Unit1: Organisation of Human Body
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
17 likes•11,544 views
Presentation about the levels of organisation: cells, tissues, organs,etc.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Skeletal system. anatomy and physiology of skeletal system. appendicular skel...

Skeletal system. anatomy and physiology of skeletal system. appendicular skel...
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (11)
Cell (ppt. lecturers for Biology,7th Edition)lecturers by Chris Romero

Cell (ppt. lecturers for Biology,7th Edition)lecturers by Chris Romero
Anatomy and Physiology; Introduction to the human body

Anatomy and Physiology; Introduction to the human body
Similar to Unit1: Organisation of Human Body
Similar to Unit1: Organisation of Human Body (20)
WCCCD - BIO 155 POWERPOINT on Ch 4 Cell Structure.pdf

WCCCD - BIO 155 POWERPOINT on Ch 4 Cell Structure.pdf
WCCCD - BIO 155 POWERPOINT on Ch 4 Cell Structure.pdf

WCCCD - BIO 155 POWERPOINT on Ch 4 Cell Structure.pdf
More from aurorabiologia
More from aurorabiologia (20)
Recently uploaded
https://app.box.com/s/4hfk1xwgxnova7f4dm37birdzflj806wGIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
This slide is prepared for master's students (MIFB & MIBS) UUM. May it be useful to all.Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptxMohd Adib Abd Muin, Senior Lecturer at Universiti Utara Malaysia
Recently uploaded (20)
GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa

aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf

Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf
Benefits and Challenges of Using Open Educational Resources

Benefits and Challenges of Using Open Educational Resources
Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism

Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism
INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf

INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf
Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx
Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx

Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx
How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI fund...

How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI fund...
Unit1: Organisation of Human Body
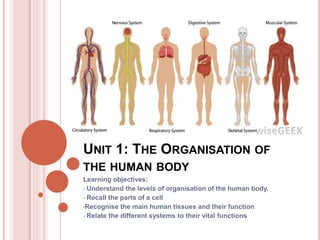
- 1. UNIT 1: THE ORGANISATION OF THE HUMAN BODY Learning objectives: • Understand the levels of organisation of the human body. • Recall the parts of a cell •Recognise the main human tissues and their function • Relate the different systems to their vital functions
- 2. 1. ORGANISATION OF LIVING MATTER 1.2 LEVELS OF ORGANISATION
- 3. IN GROUPS OF 4 1. Take a piece of paper and design your diagram including the following sections: • Subatomic level • Atomic level • Molecular level • Cellular organelles • Cellular level • Tissues • Organs • Systems • Human body 2. Cut and paste the drawings provided on your diagram 3. Explain one of the levels to the rest of the class. GROUP ACTIVITY 15 MINUTES
- 5. DEFINITIONS (PAGE 7) Cells are the basic structural and functional units that form our organism. A tissue is a group of cells of the same type and origin, which perform the same function. An organ is formed by different tissues that perform a particular function. A system is a group of organs that participate in one or more specific functions. An organism is formed by the ensemble of systems that function in a coordinated way. células tejido órgano sistema
- 6. 1.1 DEFINITION OF HUMAN BEING (PAGE 6) They are living things: They are composed of biomolecules. They are made up of cells. They perform the three vital functions (nutrition, interaction, reproduction). They are animals: Multicellular. They are eukaryote cells. They are heterotrophic.
- 7. 2. CELL STRUCTURE Cells are the basic structural and functional units that form our organism. YOUR TASK!!! Build your own model animal cell. Names on the notebook
- 8. IDEAS FOR YOUR MODEL ANIMAL CELL Jello cell Clay cell http://www.wikihow.com/Make-a-Model-Cell Pizza cell crafts Label Organelles!!
- 9. 2.2 EXCHANGE WITH THE ENVIRONMENT The cell membrane is semipermeable It only allows the passage of certain substances. Activity 7 page 8 in class
- 10. MECHANISMS FOR GOING THROUGH THE MEMBRANE A. Diffusion free passage of small molecules. BUT: ALWAYS following the concentration gradient: from higher concentration to lower concentration
- 12. B. Osmosis passage of water from the more diluted to the more concentrated medium Water molecules Any type of substance, such as glucose or salt Watch the animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/osmosis.swf
- 15. C. Active transport if the concentration of a substance is less in the exterior, but the cell needs it, the cell can use energy in order to bring it in. ATP = energy
- 16. D. Endocytosis and exocytosis for incorporating or putting out big subtances that cannot go through the cell membrane. Small vesicles are formed. Activities 8, 9, 10 and 11 page 9
- 18. 3. TISSUES AND ORGANS In the human body there are different types of cells. Cells specialise so that they can perform different tasks and different types of cells are created. DIFFERENTIATION: Process by which cells specialise.
- 19. Differentiation involves changes in: • Cell shape • Function • Activity of the cytoplasmic organelles Activities 12 and 13 page 10 Why do muscle cells have many mitochondria? Why do glandular cells have a very developed Golgi apparatus? Why do red blood cells do not have any organelles? 5 minutes to answer these questions in pairs:
- 20. 3.2 TYPES OF TISSUES Epithelial tissue
- 21. Connective tissue Bone tissueCartilaginous tissue Adipose tissue
- 22. Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Activity 17 page 11 Activities 20 and 21 page 12 Activity 23 13 page 13
- 23. 3.3 ORGANS
- 24. 4. SYSTEMS ON YOUR NOTEBOOK: Classify the following systems depending on the vital function (reproduction, nutrition or interaction) they are involved with.
- 25. Nutrition Excretory system Digestive system Circulatory system Respiratory system Reproduction Male reproductive system Female reproductive system Interaction Nervous system Sense organs Skeletal and muscular system Endocrine system ALL THESE SYSTEMS INTERACT AND WORK TOGETHER IN A COORDINATED WAY
- 26. Glossary: • Tissue • Epithelial tissue • Bone tissue • Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- 27. Pages 18 and 19: 38 40 41 42 45 50 52 READ AND UNDERSTAND SCIENCE ON YOURNOTEBOOK INPAIRS