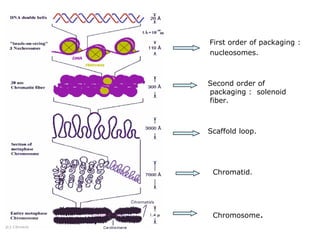
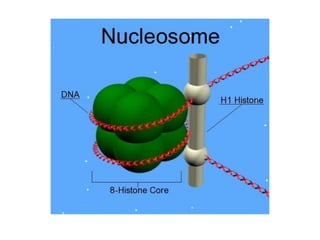
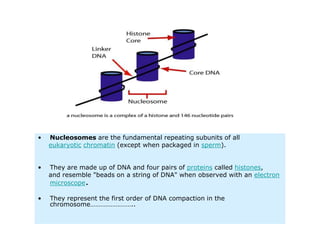
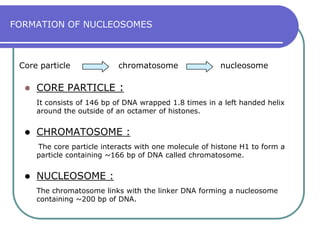
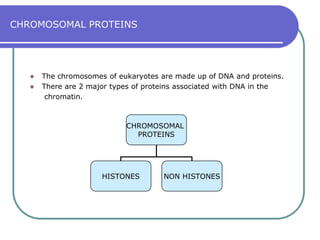
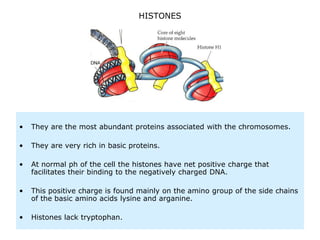
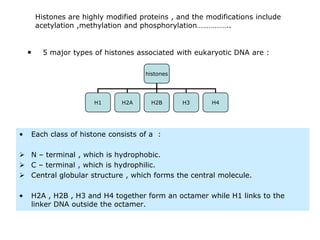
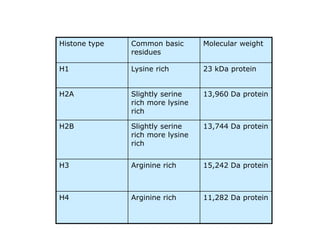
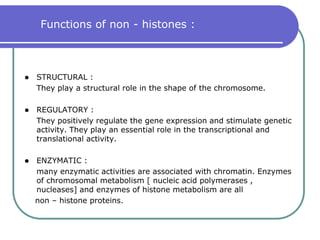
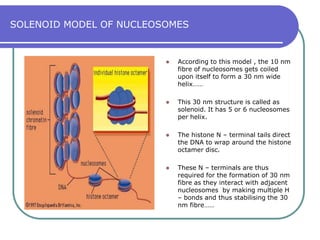
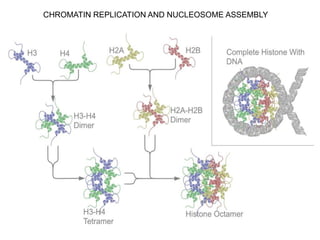
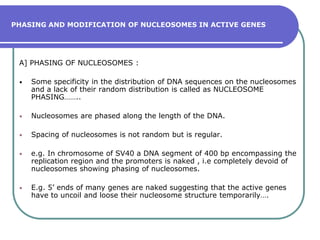
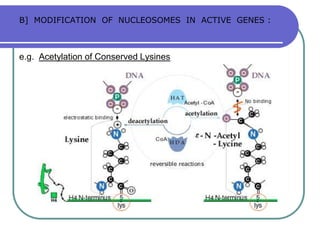
Nucleosomes are the fundamental repeating subunits of eukaryotic chromatin that package DNA into a compact structure. They are composed of 146 base pairs of DNA wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins, resembling beads on a string. This represents the first order of DNA compaction. Higher orders of compaction involve the nucleosomes winding further to form solenoid fibers, scaffold loops, chromatids, and finally full chromosomes. Nucleosomes allow the long DNA molecules to fit within cell nuclei while also regulating genetic expression.