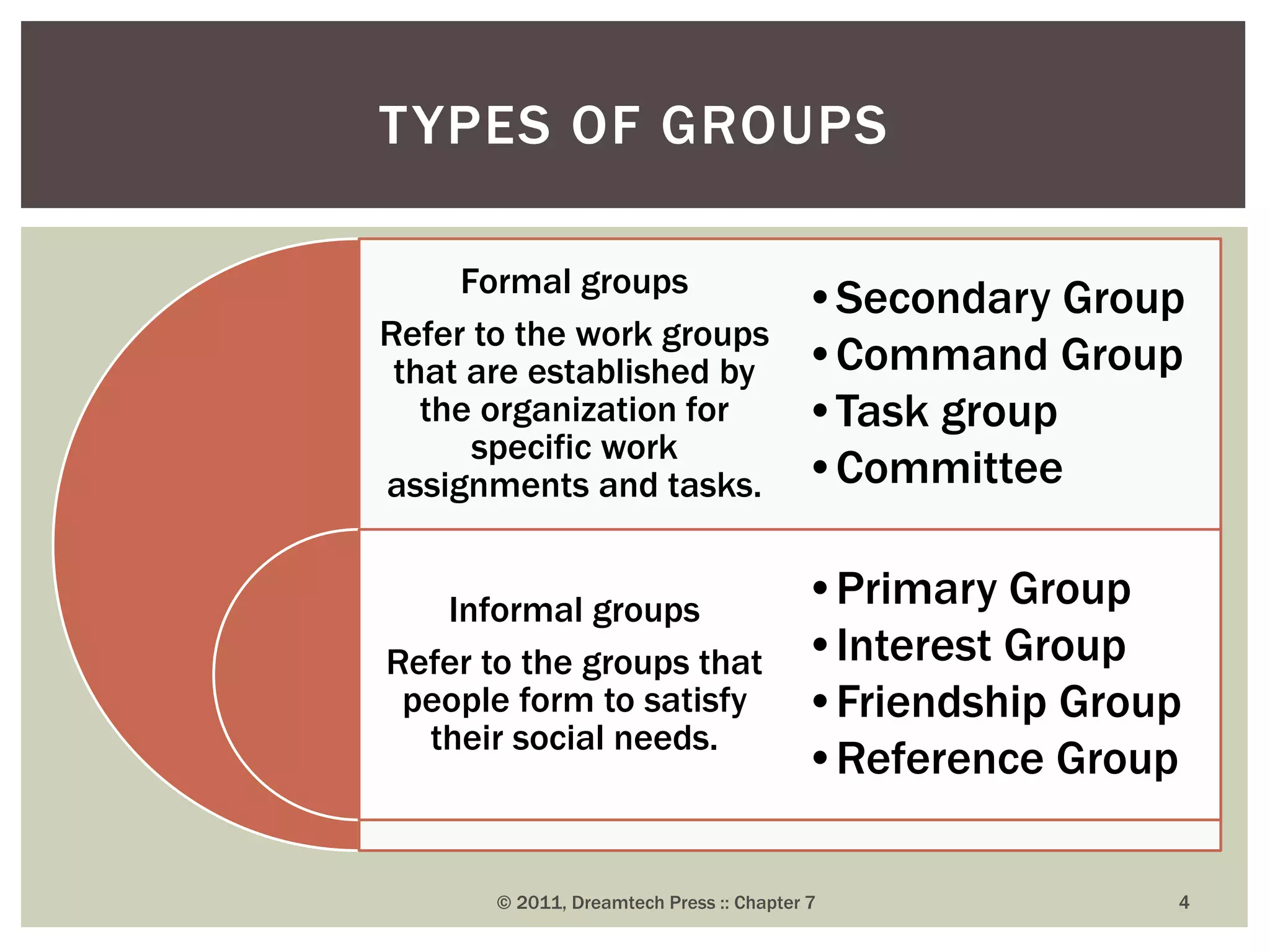
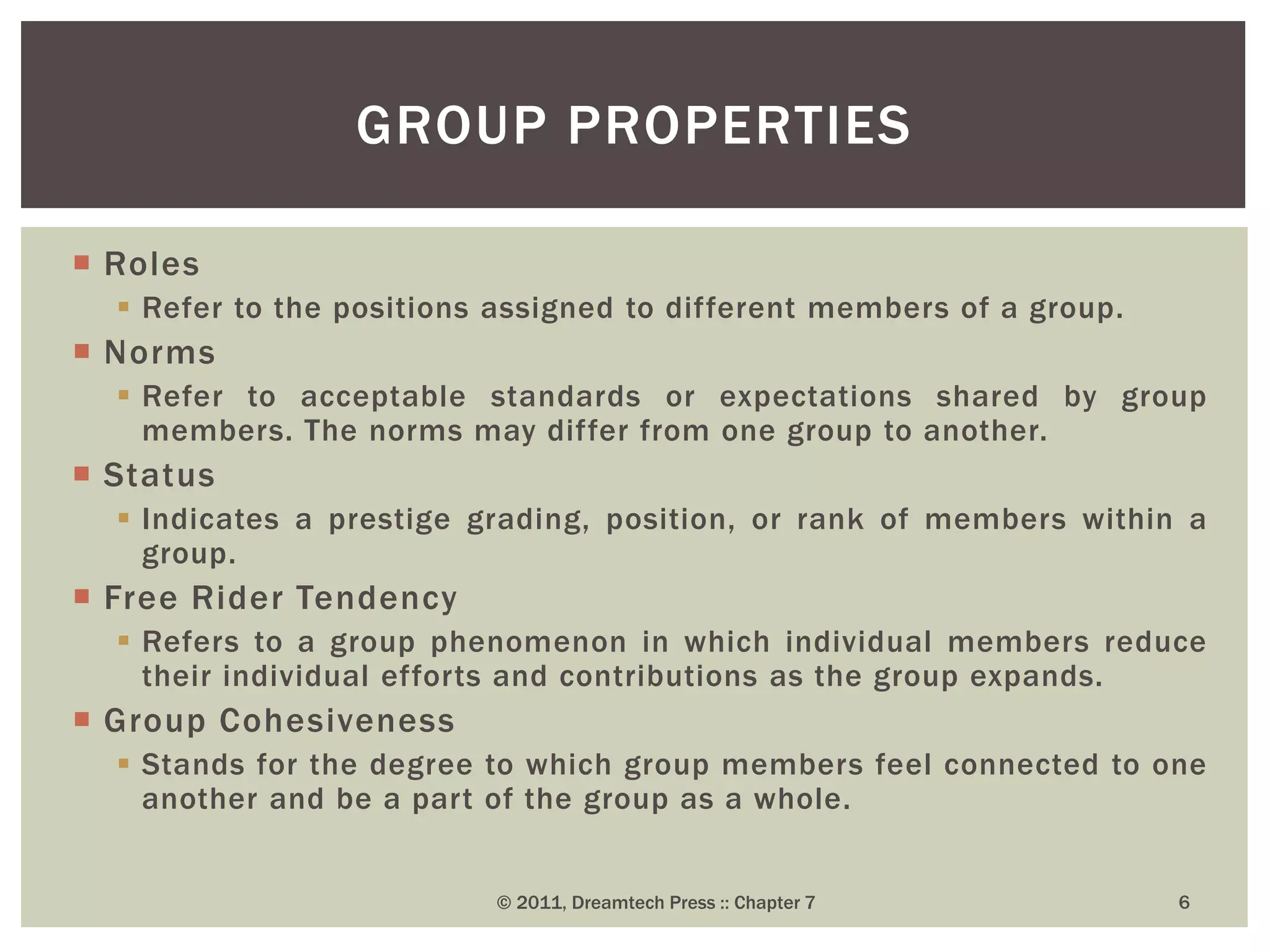
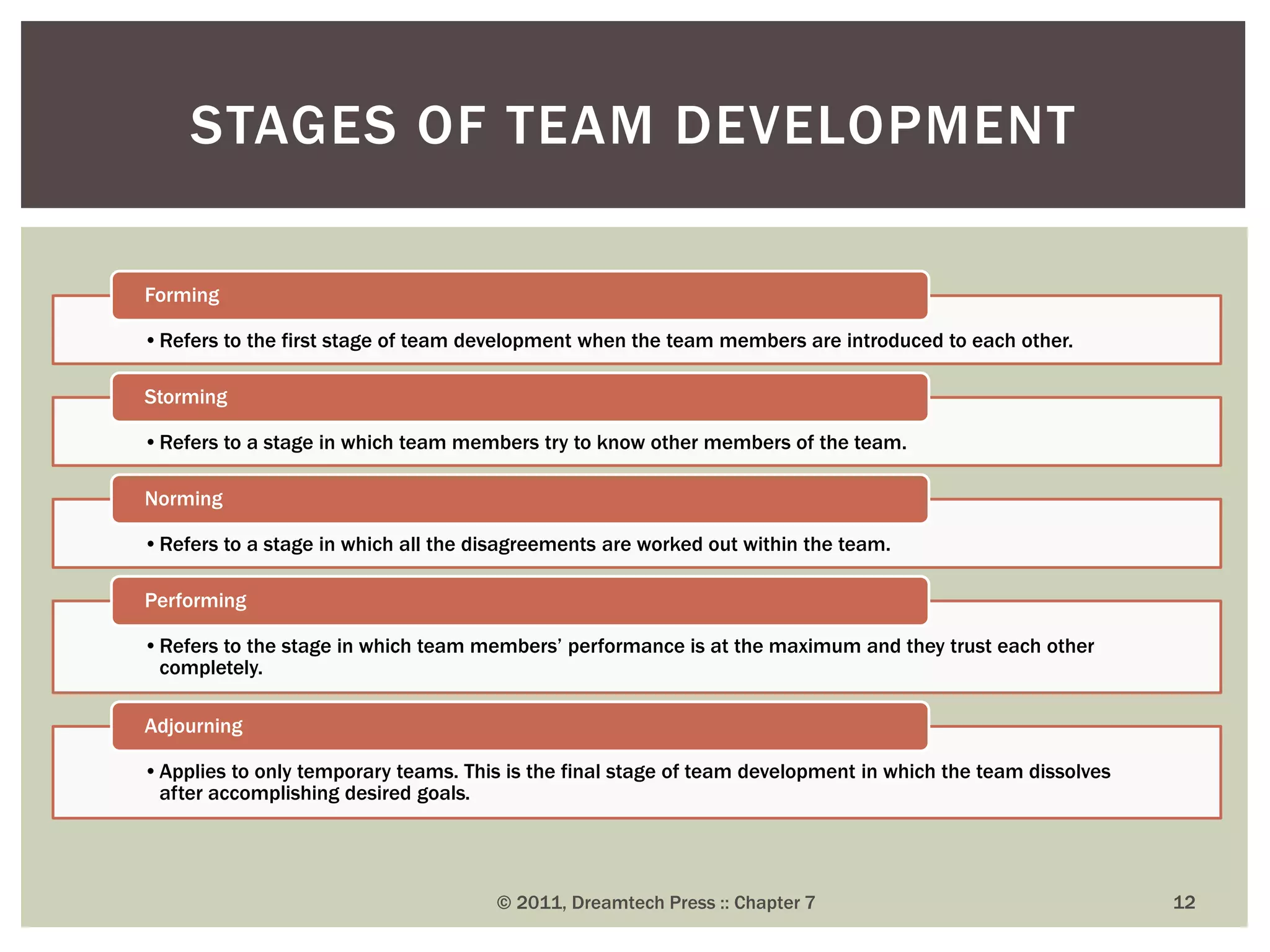
Groups and teams are important parts of any organization. A group is defined as two or more individuals who interact and share a collective identity. Groups form to fulfill members' needs for belongingness, support, security, recognition, and proximity. Both formal and informal groups exist in organizations. Team dynamics, properties like roles and norms, and concepts like groupthink must be understood to utilize groups and teams effectively. While groups focus on individual goals, teams emphasize mutual accountability and collective goals to produce outcomes through shared roles and responsibilities. The formation of cohesive and diverse groups and teams is crucial for organizational decision-making.