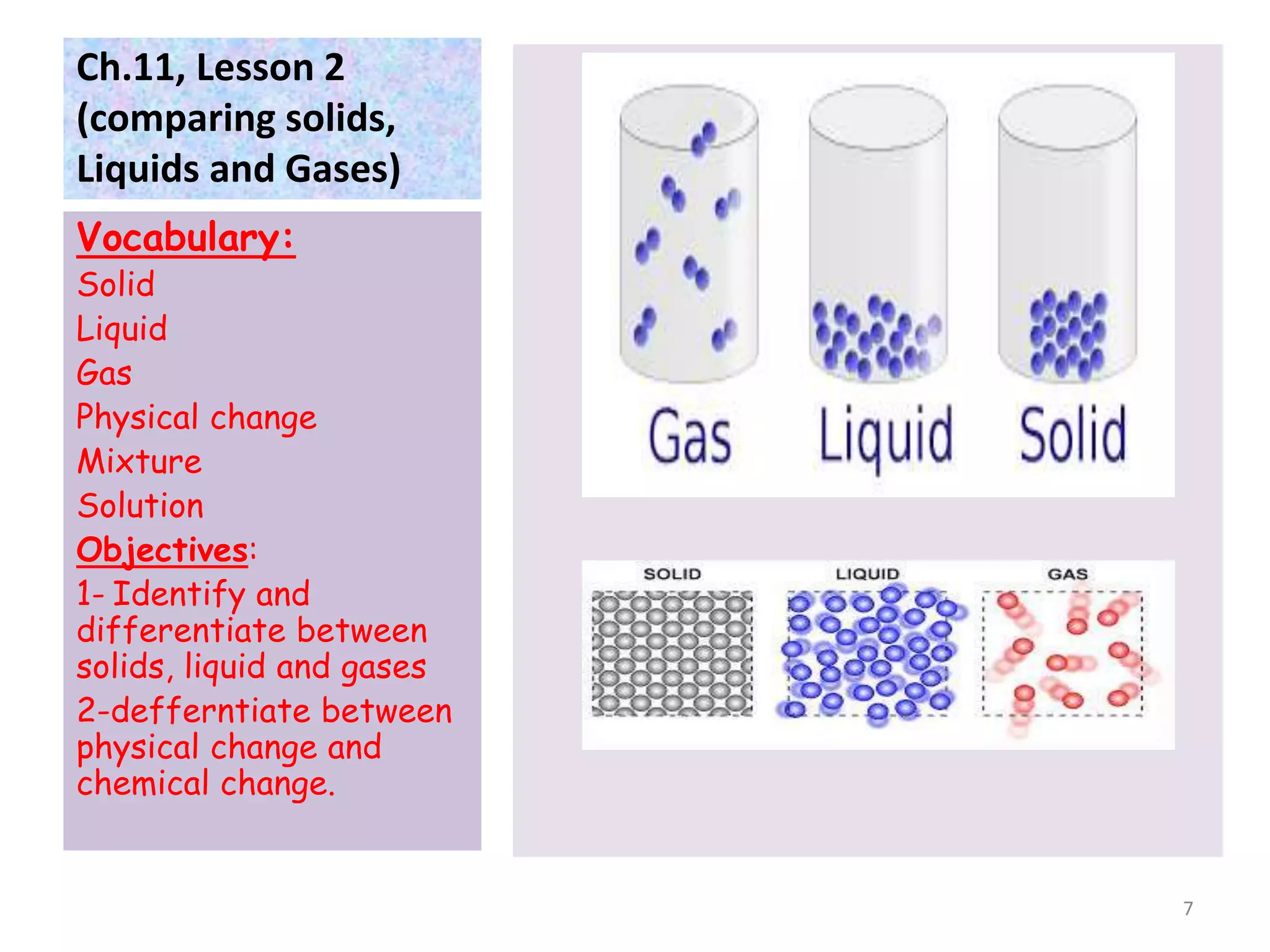
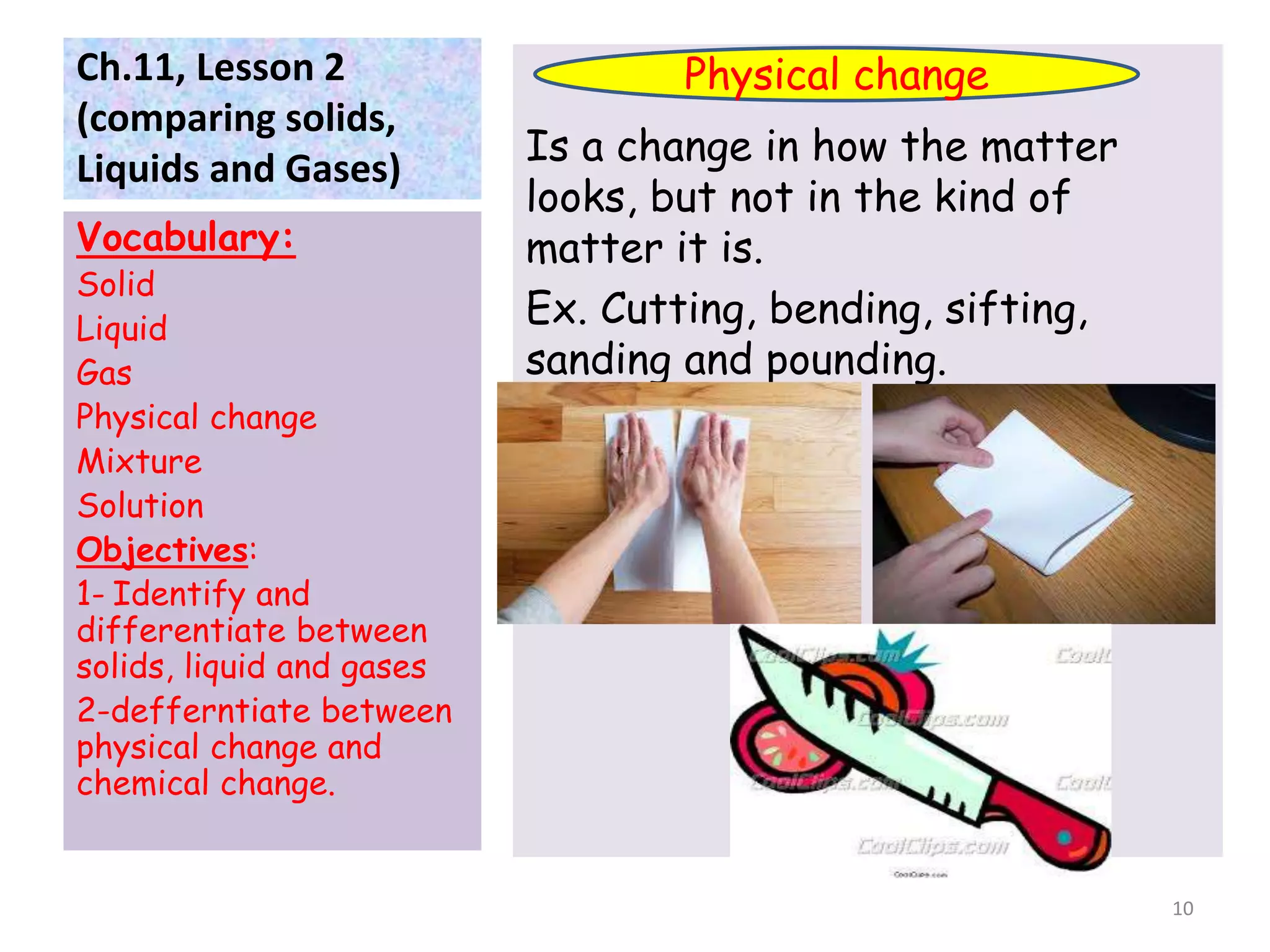
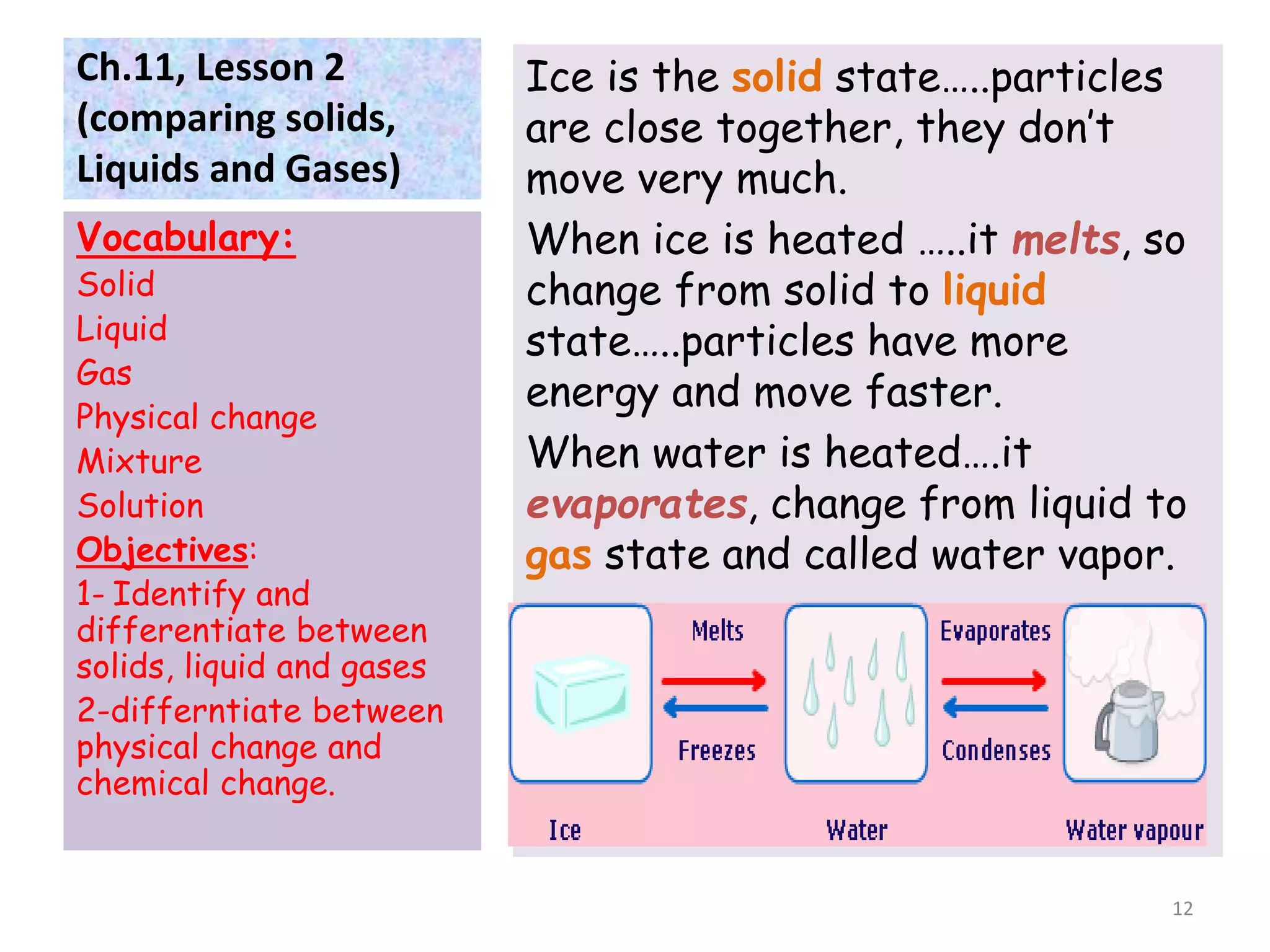
This document discusses the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It defines each state and explains how their particle arrangements differ. Solids have a definite shape and volume, while liquids have a definite volume but not shape, and gases fill their container. The document also covers physical changes like melting, freezing, and evaporation which alter a substance's state without changing its chemical makeup. Finally, it defines mixtures as combinations of materials that retain their individual properties, and solutions as mixtures where one material disseminates evenly throughout another.