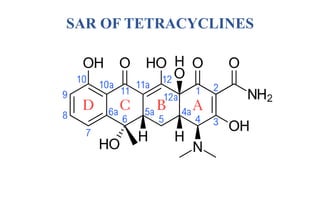
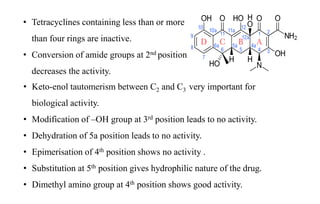
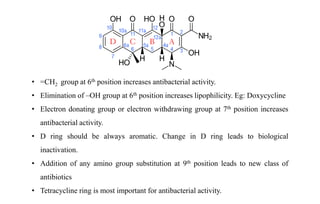
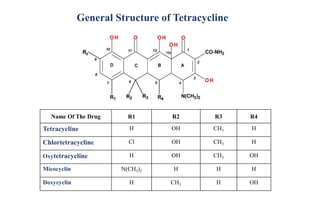
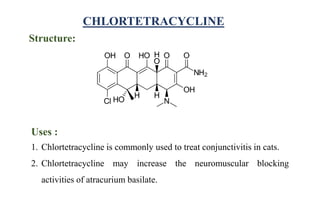
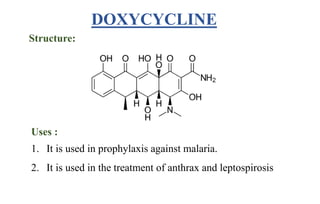
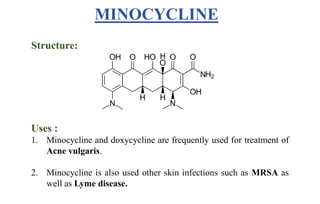
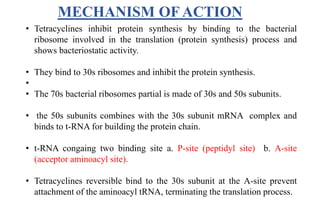
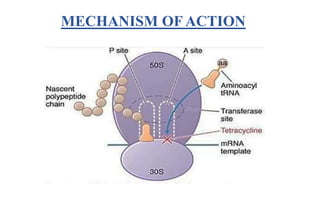
Tetracyclines are a class of broad-spectrum antibiotic drugs obtained from Streptomyces bacteria. They work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. Tetracyclines bind to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes to prevent aminoacyl-tRNA from attaching, thereby terminating translation. They are effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and are used to treat various infections. However, they can cause side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and tooth discoloration.