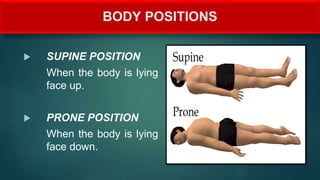
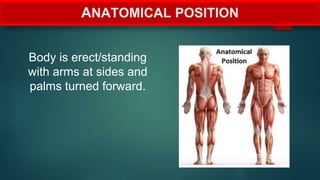
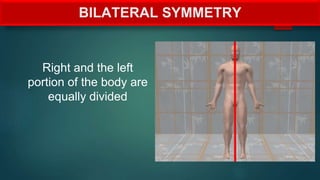
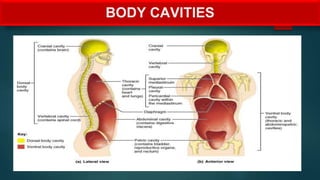
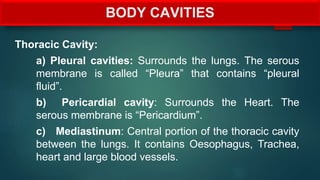
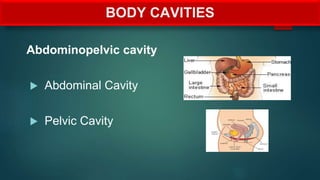
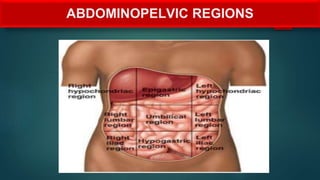
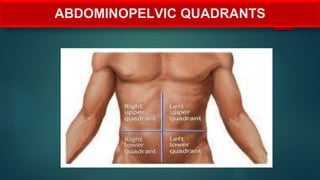
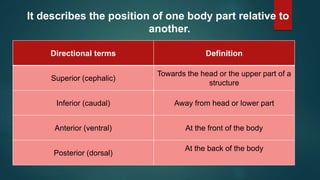
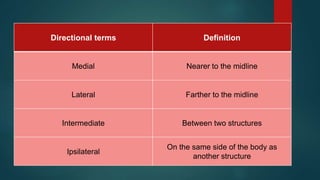
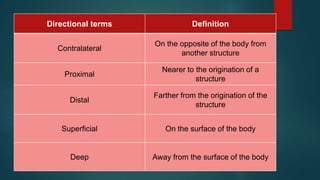
The document provides an overview of anatomy and physiology, detailing definitions, important branches, and structural organization. It discusses various body systems, components, and their respective functions, along with anatomical terminology and body planes. The content serves as an introduction to understanding the human body's structure and functions.