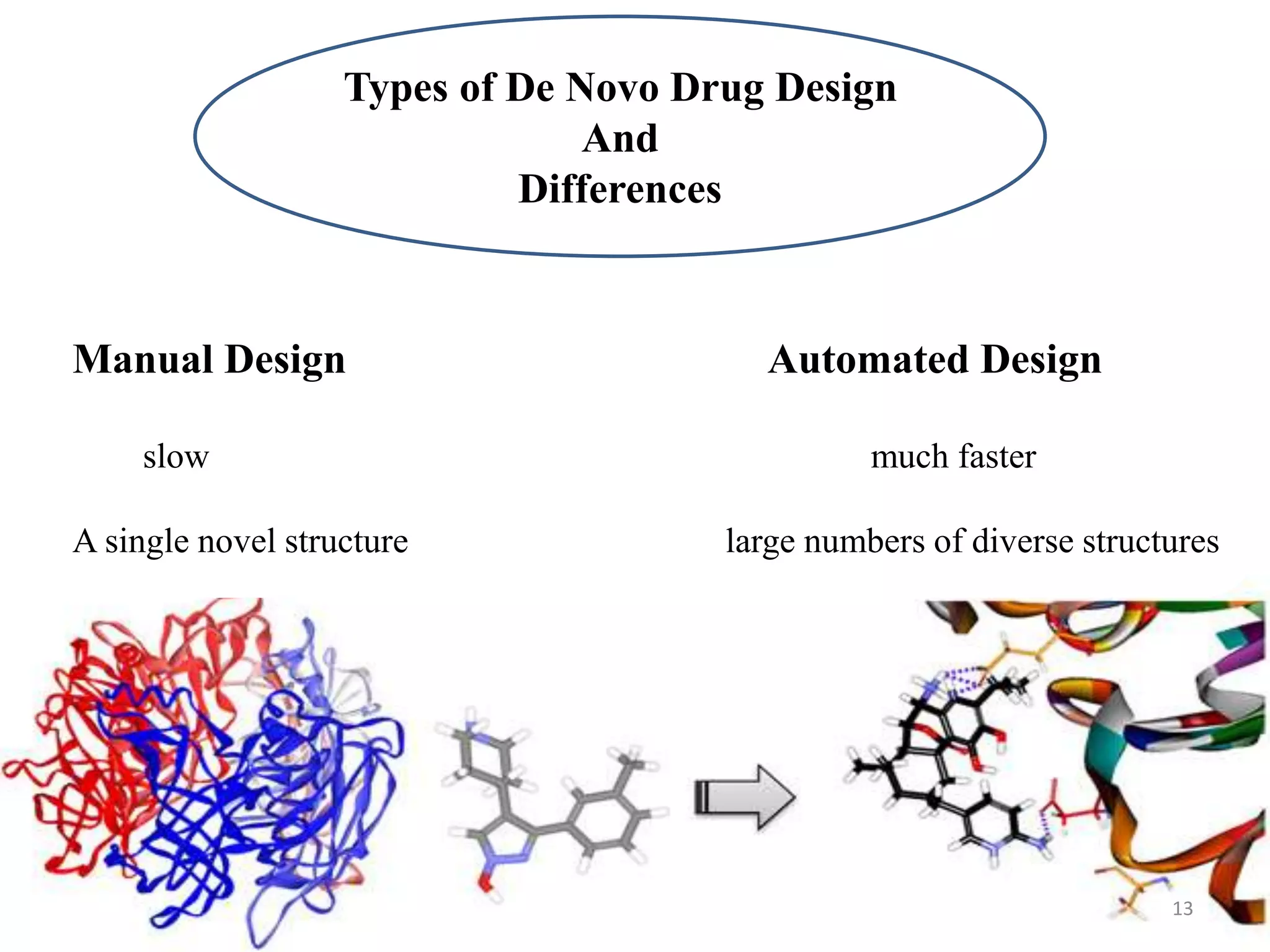
3. De novo drug design is a receptor-based approach that uses the target's 3D structure to design new molecules without existing leads. It involves building ligands that complement the active site properties through manual or automated methods.