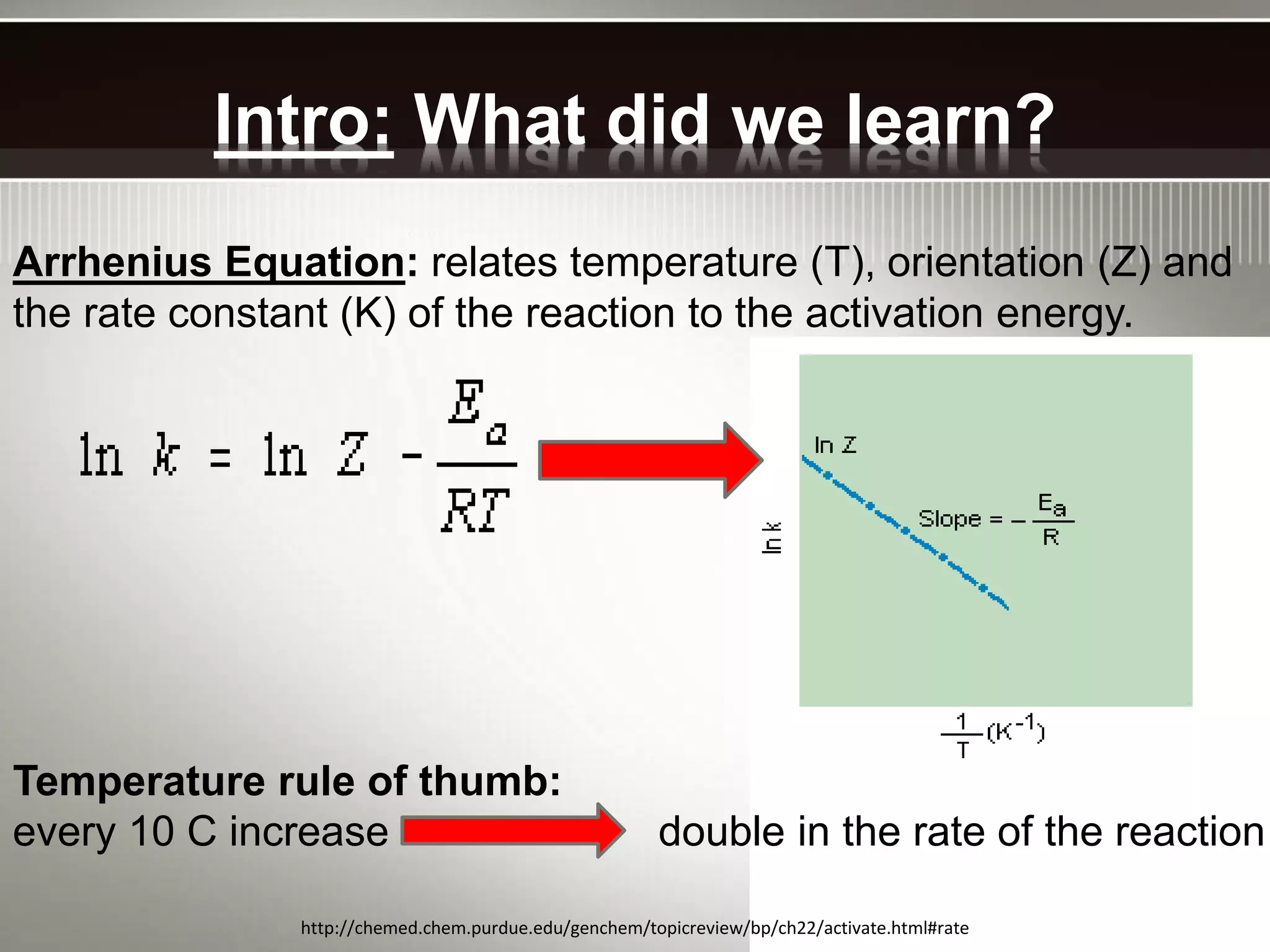
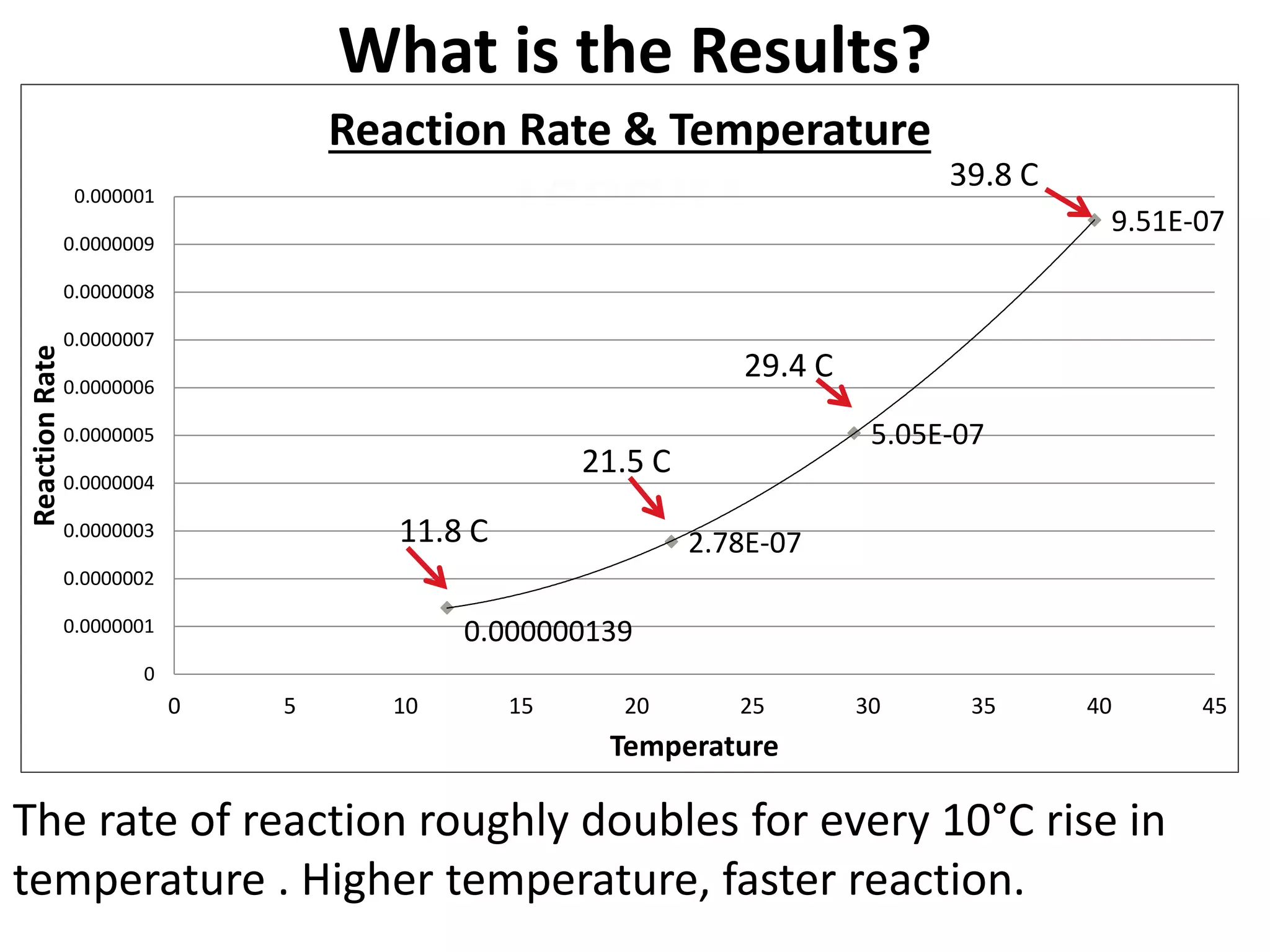
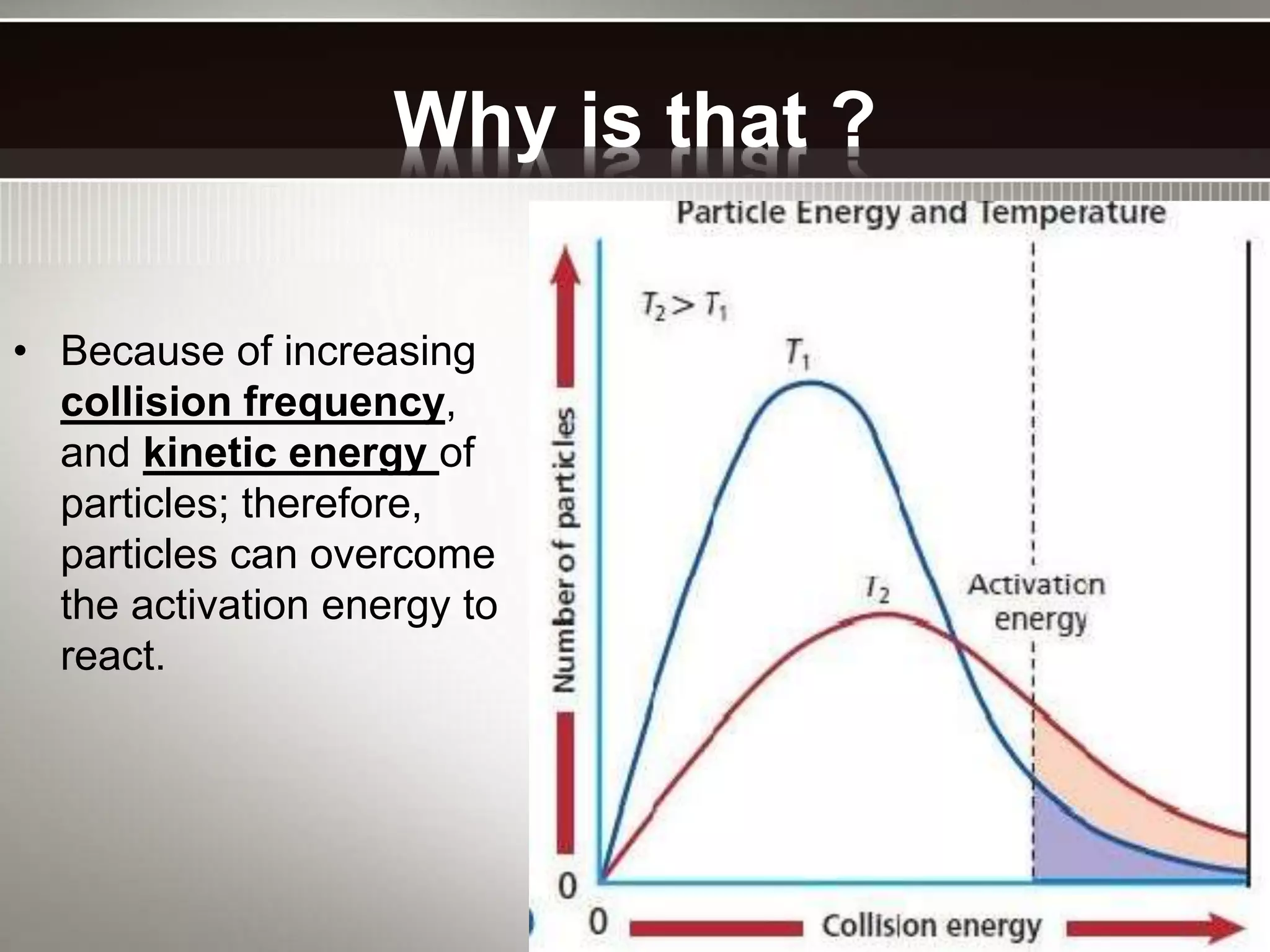
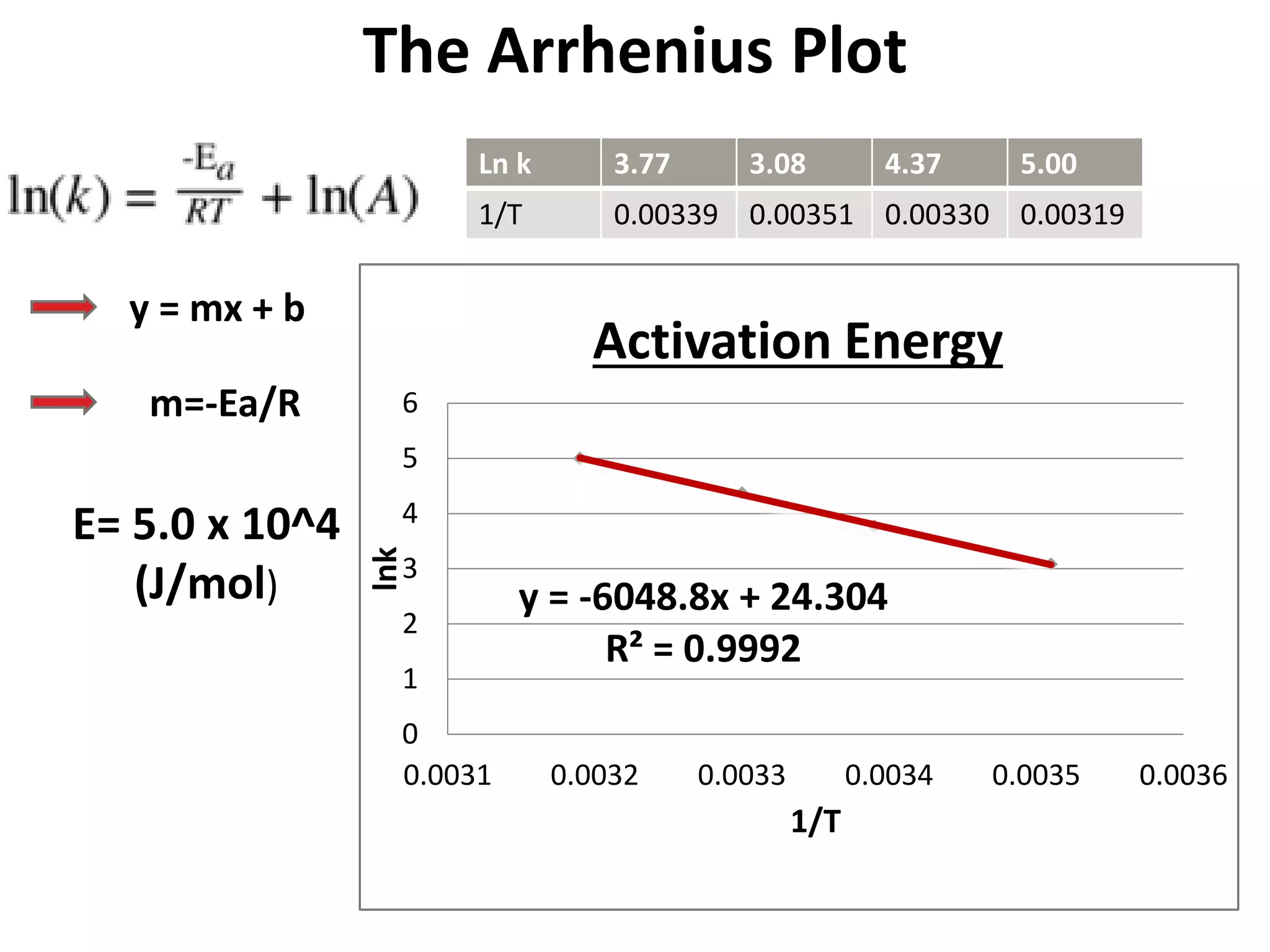
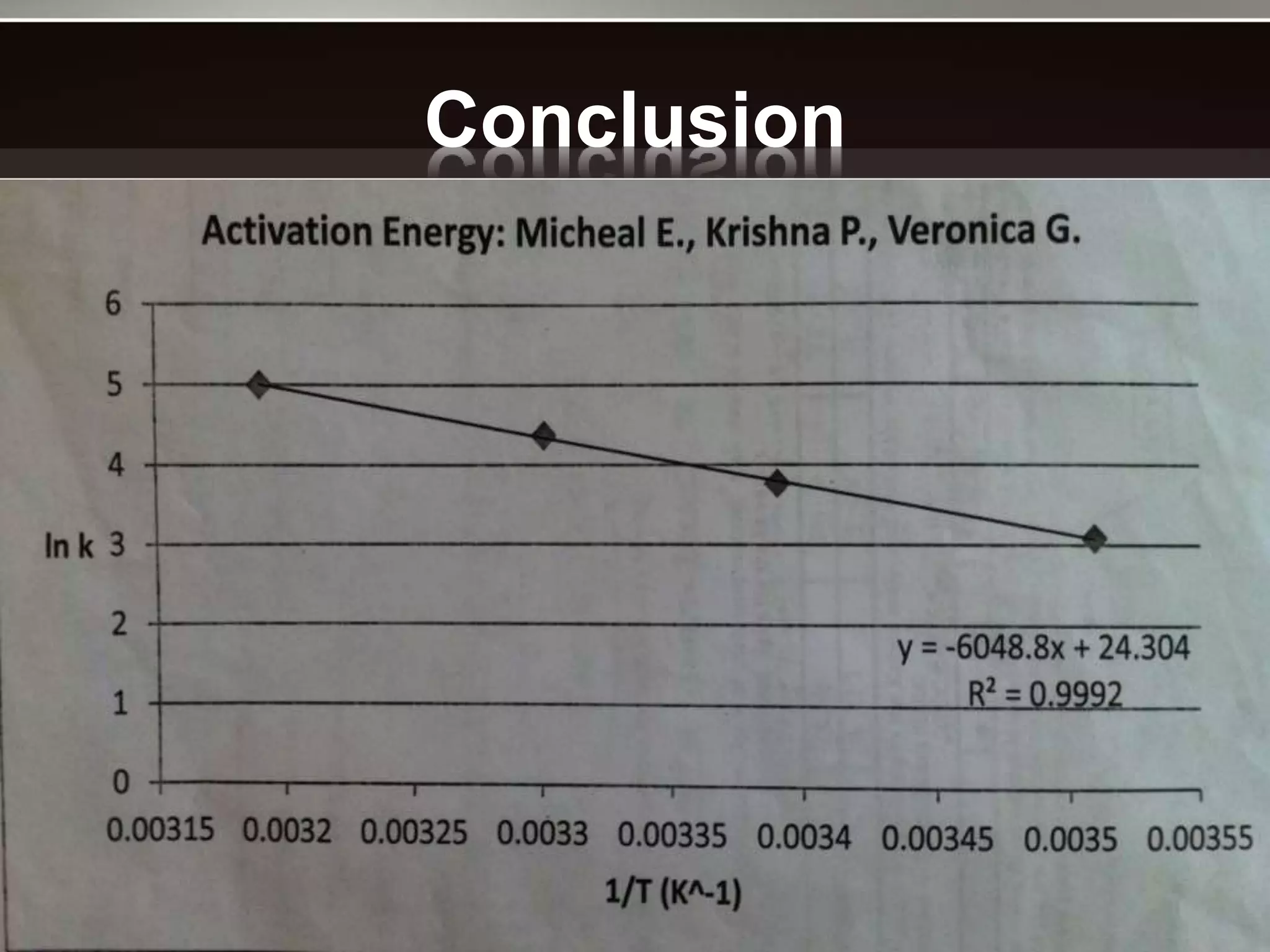
The document discusses activation energy and the Arrhenius equation. It defines activation energy as the minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. The Arrhenius equation relates temperature, activation energy, and the rate constant of a reaction. The document then summarizes an experiment that demonstrates how reaction rate increases with temperature by measuring four reactions at different temperatures and constructing an Arrhenius plot from the results.