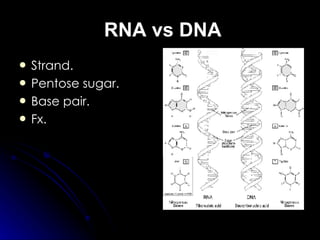
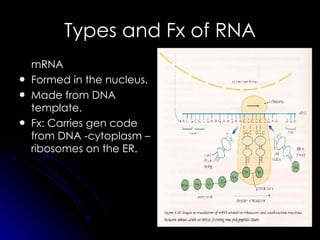
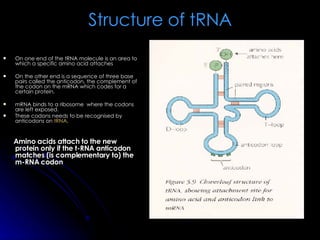
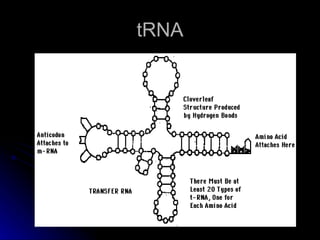
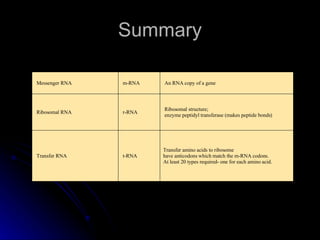
RNA differs from DNA in its sugar (ribose vs deoxyribose), bases (uracil replaces thymine), and structure (usually single-stranded instead of double helix). There are several types of RNA, including messenger RNA (mRNA) which carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA) which transfers amino acids to ribosomes using anticodons that match mRNA codons, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) which makes up ribosomal structure and acts as an enzyme during protein synthesis.