Tissue its types, structure and function
- 1. Chapter # 02 TISSUE Amjad Khan Afridi
- 2. • Tissue is group of cells, which have similar in origin, structure and function are called as “Tissues”. • Tissue is the groups of cells which perform specialized activity of the body. • The word tissue comes from a form of an old French verb meaning “to weave نناُب ”. • The study of tissue is called “Histology”. • In plants, tissues are divided into three types: vascular, ground, and epidermal.
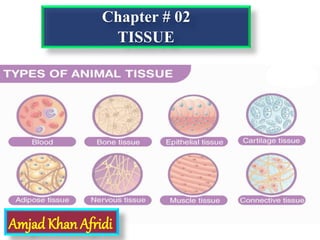
- 3. According to the structure and function the body tissues can be grouped . Fundamental types of tissues – there are 4 types of human tissues In plants, tissues are divided into three types: vascular, ground, and epidermal.
- 5. Epithelial tissue • Epithelial tissue, or epithelium, covers the surfaces of organs including the skin, the trachea, the reproductive tract, and the digestive tract’s inner lining. • Function: • Protection: It creates a barrier that helps protect the underlying organs from friction and injury. • Secretion: it also has roles in absorbing water and nutrients, secreting enzymes or hormones and removal of waste,.
- 6. All of the body’s glands are formed from ingrowths of epithelium. Some common epithelial tissue diseases are skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis, which both cause rashes. When cancer develops from epithelial tissue, it is called a carcinoma. Epithelial cells in the airways are also responsible for asthma, which is characterized by inflammation of the airways that leads to shortness of breath.
- 7. Epithelial Tissue can further classified as; A. Simple epithelium B. Compound epithelium A. Simple Epithelium • Its made of a single layers of cell • Its subdivided into 4 types i. Squamous epithelium ii. Cuboidal epithelium iii. Columnar epithelium iv. Ciliated epithelium
- 8. I. Squamous epithelium The squamous epithelium is composed of epithelial cells that are particularly flat, cells are wider than tall, and appear polygonal when viewed atop. It gives a smooth, low-friction surface, which allows easy movement of fluids over it.
- 9. II. Cuboidal epithelium This type of epithelium consists of a single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells which have large, spherical and central nuclei.
- 10. III. Columnar epithelium The columnar epithelium is composed of epithelial cells that are column-shaped. The cell comprising the columnar epithelium is taller than it is wide. Its height is approximately four times its width.
- 11. IV. Ciliated epithelium Ciliated epithelium is a thin tissue that has hair-like structures on it. These hairs, called cilia, move back and forth to help move particles out of our body. We find ciliated epithelial tissue in our respiratory tract and in the fallopian tubes of women.
- 13. I. Stratified squamous epithelium Composed of more than one layer of epithelial cells. Stratified squamous epithelium is a type of tissue found covering and lining parts of the body. In this tissue, cells are flattened, joined tightly together, and stacked. Found in the outermost layer of the skin and the linings of esophagus, mouth, and female reproductive organ.
- 14. I. Stratified squamous epithelium
- 15. I. Stratified squamous epithelium The stratified squamous epithelium provides protection against; o Mechanical stress, o Chemical abrasions, o Pathogens, o Desiccation and even radiation. The keratinized epithelium present on the surface of the skin blocks out the harmful radiation and prevents the exposure of internal tissues and organs to the radiation.
- 16. Its composed of multi layers of cells (4 to 6 layers) These cells are called transitional because they can undergo a change in their shape and structure Also called urothelium because it lines urinary ducts, urethra, urinary bladder and renal calyxes Its variable in appearance In relaxed state its looks like stratified cuboidal epithelium, while when stretched the cells become squamous shaped. Location: • Found urinary ducts, urethra, urinary bladder and renal calyxes II. Transitional epithelium
- 17. Columnar / Cuboidal cells Polyhedral Cells / Intermediate cells Umbrella cells
- 18. 2. Connective Connective tissue connects or separates groups of other tissues. It is found in between all the other tissues and organs in the body. • Connective tissue is made up of cells and ground substance, which is a gel that surrounds cells. • Most connective tissue, except for lymph and blood, also contains fibers, which are long, narrow proteins.
- 19. • Fibers can be collagenous, which bind bones to tissues; – Elastic fiber, which allow organs like the lungs to move; – or reticular fiber, which provide physical support to cells. • Connective tissue also allows oxygen to diffuse from blood vessels into cells. • About 1 in 10 people are have a disorder involving connective tissue. • Some connective tissue disorders include sarcomas, Marfan syndrome, lupus, and scurvy, which is a Vitamin C deficiency that leads to fragile connective tissue.
- 21. Major functions of connective tissue include: 1) Binding and supporting, 2) Protecting, 3) Insulating, 4) Storing reserve fuel, and 5) Transporting substances within the body
- 22. Types of connective tissue 1. Connective tissue proper 2. Cartilage 3. Bone 4. Blood
- 23. 3. Muscle Tissues • Muscle tissue comprises all the muscles in the body • Have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts • There are three types of muscle tissue: 1. Skeletal muscle, 2. Cardiac muscle, and 3. Smooth muscle.
- 24. • Skeletal muscle anchors tendons to bones and allows the body to move. • Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and contracts to pump blood. • Smooth muscle is found in the intestines, where it helps move food through the digestive tract, and it is also found in other organs like blood vessels, the uterus, and the bladder.
- 25. 4. Nervous Tissue • Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, which are all parts of the nervous system. • It is made up of neurons, which are nerve cells, and neuroglia, which are cells that help nerve impulses travel. • Nervous tissue is grouped into four types: – gray matter and white matter in the brain, and nerves and ganglia in the peripheral nervous system.
- 26. • The main difference between gray and white matter is that axons of the neurons in gray matter are unmyelinated, while white matter is myelinated. • Myelin is a white, fatty substance that insulates neurons and is vital for nervous system functioning.
- 27. Functions of the Nervous Tissue •Memory and learning •Voluntary movement control •Regulates & controls body functions •Generates & transmits nerve impulses •Supports and protects impulse generating neurons.
- 28. Thank You 2nd December, 2021
Editor's Notes
- to weave: make (a complex story or pattern) from a number of interconnected elements.
- Epithelial tissue, also called “Epithelium” or “Covering Tissue”,
- The important functions of the simple cuboidal epithelium are secretion and absorption. This epithelial type is found in the small collecting ducts of the kidneys, pancreas, and salivary glands.
- The simple columnar epithelium is mainly involved in secretion, excretion, and absorption. The ciliated type can be found in the bronchi, uterine tubes, the uterus, and part of the spinal cord. These epithelia are capable of moving mucus or other substances through the beating of their cilia.
- Squamous epithelial tissue protects the underlying parts of the body from mechanical injury, pathogens and desiccation. It also forms a selectively permeable surface where filtration and transportation of substances can occur. Found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment
- Squamous epithelial tissue protects the underlying parts of the body from mechanical injury, pathogens and desiccation. It also forms a selectively permeable surface where filtration and transportation of substances can occur. Found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment
- Squamous epithelial tissue protects the underlying parts of the body from mechanical injury, pathogens and desiccation. It also forms a selectively permeable surface where filtration and transportation of substances can occur. Found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment
- https://biologydictionary.net/transitional-epithelium/ Transitional epithelium : Lesson Summary. Transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder. These cells are called transitional because they can undergo a change in their shape and structure. Found where expression is needed
- The cells in the transitional epithelium are pear-shaped or round, but as tissue is stretched, cells become flattened, giving the appearance of stratified squamous epithelium.
- Ground substance: Also called matrix. the homogeneous substance in which the fibers and cells of connective tissue are embedded.
- Sarcoma: A type of cancer that begins in bone or in the soft tissues of the body, including cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, fibrous tissue, or other connective or supportive tissue. Marfan syndrome: Marfan syndrome is an inherited disorder that affects connective tissue Lupus is a disease that occurs when your body's immune system attacks your own tissues and organs (autoimmune disease) Scurvy is a state of dietary deficiency of vitamin C (ascorbic acid).
- Insulating: "protect from heat, cold, or noise,“ Storing reserve fuel
- Peripheral nerves reside outside your brain and spinal cord. They relay information between your brain and the rest of your body. The peripheral nervous system is divided into two main parts: Autonomic nervous system (ANS): Controls involuntary bodily functions and regulates glands. Neuroglia, also called glial cell or glia, any of several types of cell that function primarily to support neurons Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies found throughout the body. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and carry nerve signals to and from the central nervous system.
