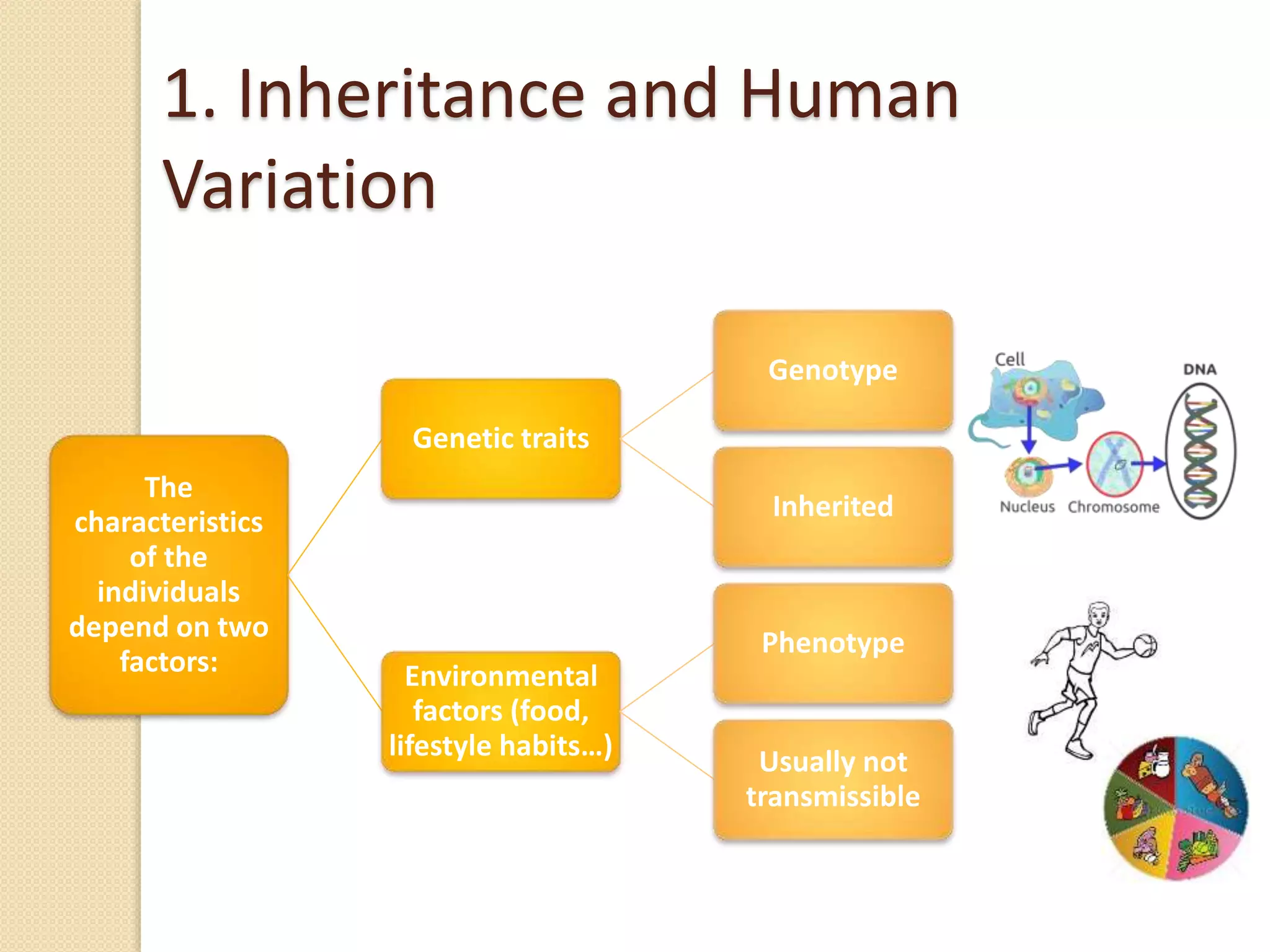
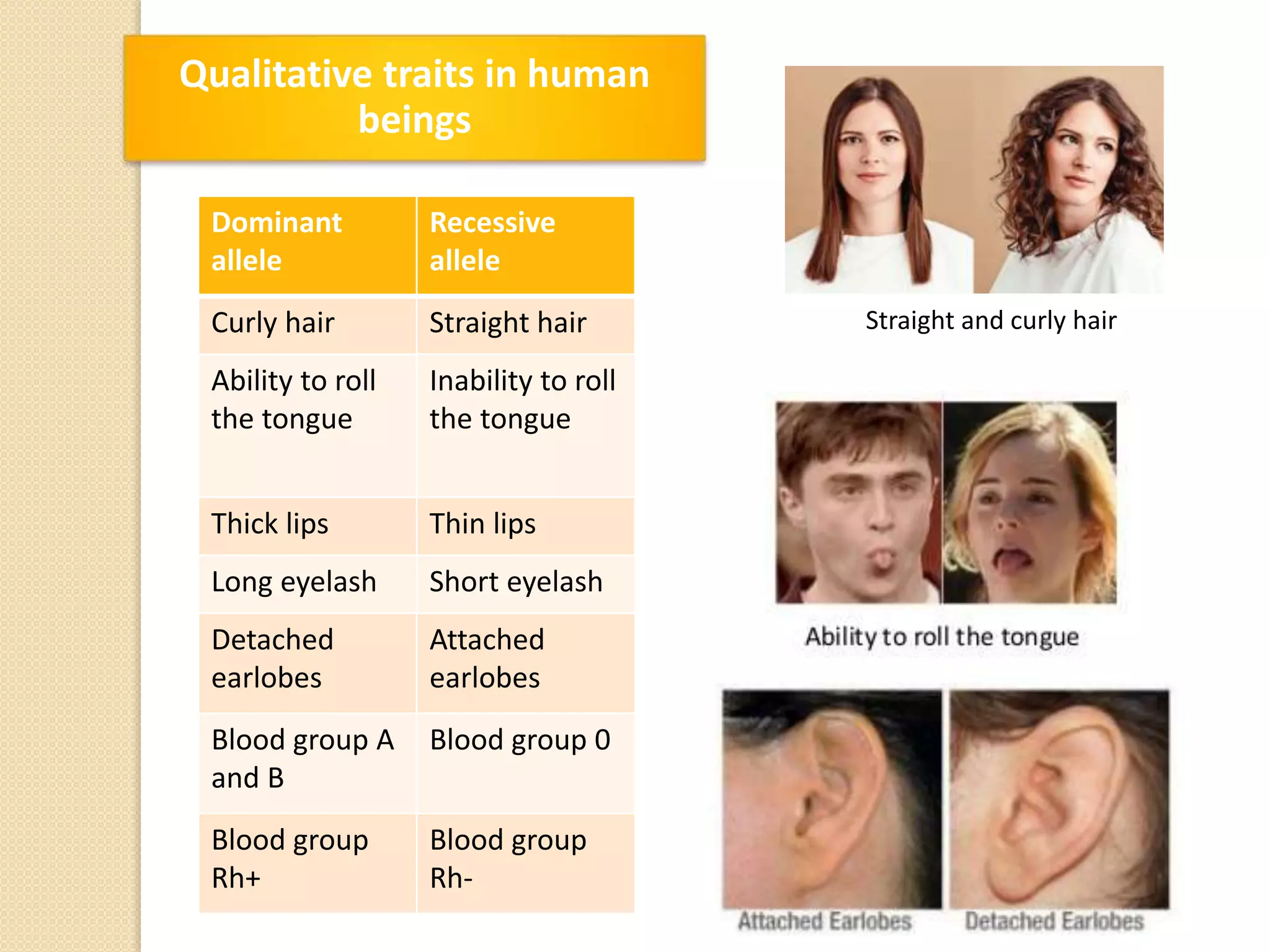
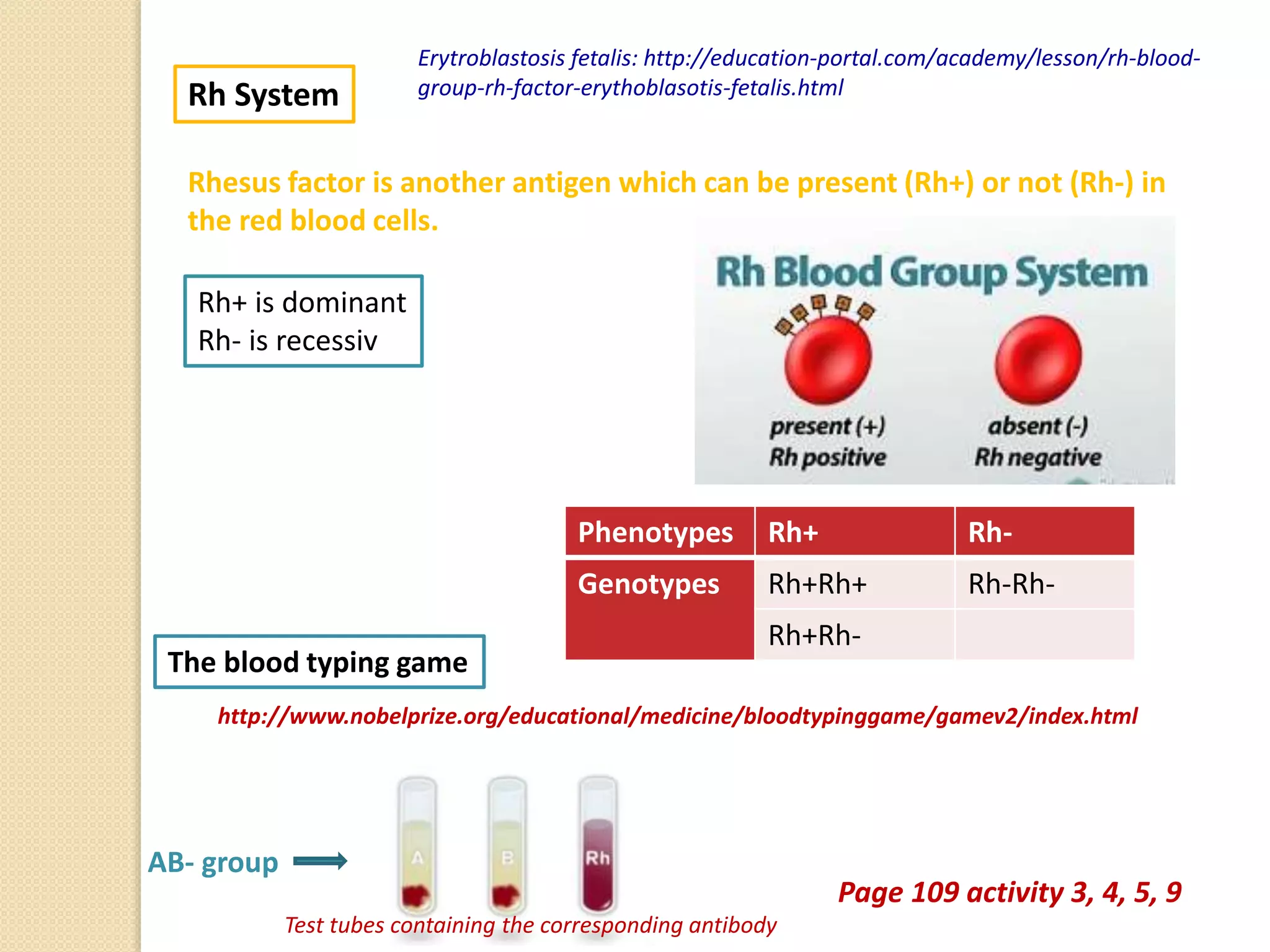
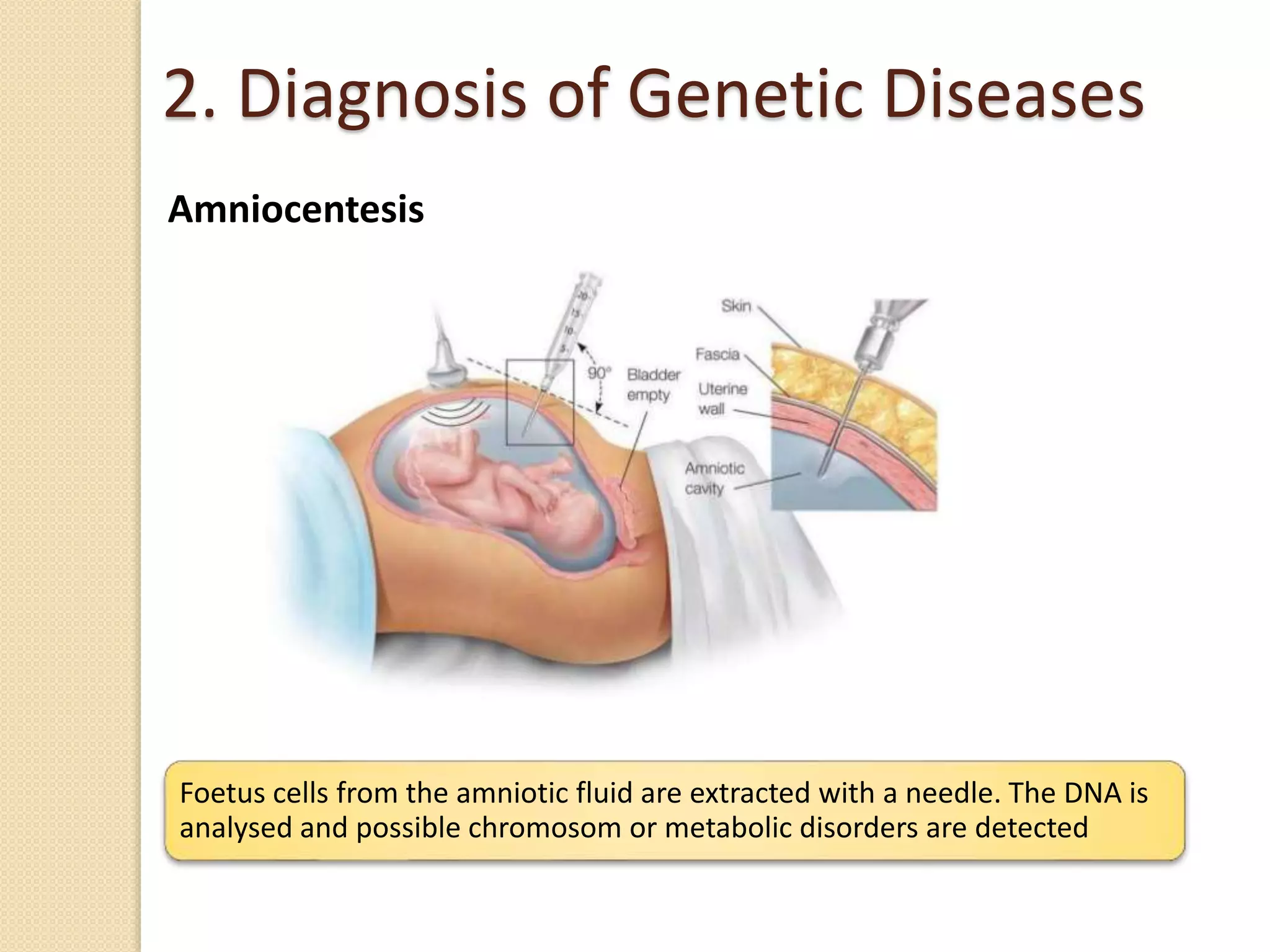
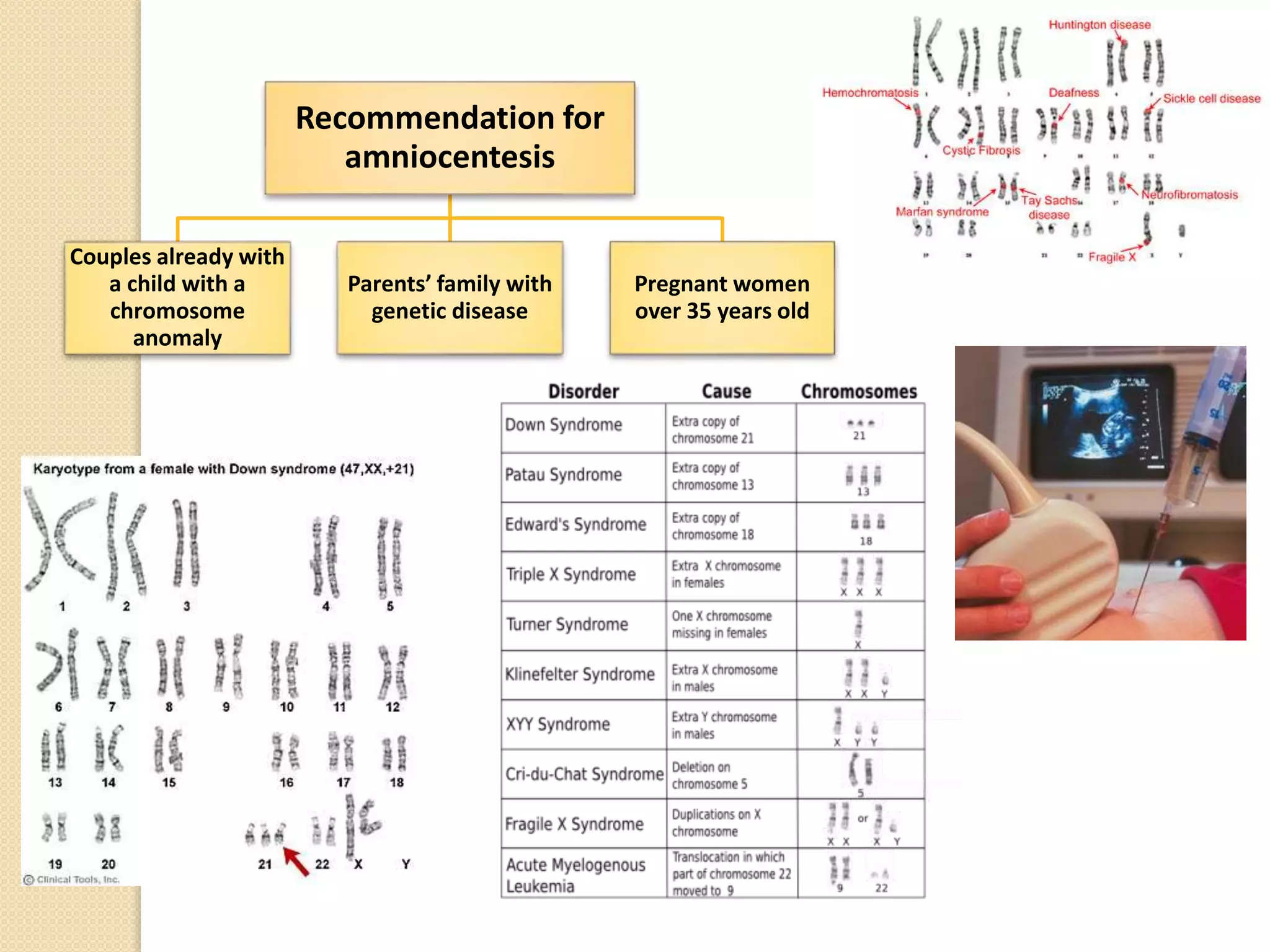
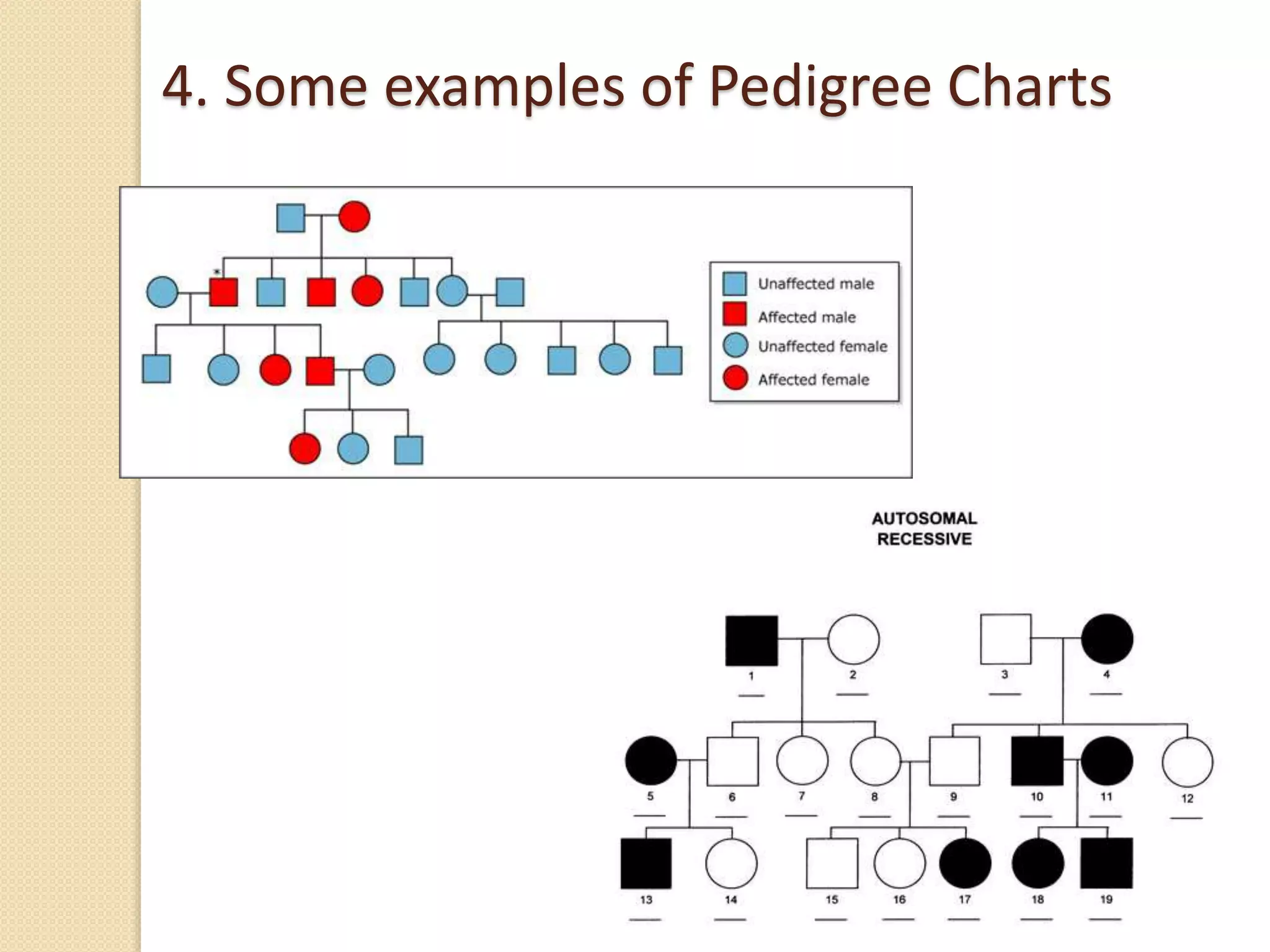
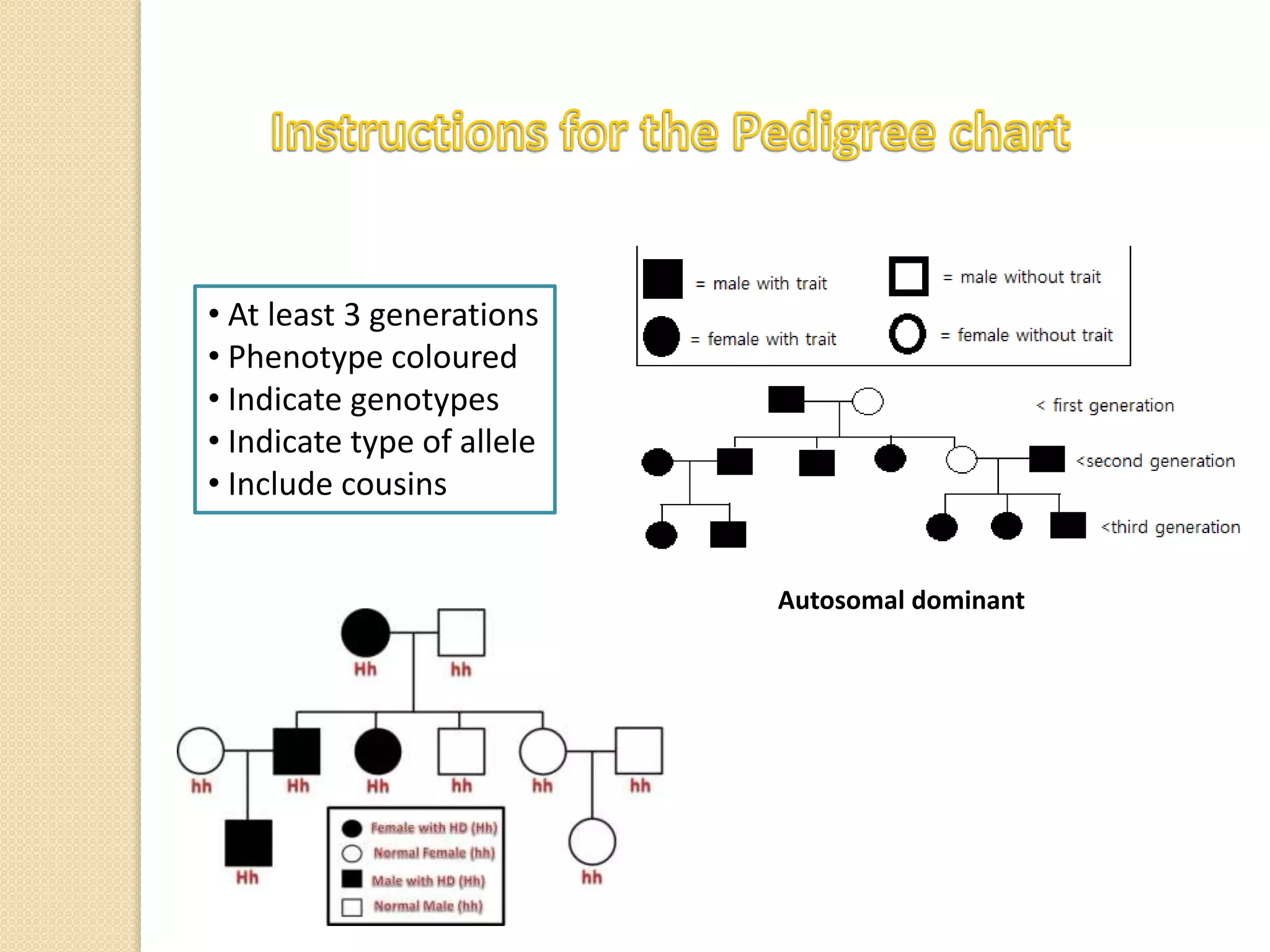
This document discusses human genetics and genetic disorders. It covers inheritance and human variation, including dominant and recessive traits. Quantitative traits like skin and eye color are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. The document also discusses genetic diagnosis through amniocentesis and common genetic disorders such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and those linked to the X chromosome like color blindness and hemophilia. Pedigree charts are presented as a way to track inheritance of genetic traits across generations.