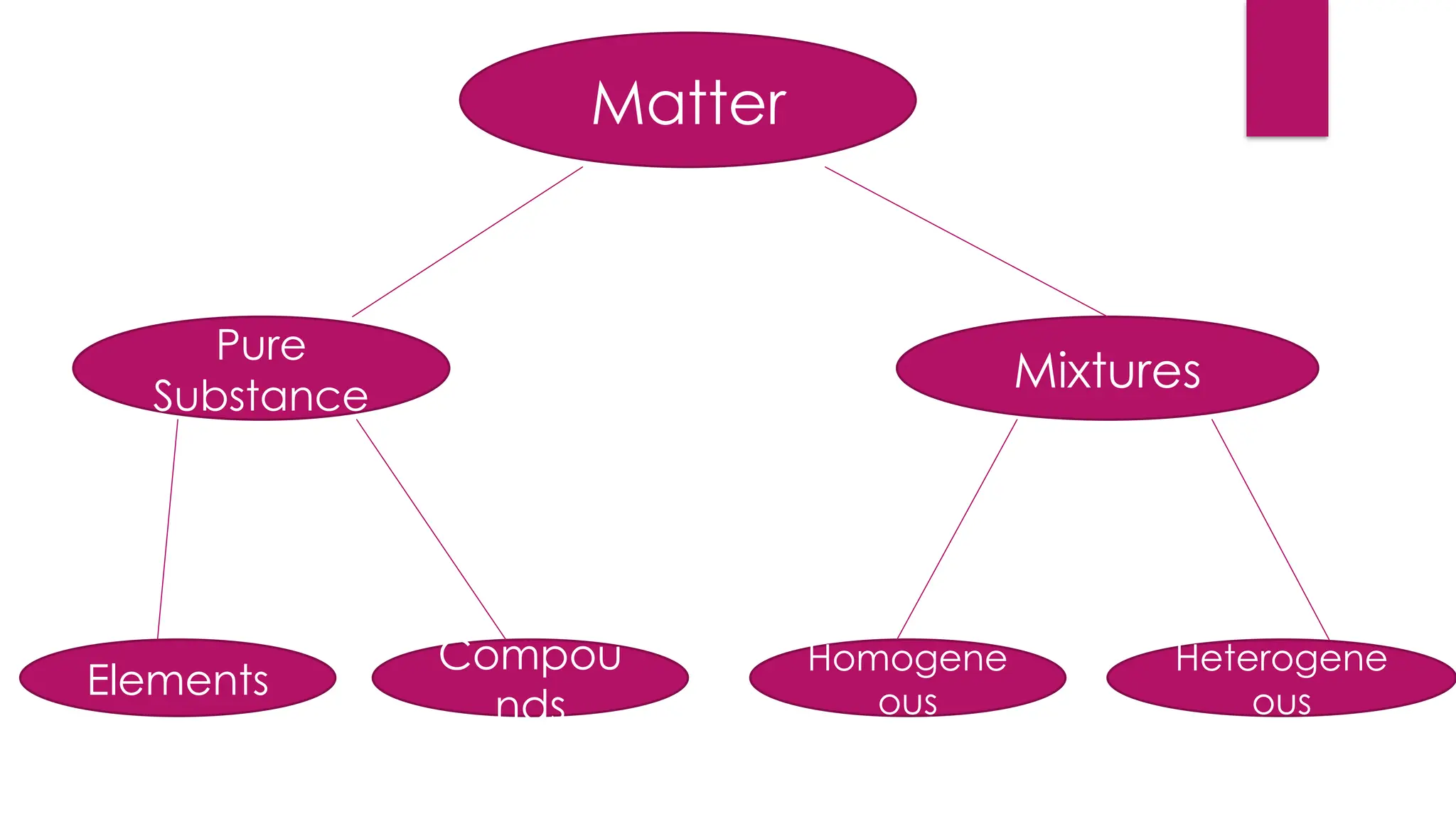
The document outlines the differences between compounds and mixtures, emphasizing key definitions and characteristics of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. It details three methods for separating mixtures: filtration, distillation, and chromatography, along with their applications in real-world scenarios. Homework requires students to select one separation method to explain and illustrate.