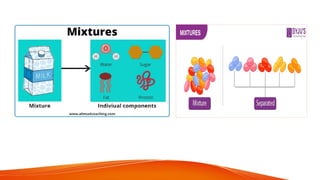
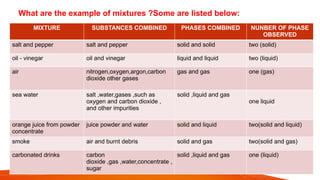
science ppt for students that The PowerPoint presentation titled "Stages of Human Growth and Development" is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the different phases of human life from infancy through late adulthood. It begins with a title slide that captures attention with a collage of diverse individuals at various life stages. The introduction outlines the purpose of the presentation, emphasizing the significance of understanding human development. The subsequent slides systematically explore each stage, starting with Infancy (0-2 Years), where rapid physical growth occurs alongside significant cognitive milestones, such as the development of object permanence. The emotional and social aspects highlight the formation of attachments with caregivers.
The presentation progresses into Early Childhood (2-6 Years), focusing on steady growth, language acquisition, and the importance of play in socializing and forming a self-concept. As it moves into Middle Childhood (6-12 Years), it highlights logical thinking development, peer relationships, and the role of education. The adolescent stage (12-18 Years) captures the impactful changes of puberty, identity exploration, and the challenges of peer pressure.
Transitioning into Early Adulthood (18-40 Years), the presentation addresses peak physical health, crucial decision-making concerning education and career, and the significance of intimate relationships. It then shifts to Middle Adulthood (40-65 Years), discussing the onset of aging signs, experience-based knowledge, and generativity, the desire to contribute to the next generation.
Finally, the presentation concludes with Late Adulthood (65+ Years), emphasizing health maintenance, cognitive functions, and the reflections on life. Each section features relevant visuals and infographics to aid understanding, ensuring clarity and engagement throughout. The presentation wraps up with a conclusion that summarizes the importance of the stages of human growth, inviting discussion and questions from the audience, while maintaining a cohesive design with consistent themes, colors, and fonts. This approach ensures a comprehensive yet engaging exploration of human development As the presentation transitions into Early Childhood (2-6 Years), it emphasizes the importance of imaginative play, which fosters social skills, language development, and self-concept formation. Visual aids, such as pictures of children engaged in cooperative play, enhance the narrative by illustrating these concepts in action.
The Middle Childhood (6-12 Years) segment highlights the development of logical thinking and the acquisition of academic skills, noting how peer relationships begin to play a significant role in social development. Emphasis is placed on the cognitive shifts as children move from egocentric perspectives to understanding others’ viewpoints, marking a critical phase in their social development.
In discussing Adolescence (12-18 Years), the presentation