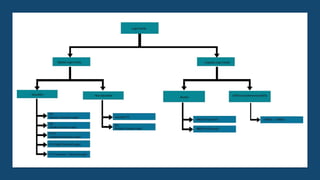
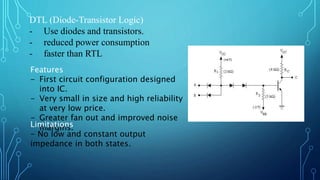
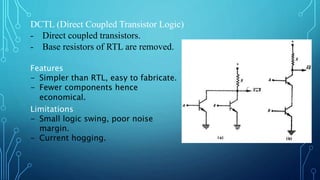
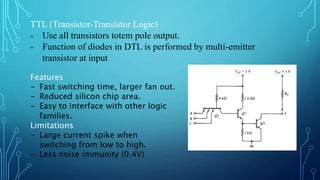
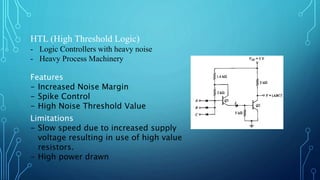
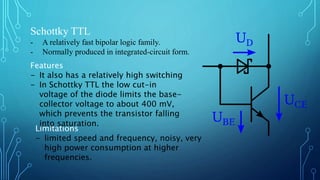
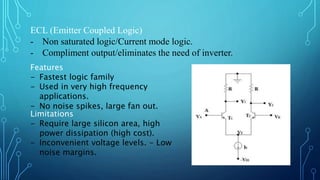
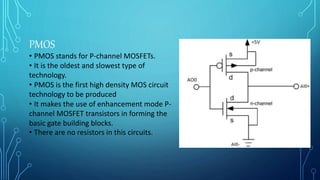
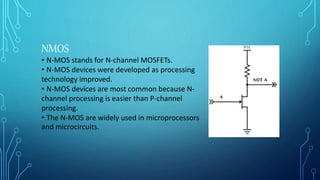
The document discusses the evolution of digital logic families in computer engineering, focusing on various types such as bipolar, unipolar, and CMOS logic families, each with distinct features and limitations. Key characteristics of these logic families include fan-in, fan-out, power dissipation, propagation delay, noise margin, and speed-power product. Understanding these unique attributes allows for optimization in circuit design.