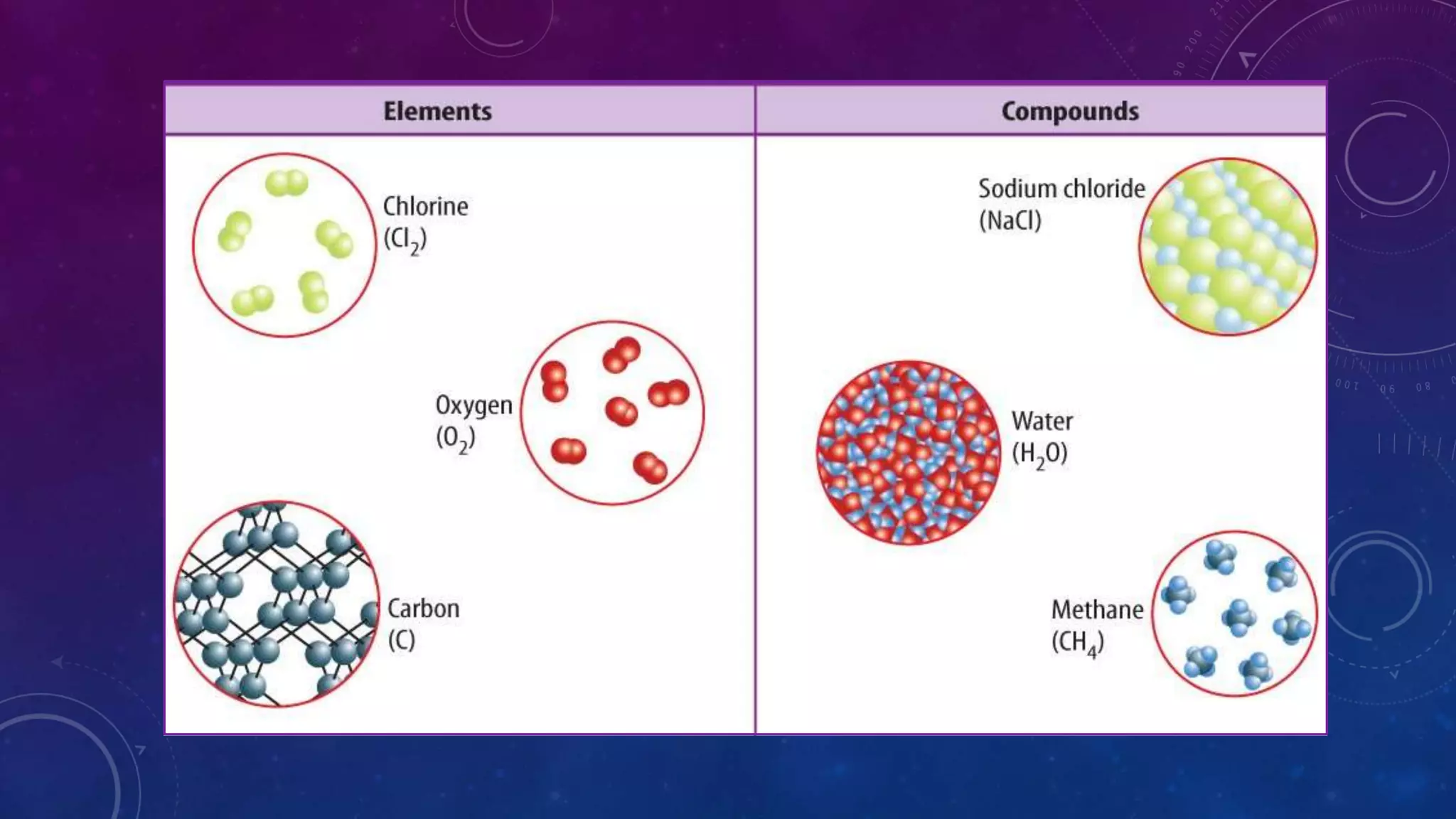
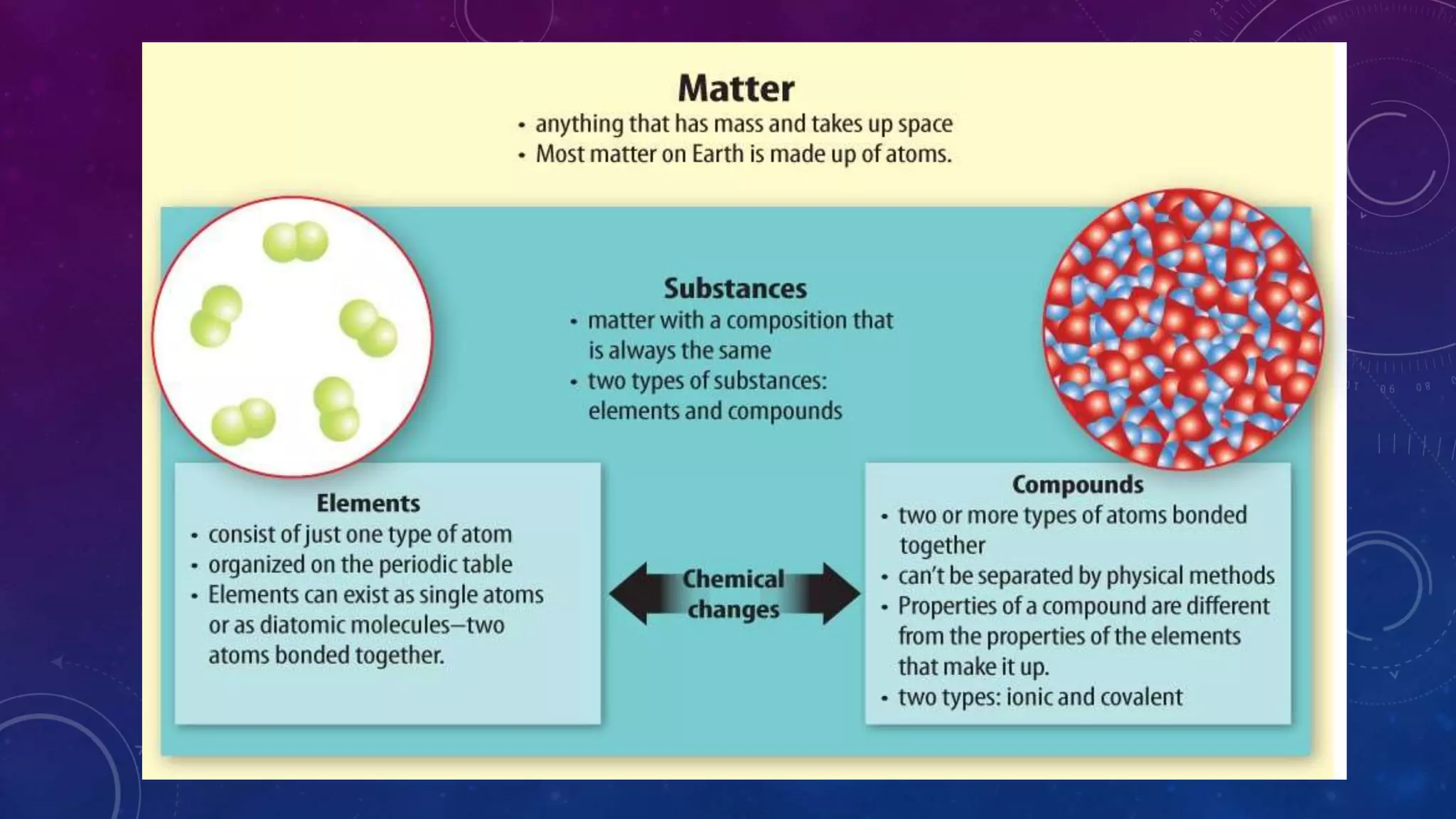
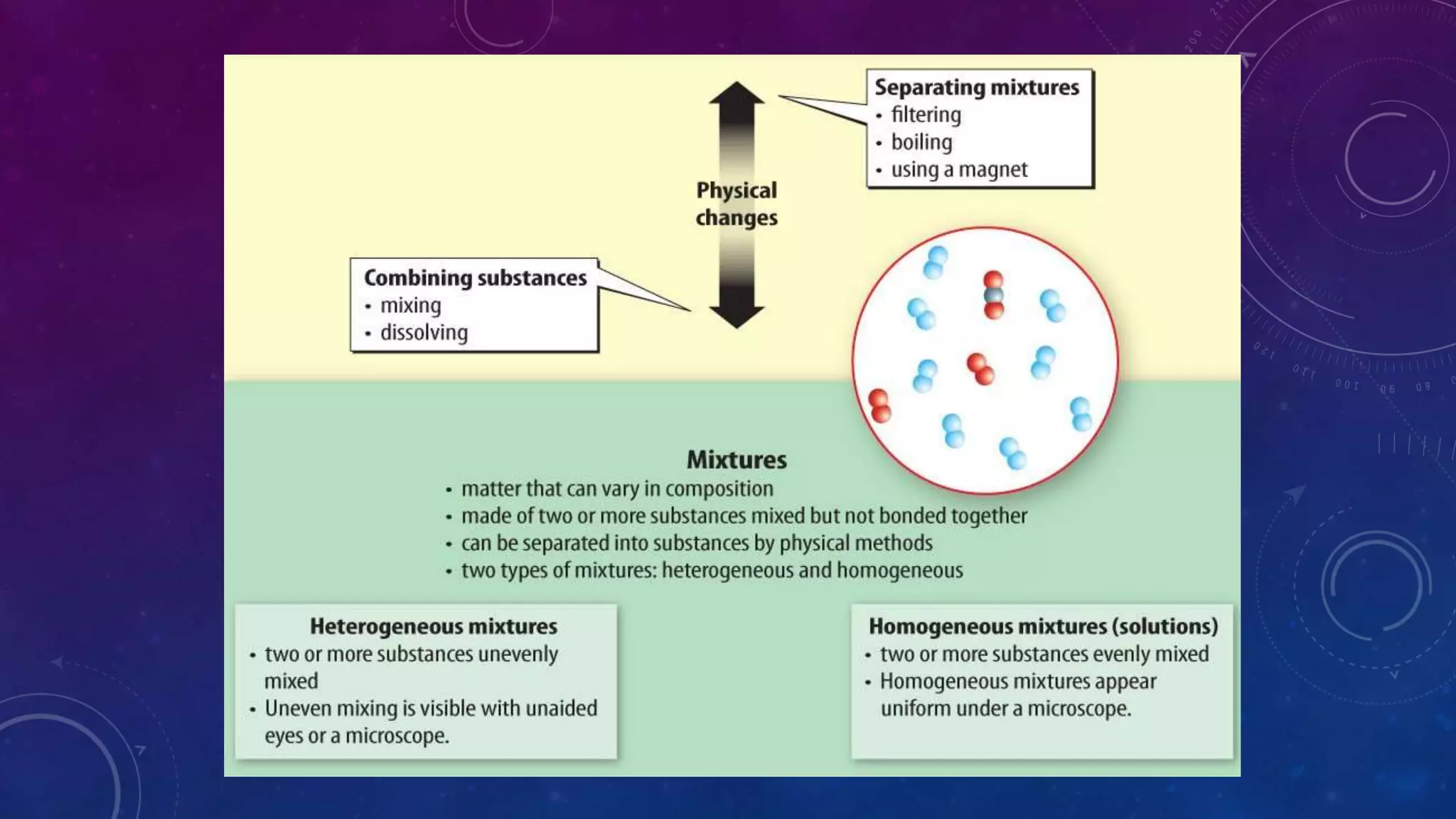
This document discusses substances, mixtures, and the differences between them. It defines a substance as matter that always has the same composition, while a mixture's composition can vary. Mixtures can be either heterogeneous, with unevenly distributed parts visible to the eye, or homogeneous, with components mixed evenly down to the atomic or molecular level. Common examples of mixtures discussed are granite rock and air. The document also categorizes mixtures as solutions, suspensions, or colloids based on particle size. Compounds are different from mixtures as their properties result from chemical bonding rather than just physical blending of substances.