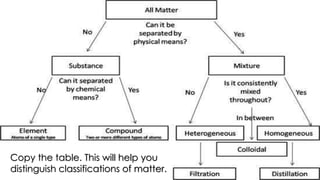
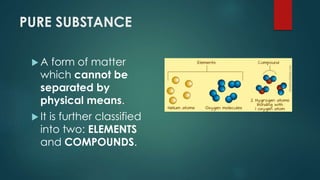
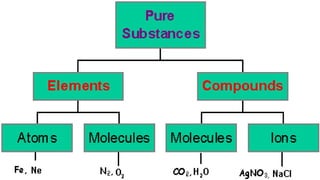
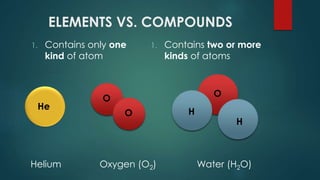
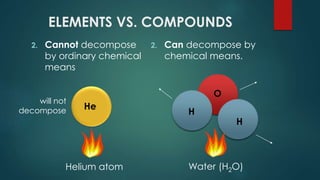
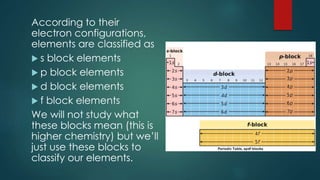
The document outlines the differences between elements and compounds, highlighting that elements consist of a single kind of atom while compounds are made up of two or more kinds of atoms. It also categorizes matter into metals, metalloids, and nonmetals, with a brief mention of the law of definite composition in compounds. Additionally, the document includes examples and classification exercises related to the periodic table.