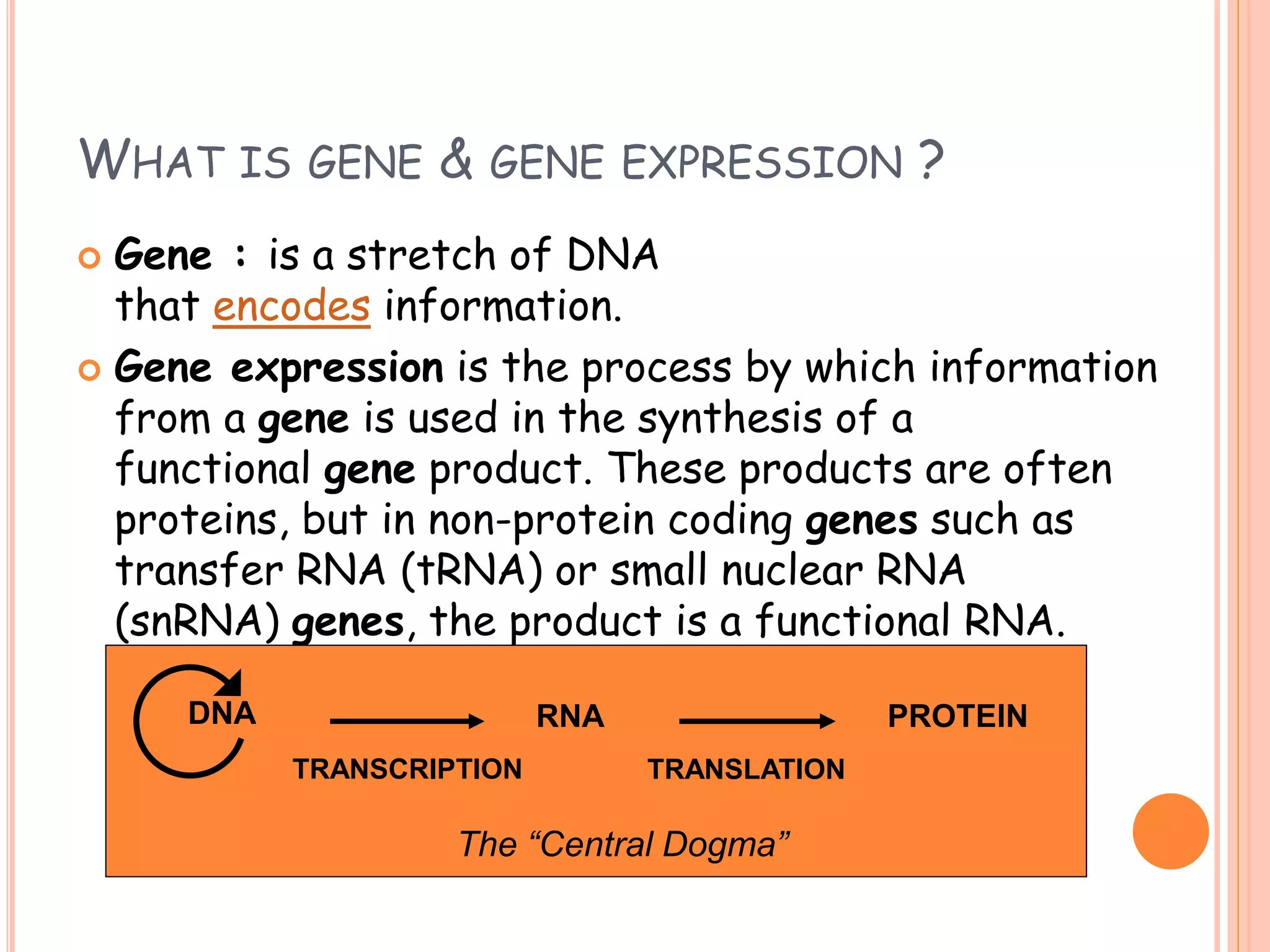
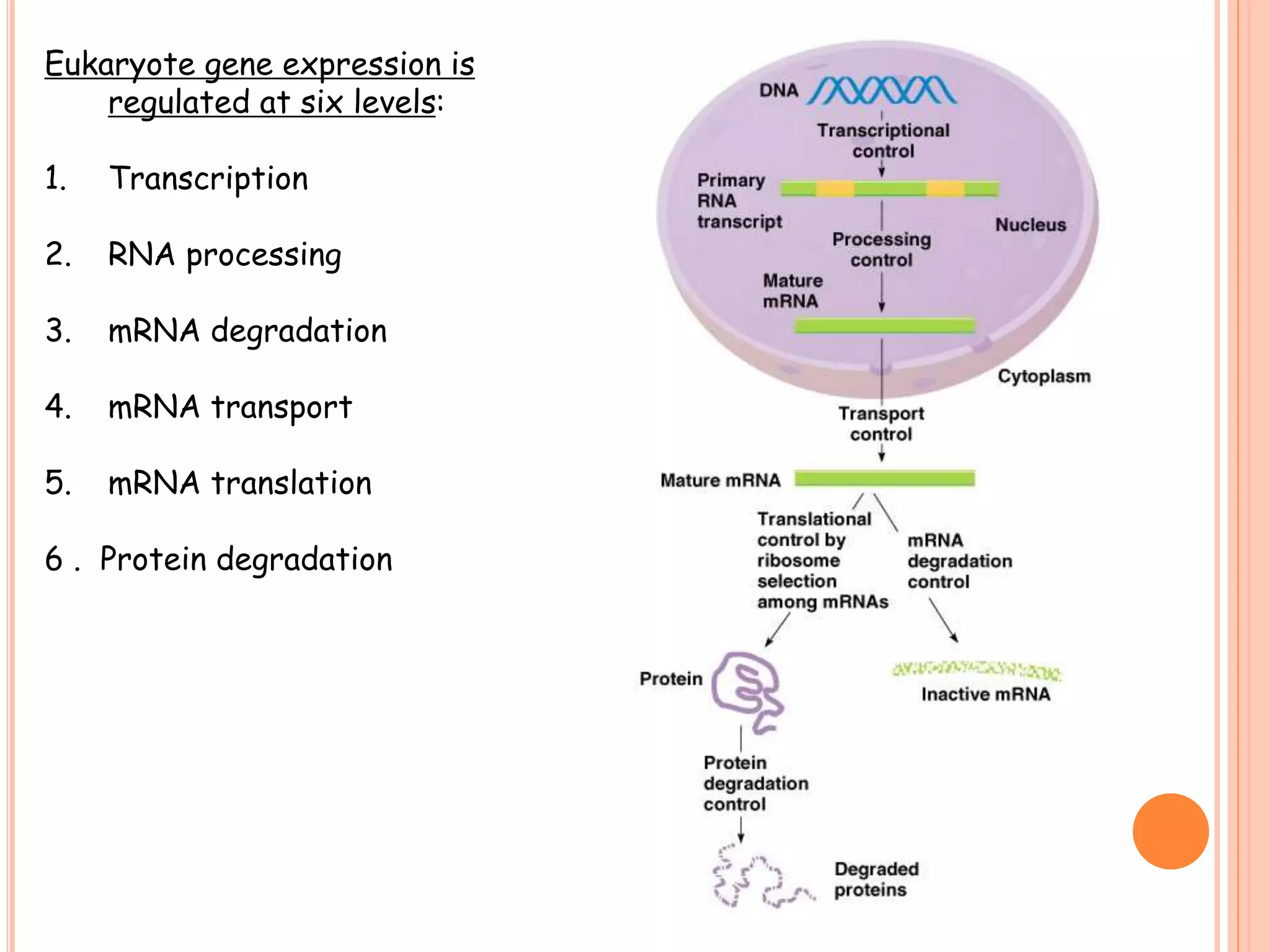
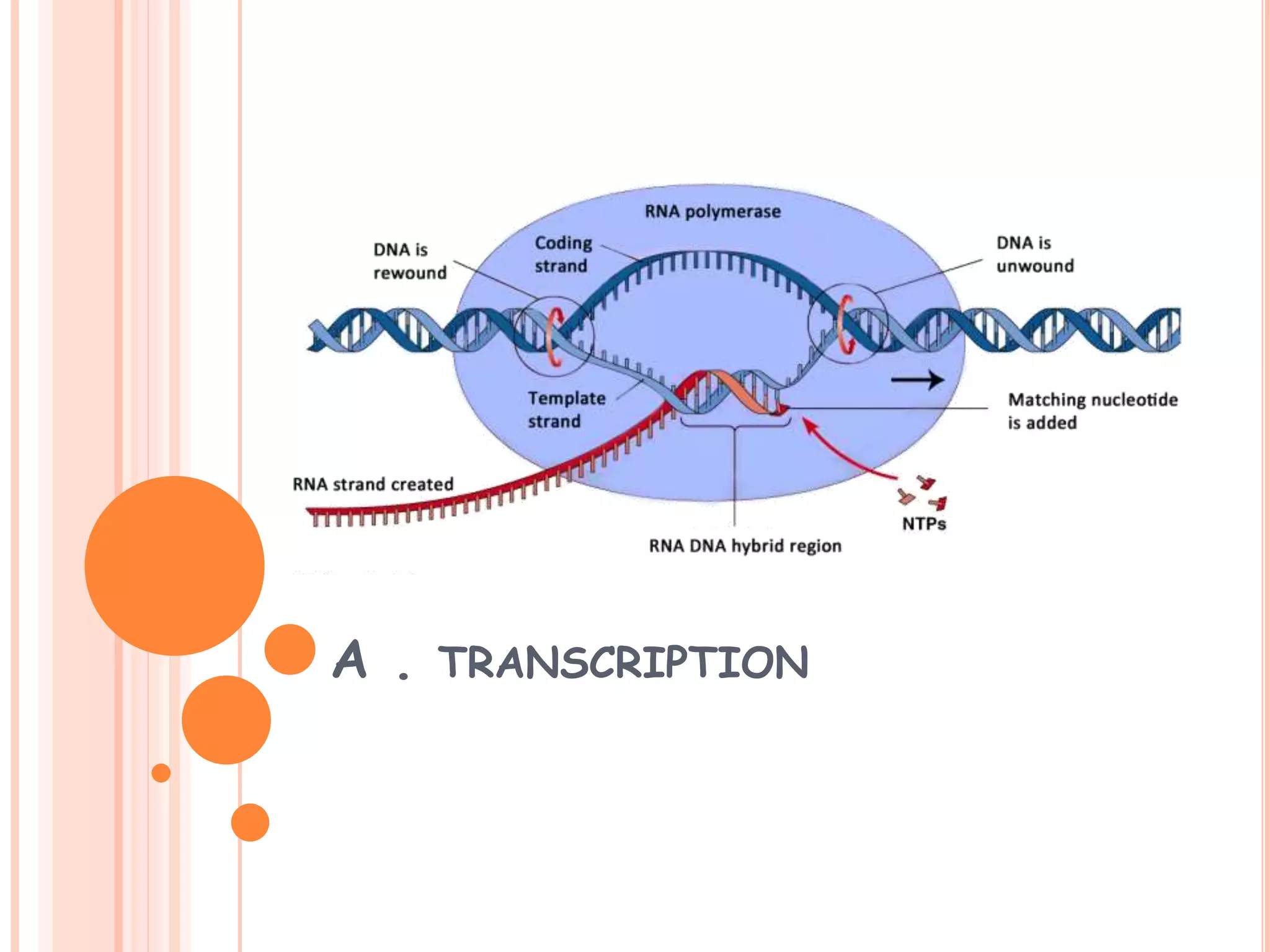
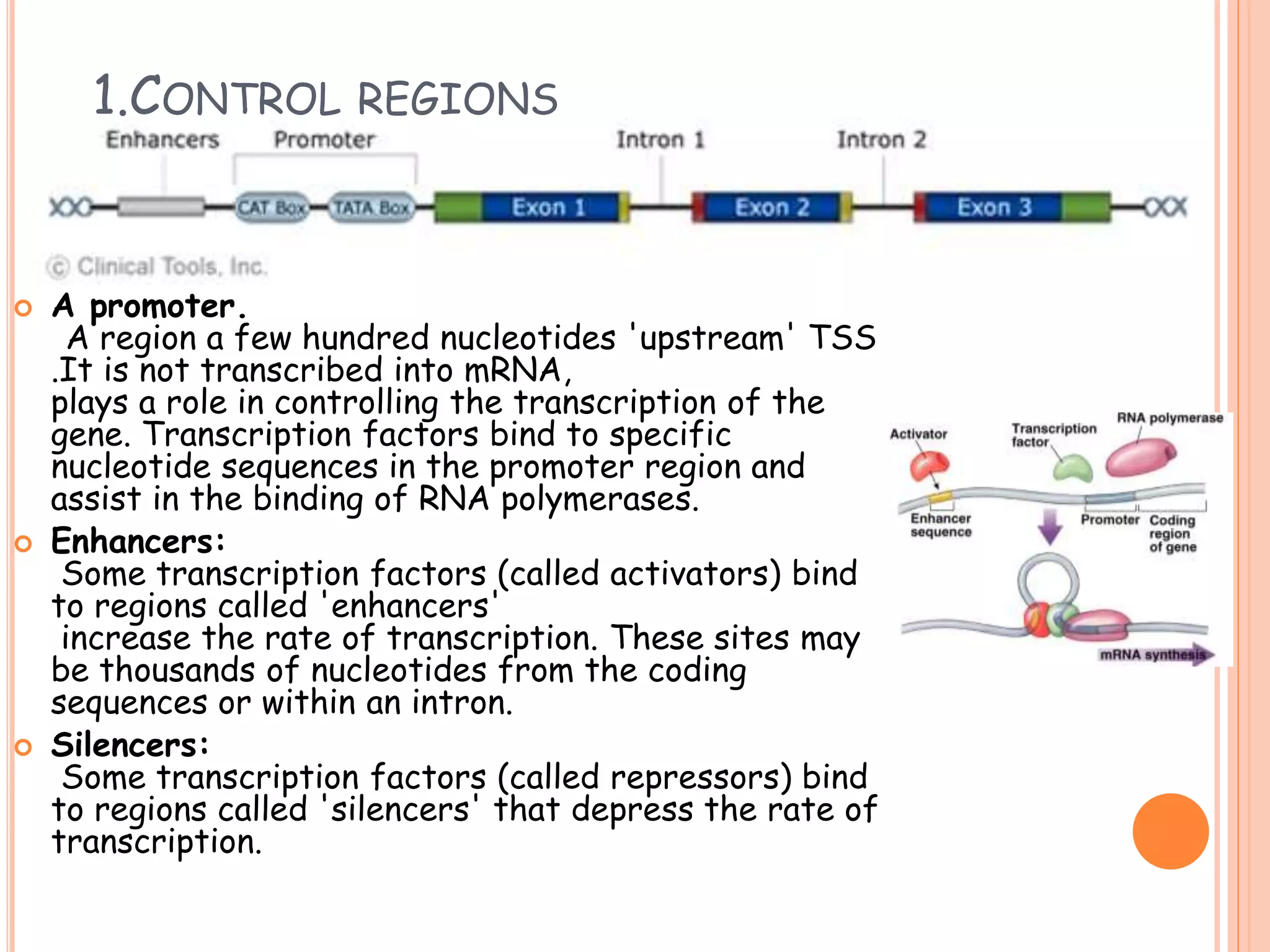
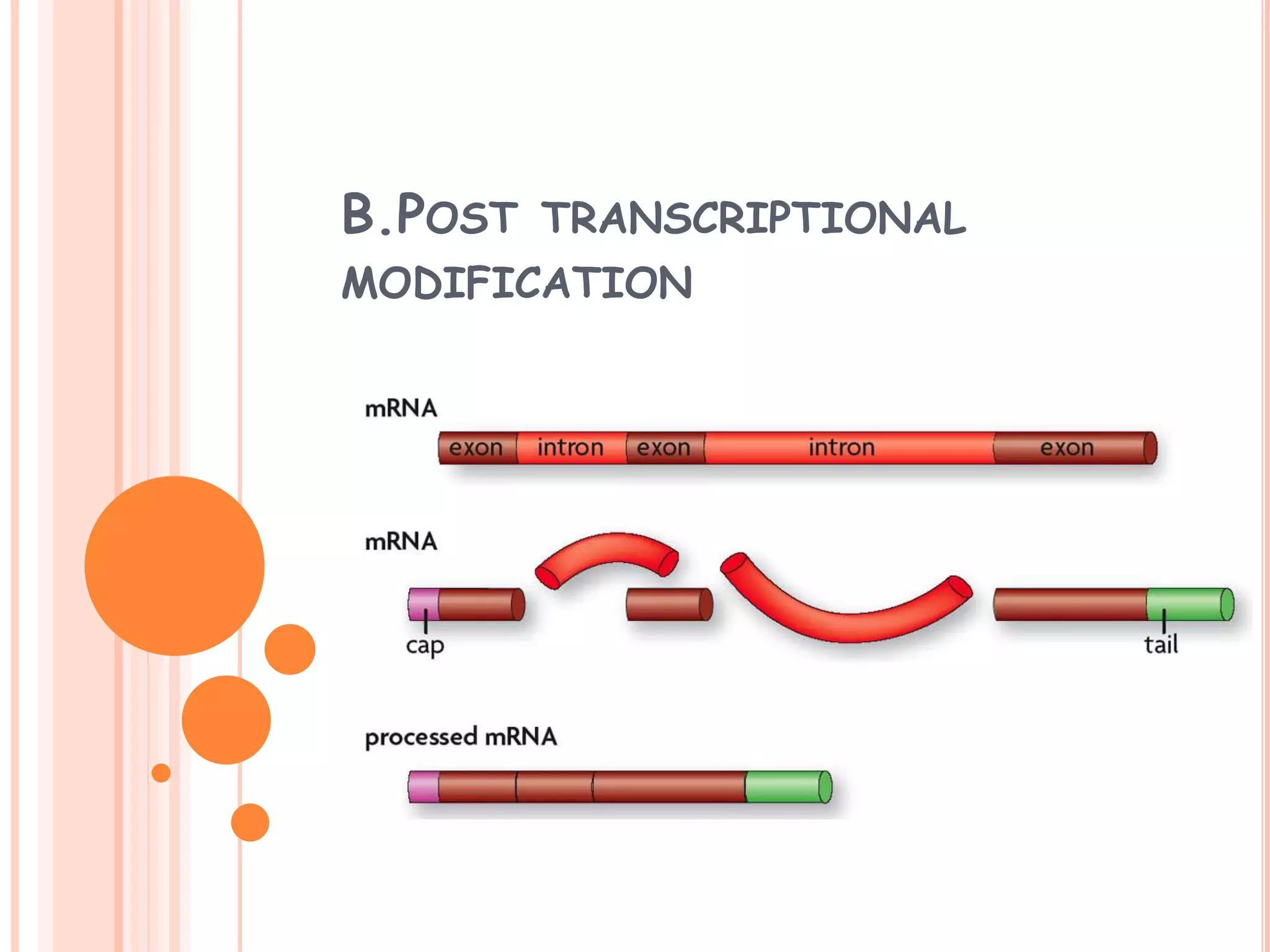
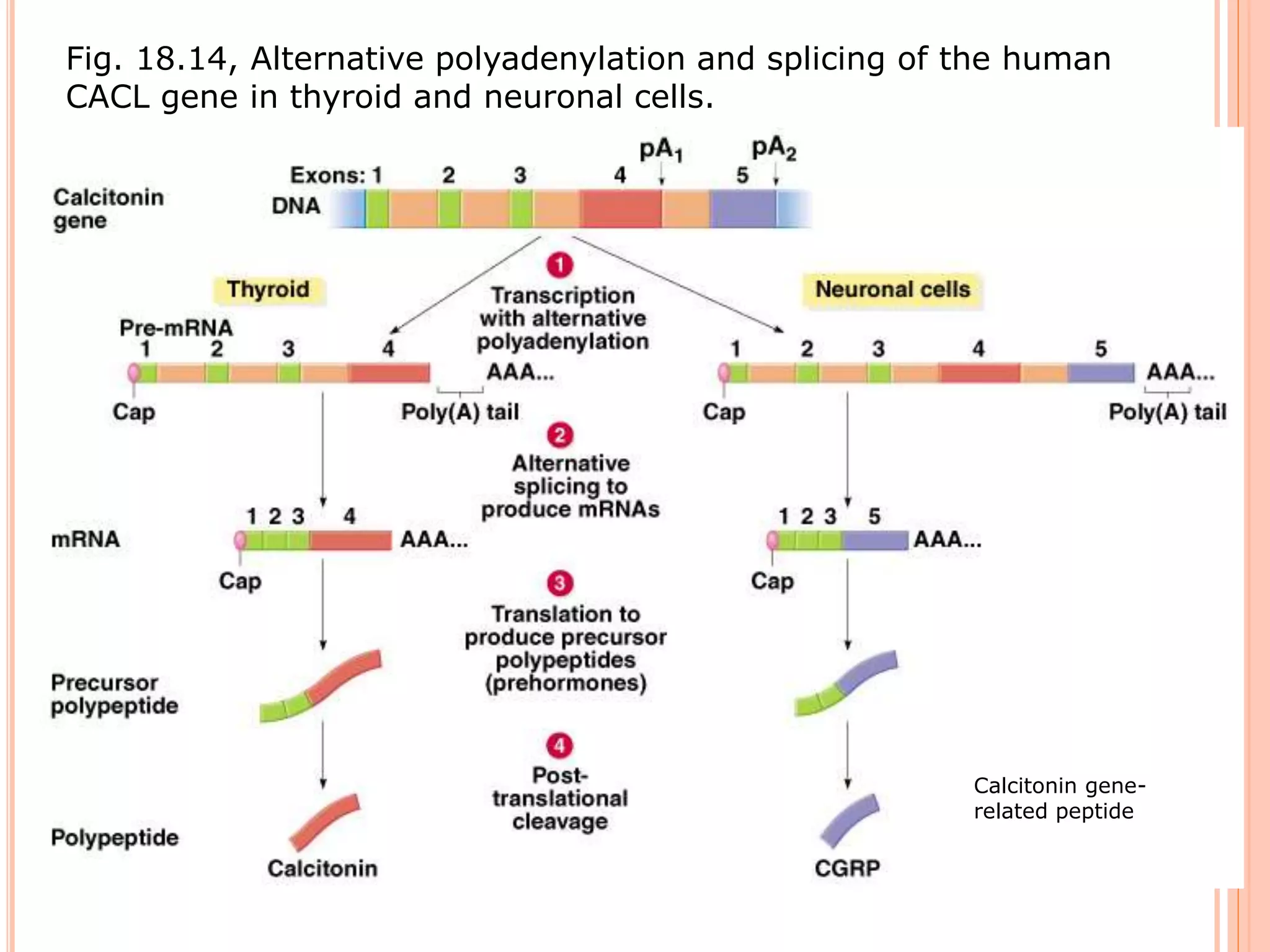
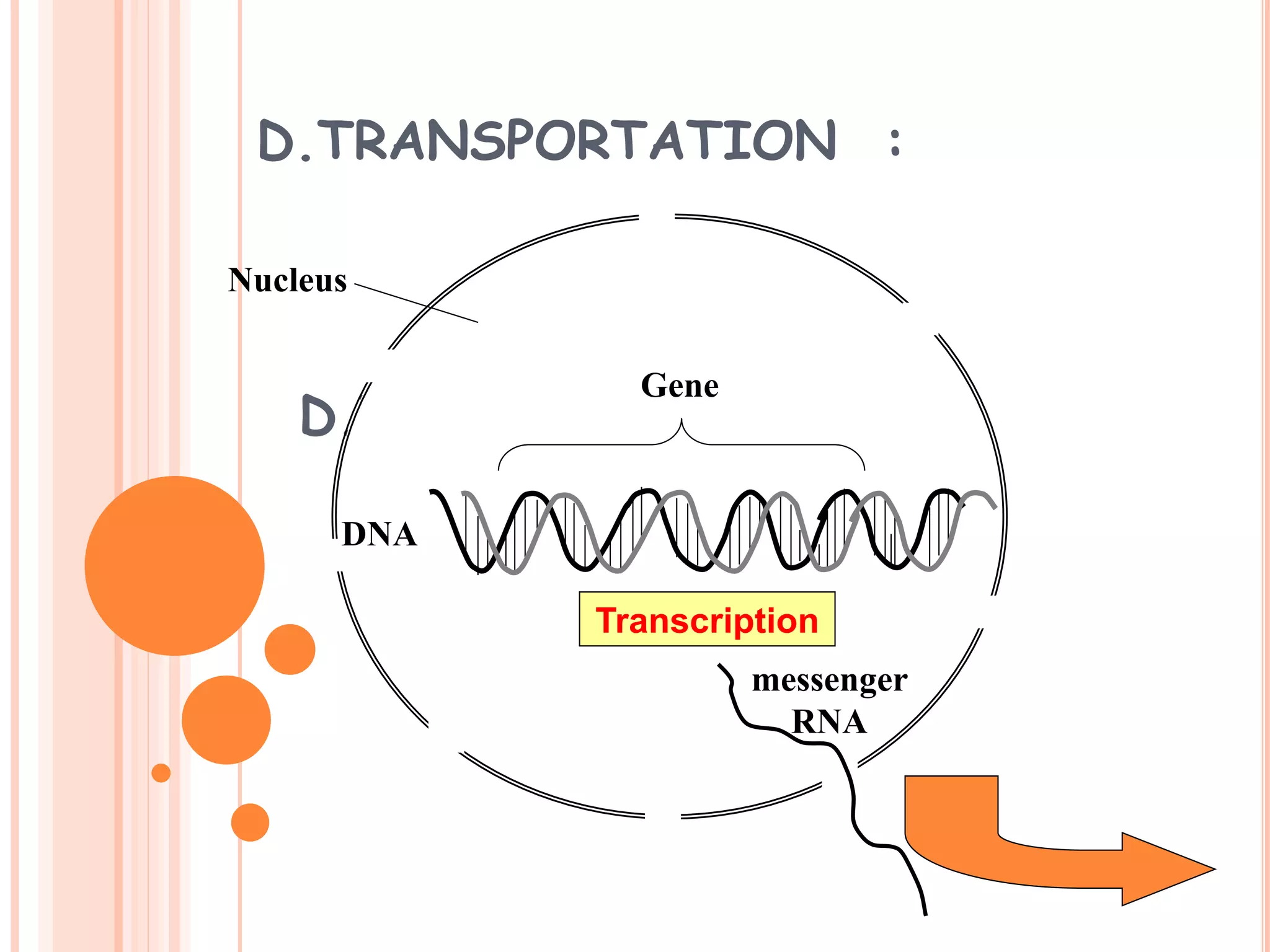
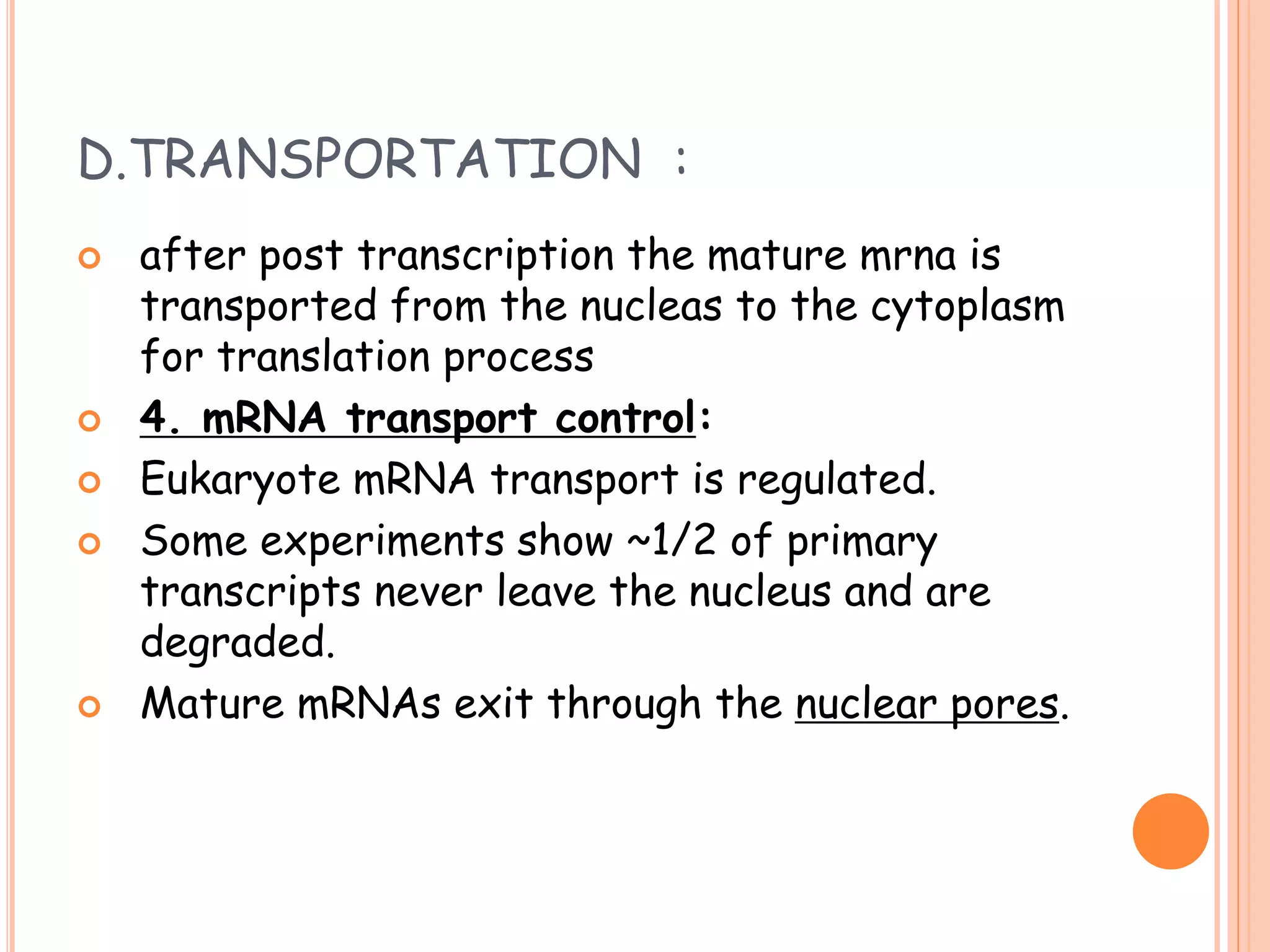
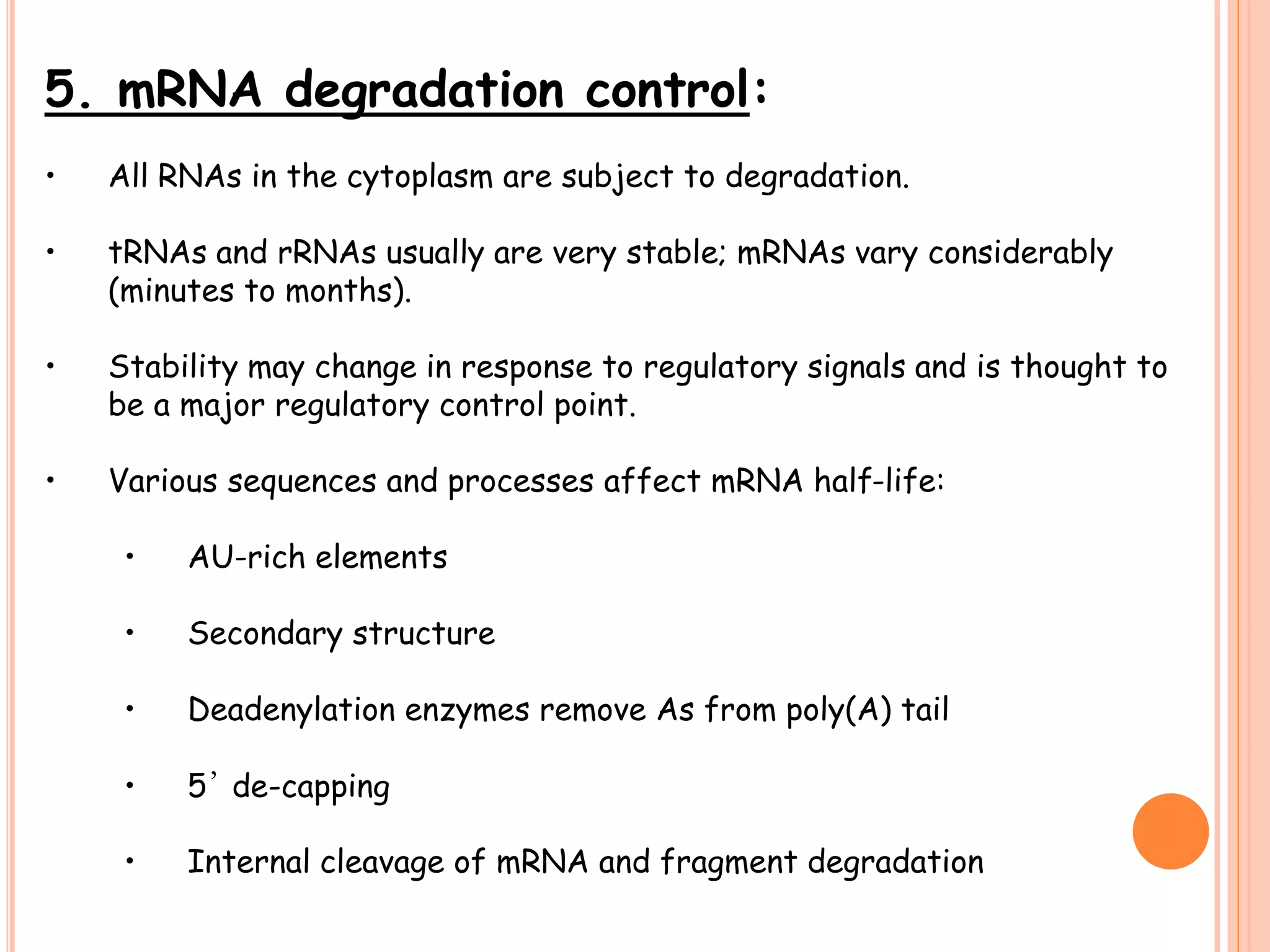
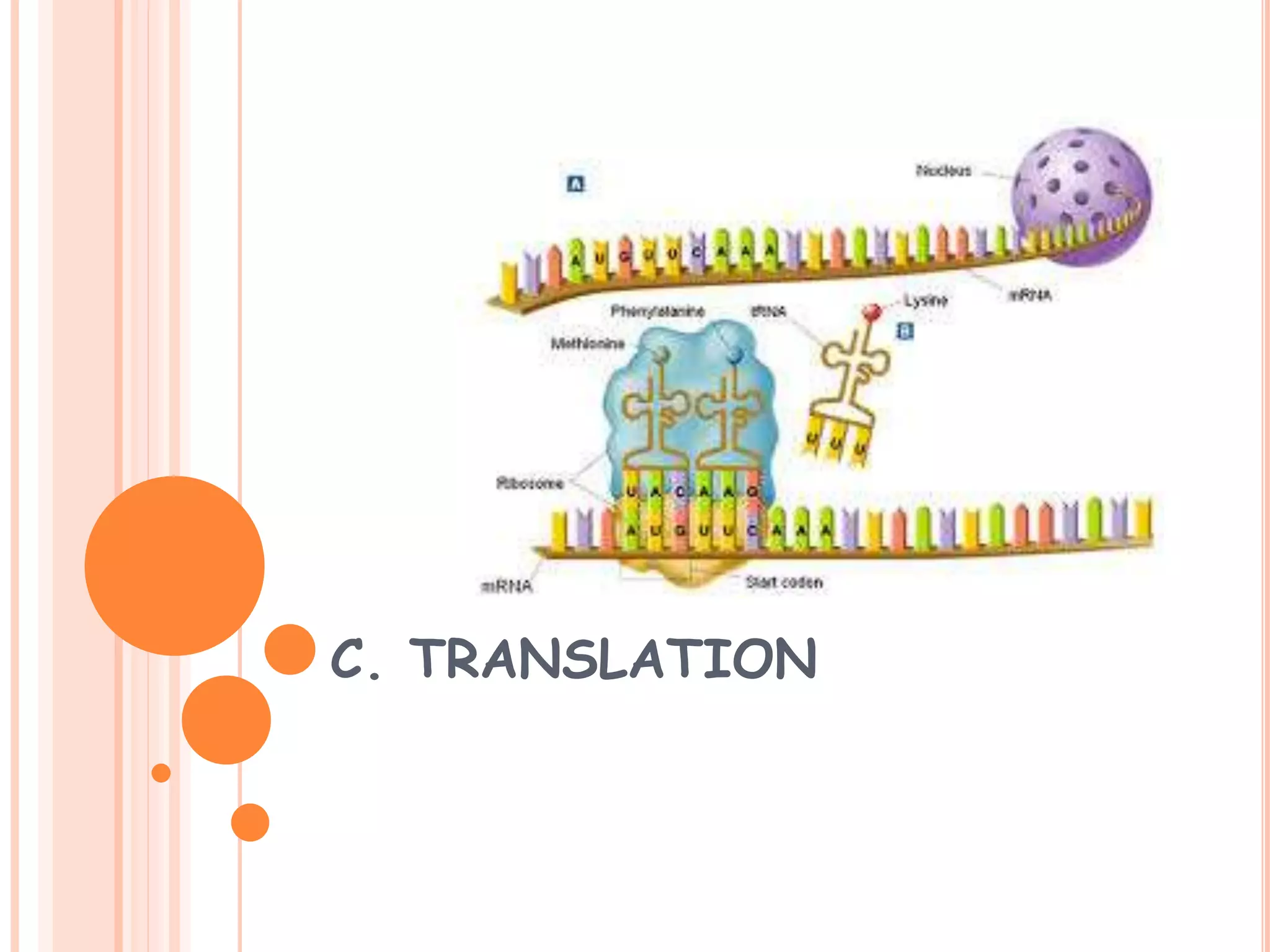
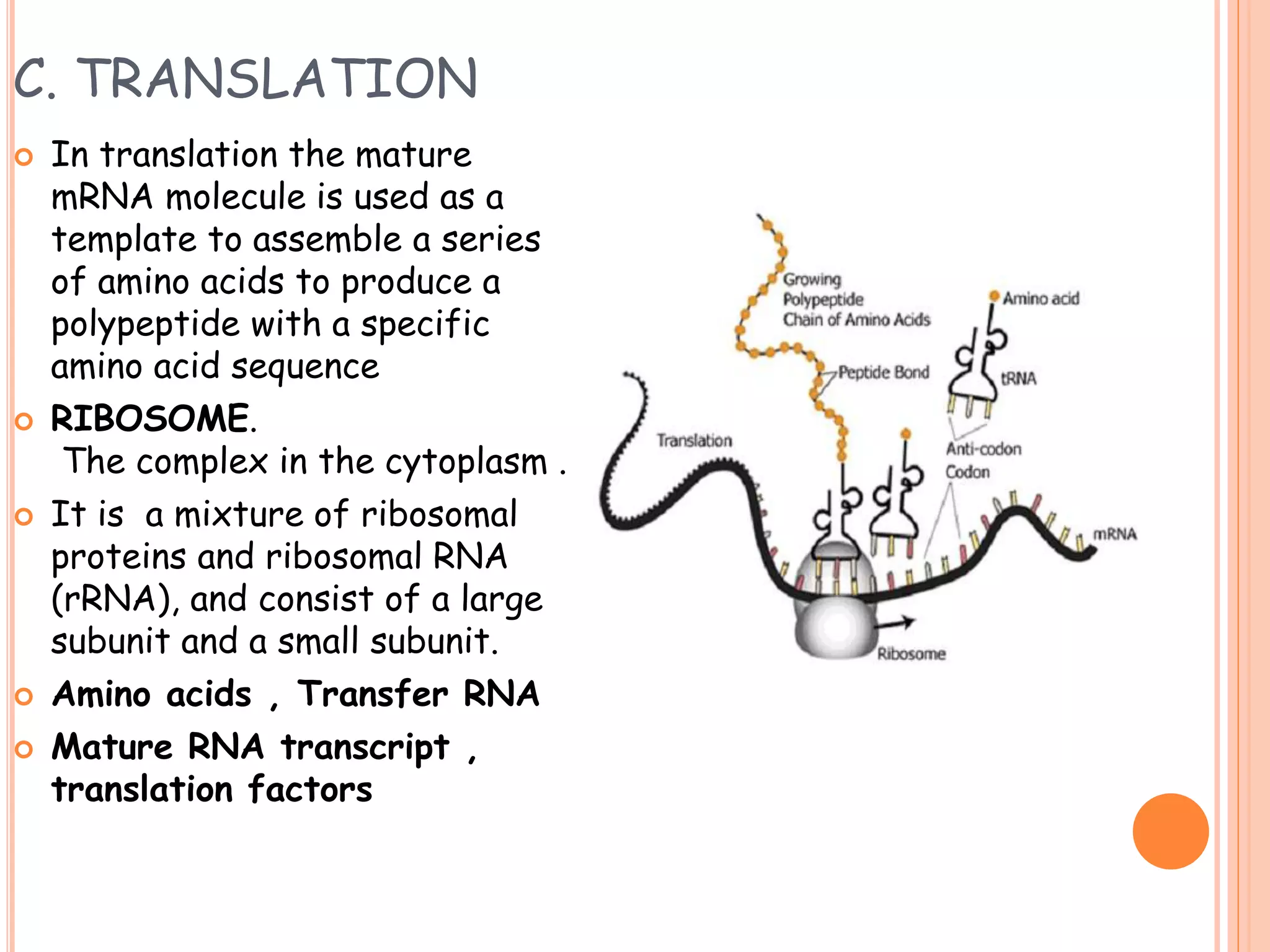
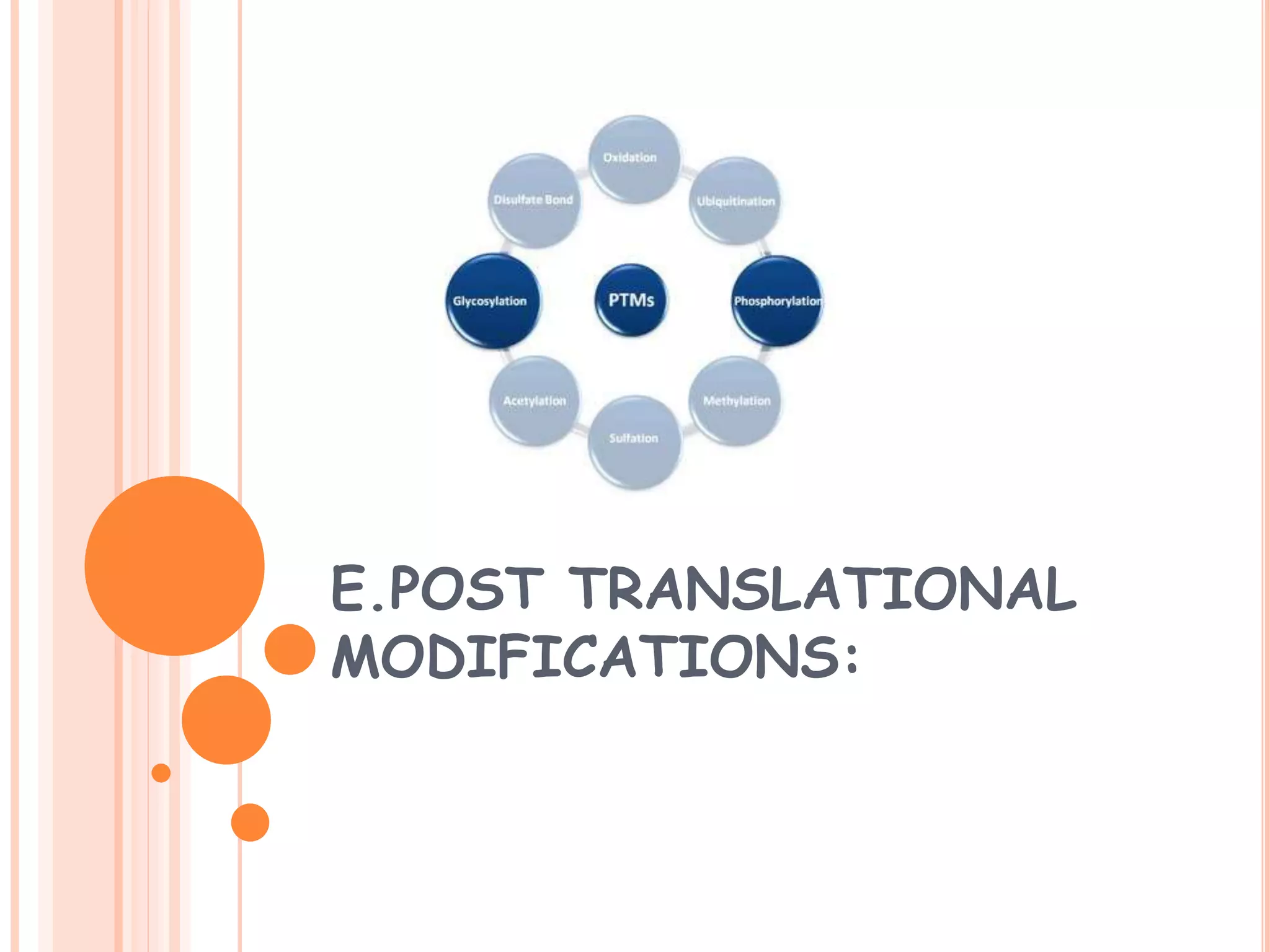
This document summarizes the process of gene expression in three main steps: transcription, post-transcriptional modification, and translation. It first defines a gene as a stretch of DNA that encodes information. During transcription, RNA polymerase produces messenger RNA from DNA. The mRNA then undergoes post-transcriptional modification like capping, splicing, and polyadenylation. The mature mRNA is transported to the cytoplasm for translation by ribosomes into proteins. Additional post-translational modifications can occur to proteins after translation. Gene expression is regulated at multiple levels including transcription, RNA processing, translation and protein degradation.