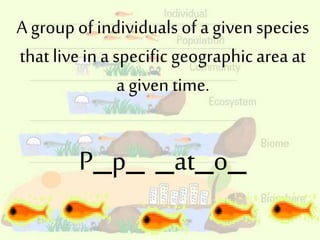
1. The document discusses the different levels of biological organization from atoms to the biosphere.
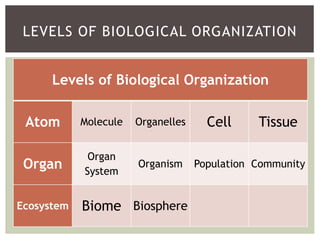
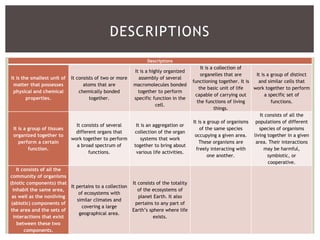
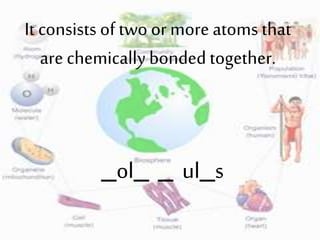
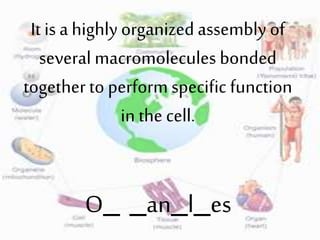
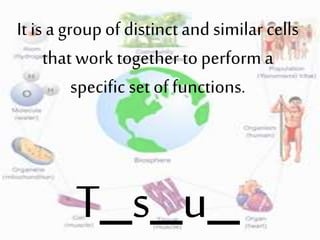
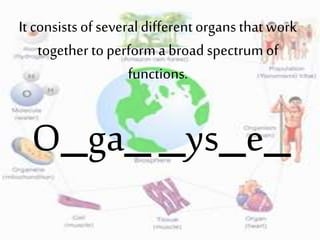
2. It provides descriptions and examples for each level, from the smallest levels of atoms and molecules, to organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and the biosphere.
3. The levels of organization show how simple structures combine to form more complex living things, with implications that harm at one level can affect higher levels of organization.



![[http://ed.ted.com/lessons/making-sense-of-how-life-fits-
together-bobbi-seleski]
MAKING SENSE OF HOW LIFE FITS
TOGETHER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/levelsoforganization-151109052955-lva1-app6892/85/Levels-of-organization-4-320.jpg)