Embed presentation

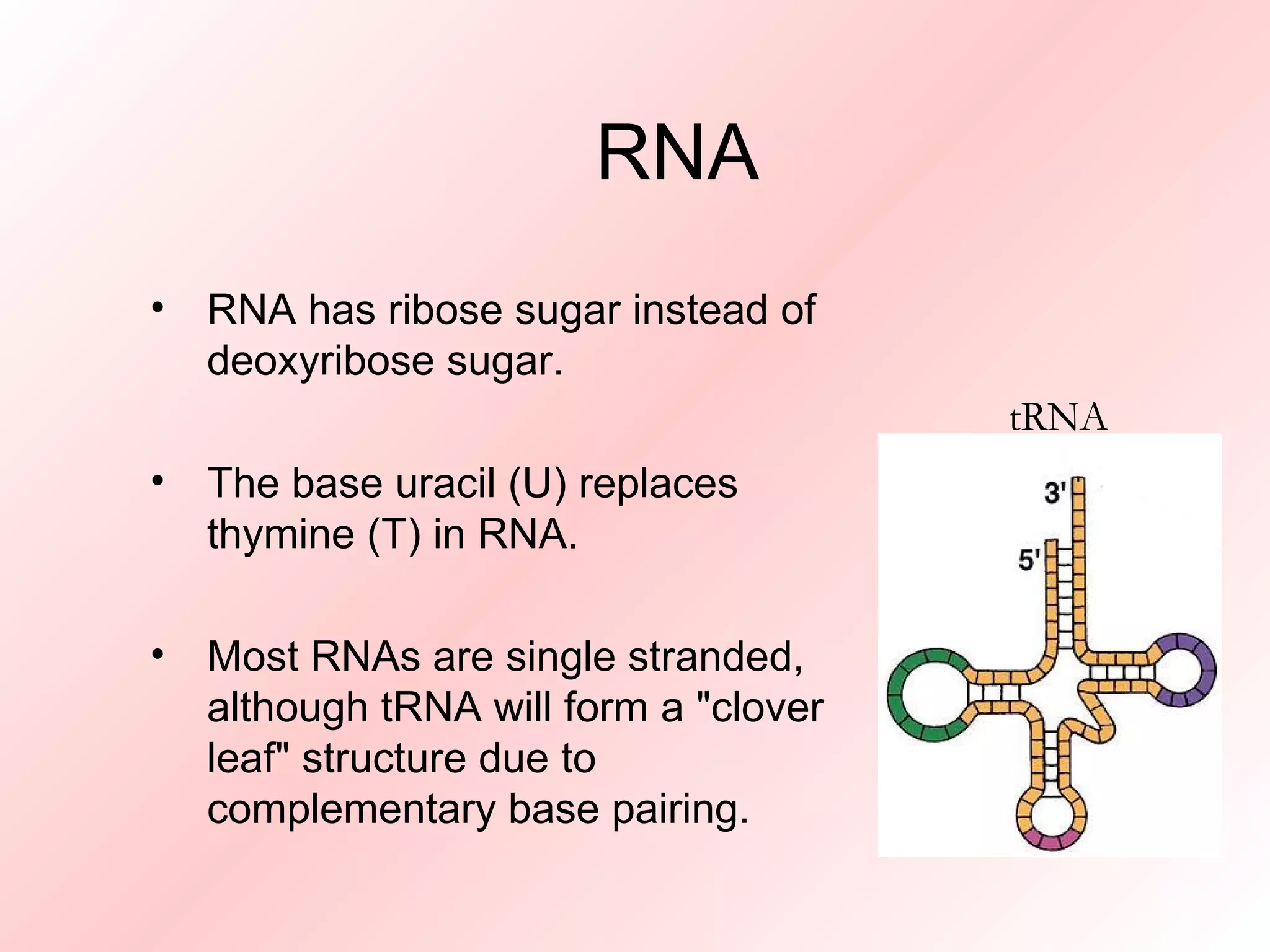
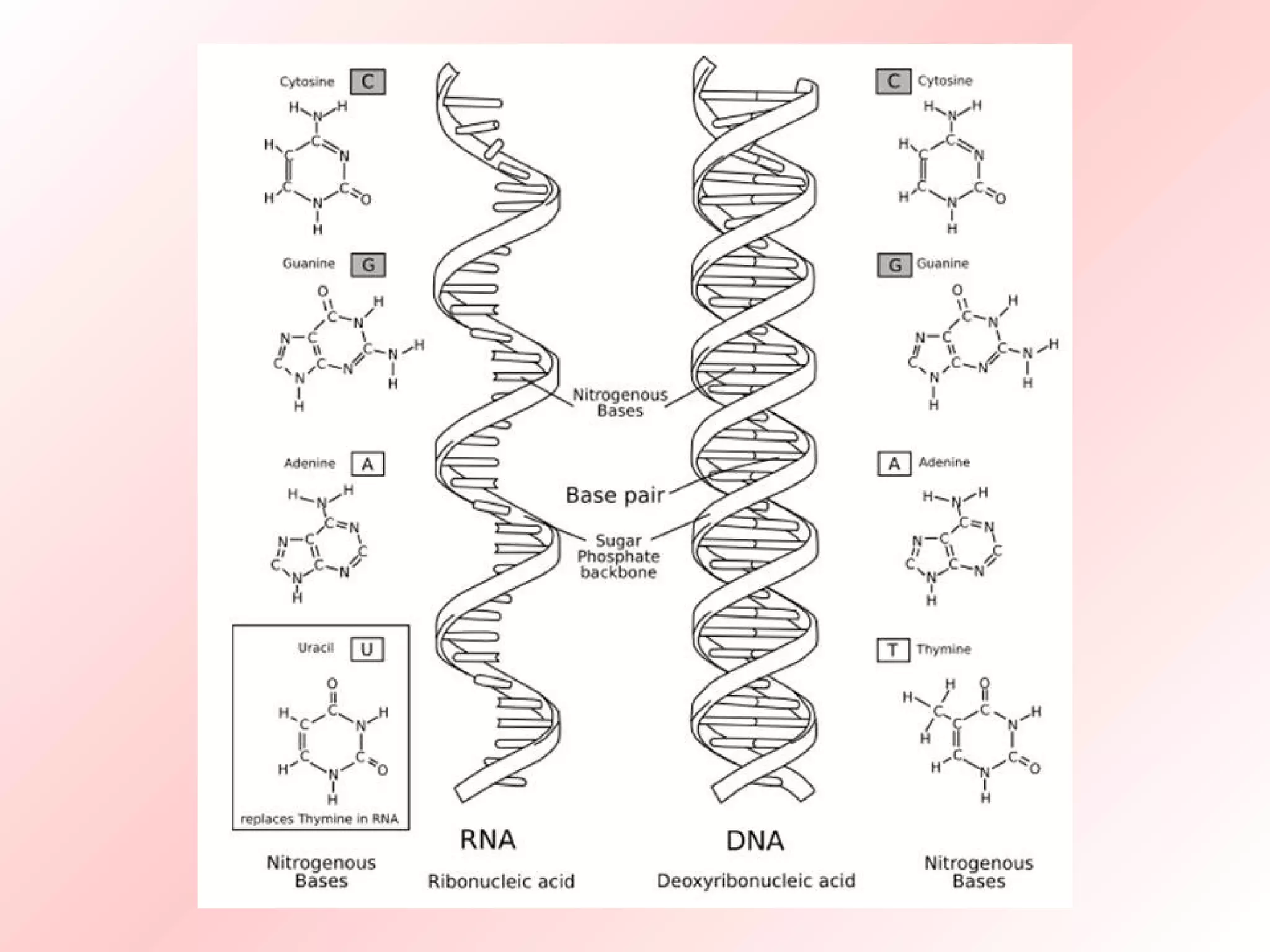

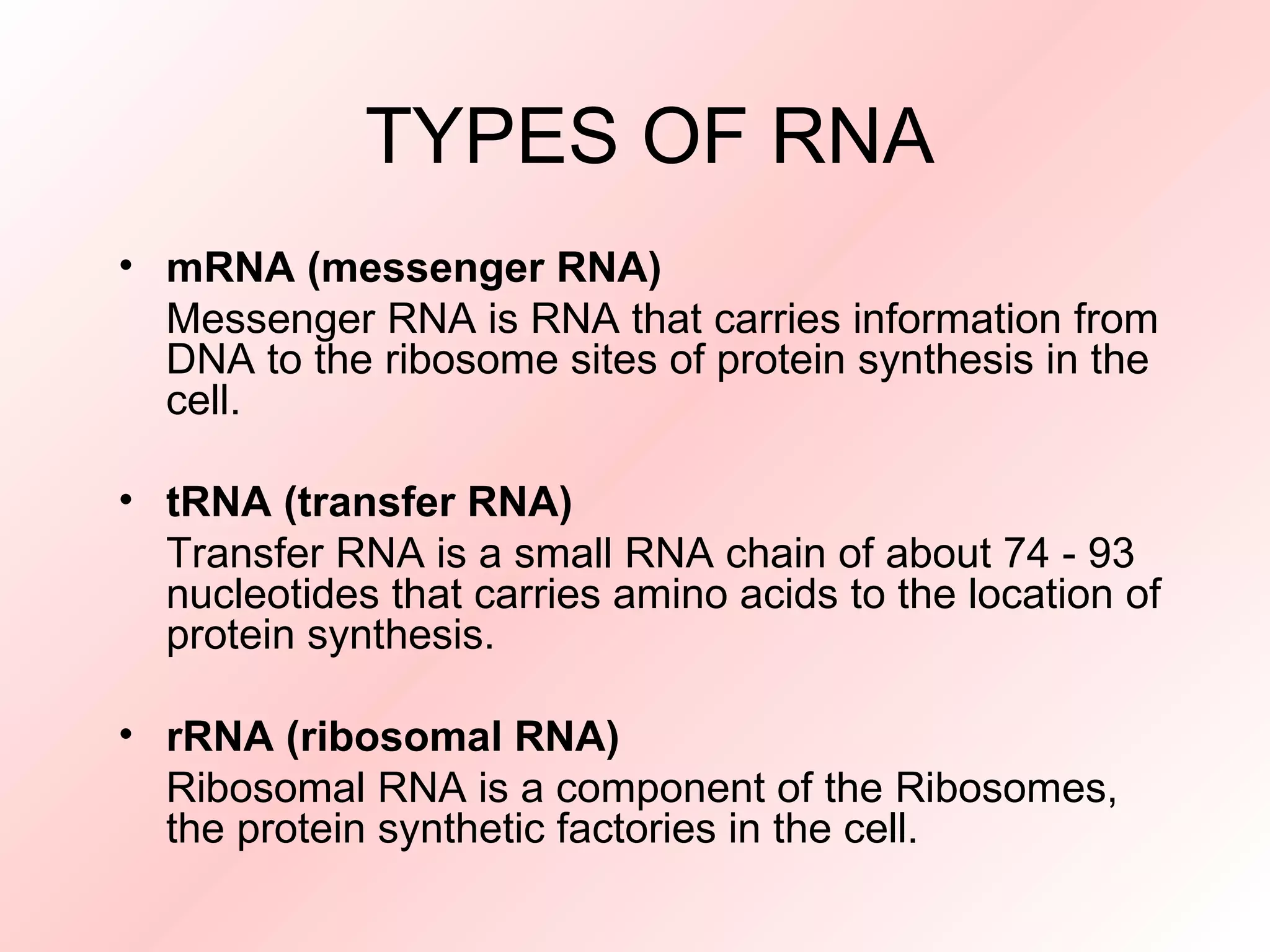
RNA contains ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose and uracil replaces thymine. Most RNA is single-stranded but tRNA forms a cloverleaf structure through complementary base pairing to carry amino acids to protein synthesis. DNA is found mainly in the nucleus while RNA exists in both the nucleus and cytoplasm, including messenger RNA which transports information from DNA to ribosomes, transfer RNA which carries amino acids, and ribosomal RNA which is a component of ribosomes for protein production.




