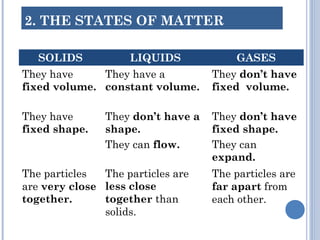
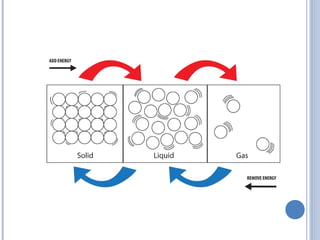
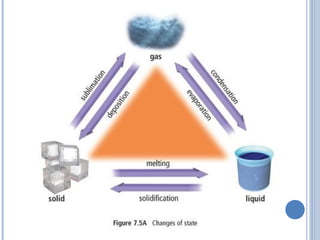
1. Matter is everything that has mass and volume and exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. The document defines the key properties of each state.
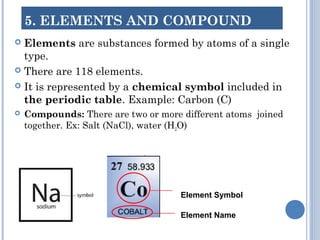
2. Atoms are the smallest particles that make up all matter. Atoms can join together to form molecules or exist as individual elements. Elements are made of a single type of atom, while compounds contain two or more different types of atoms.
3. Pure substances like elements and compounds are uniform throughout, while mixtures contain two or more substances that can be separated. Examples of mixtures include solutions, alloys, and suspensions.