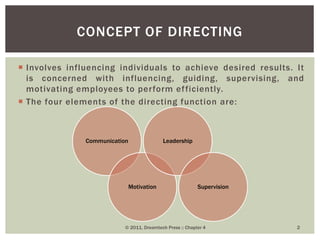
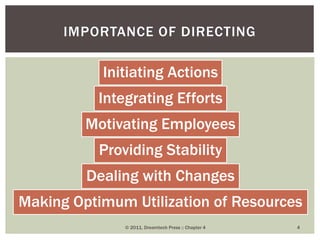
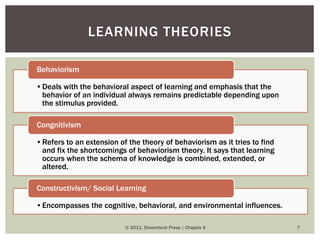
This document discusses key concepts in management functions including directing, personality, attitude, learning theories, perception, supervision, and motivation. It defines directing as influencing employees to perform efficiently through communication, motivation, leadership, and supervision. Personality is described as unique physical, mental and moral qualities. Attitude has cognitive, affective and behavioral components. Learning theories covered are behaviorism, cognitivism and constructivism. Perception involves receiving, selecting, organizing and interpreting sensory data. Supervision oversees subordinates' work through commanding, guiding and controlling. Motivation aims to improve employee performance and efficiency.