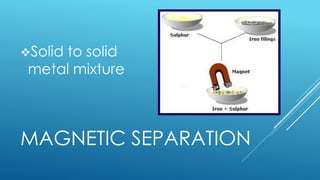
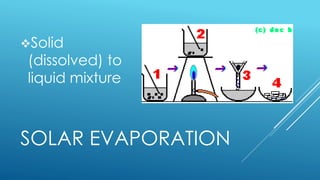
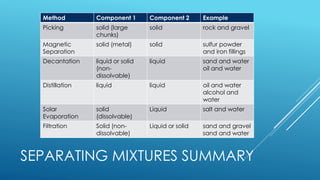
The document outlines the concept of mixtures, differentiating between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, along with methods for separating them. It provides definitions, examples, and classification activities related to mixtures, including practical separation techniques such as filtration and distillation. The lesson also encourages students to relate the topic to their daily lives and spiritual reflections.