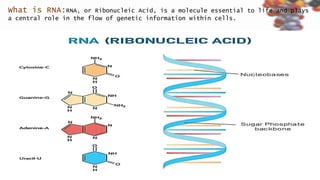
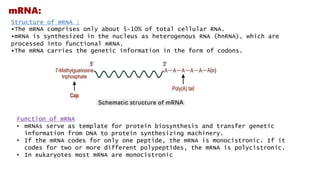
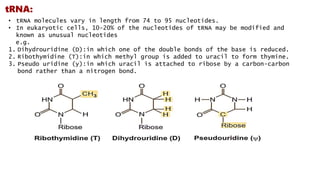
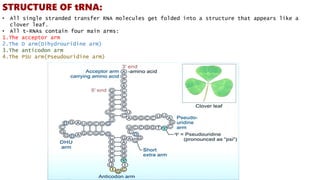
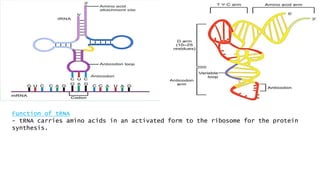
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is crucial for genetic information flow in cells and typically exists as a single-stranded molecule composed of ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases, with uracil replacing thymine. The main types of RNA include messenger RNA (mRNA), which serves as a template for protein synthesis; transfer RNA (tRNA), which carries amino acids to the ribosome; and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which forms the structural and functional core of ribosomes. Additional types of RNA in eukaryotes include small nuclear RNA (snRNA), microRNA (miRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), and small cytoplasmic RNA (scRNA), each of which plays distinct roles in gene regulation and RNA processing.