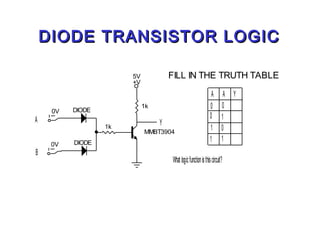
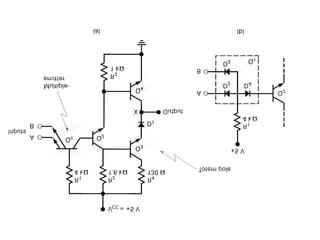
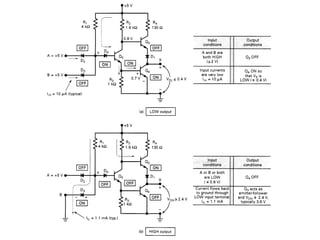
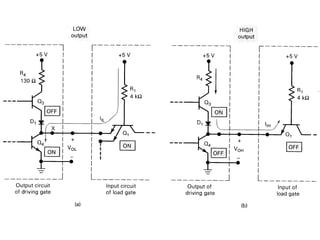
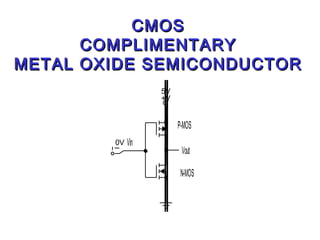
This document discusses different types of logic families used in digital electronics, including TTL, CMOS, and ECL. It provides information on what each acronym stands for and the typical voltage levels for logic 0 and 1 inputs. It also lists some key differences between TTL and CMOS logic families. The document also includes vocabulary terms and circuit diagrams to illustrate MOSFET, CMOS, and ECL logic technologies.