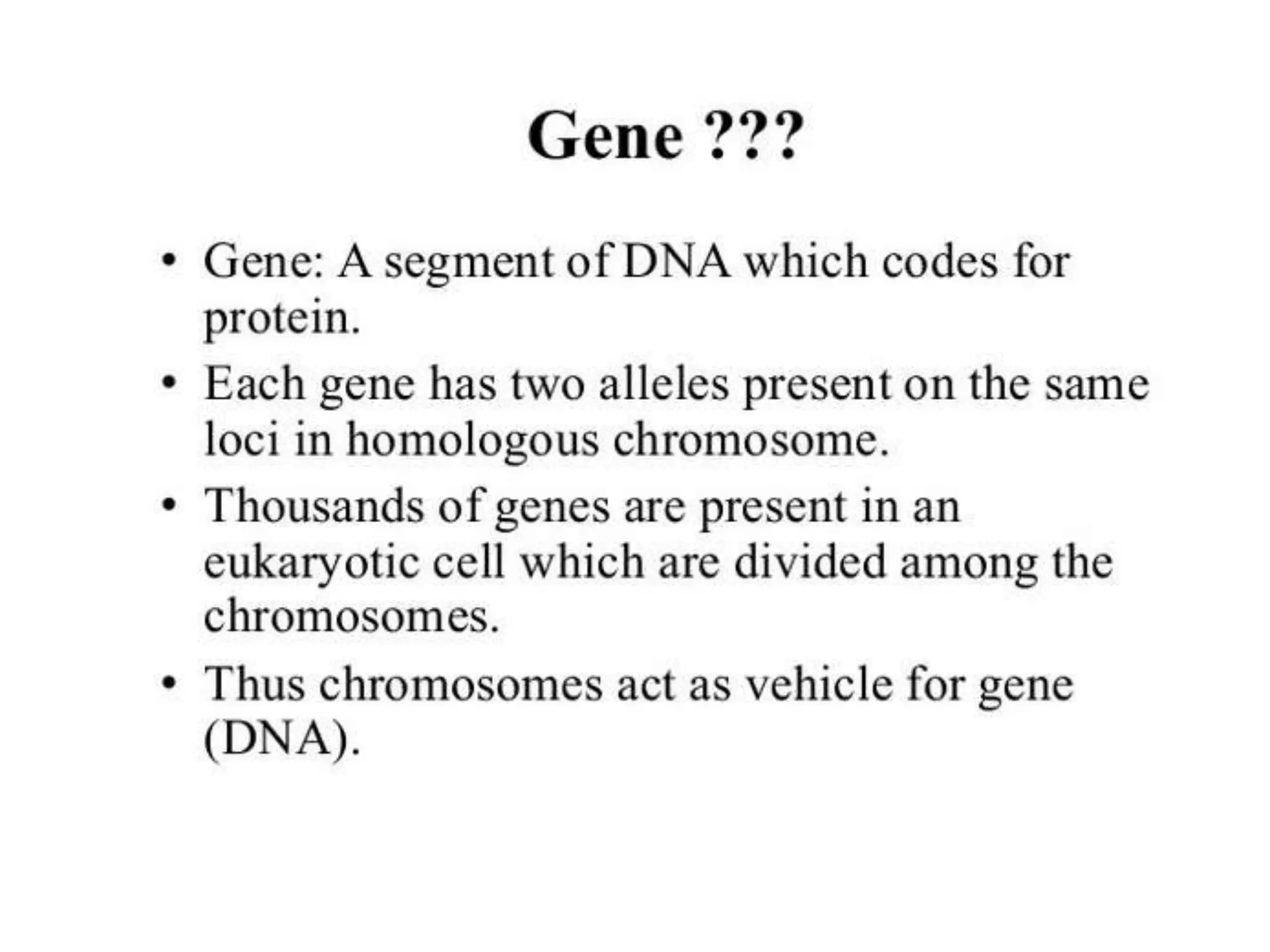
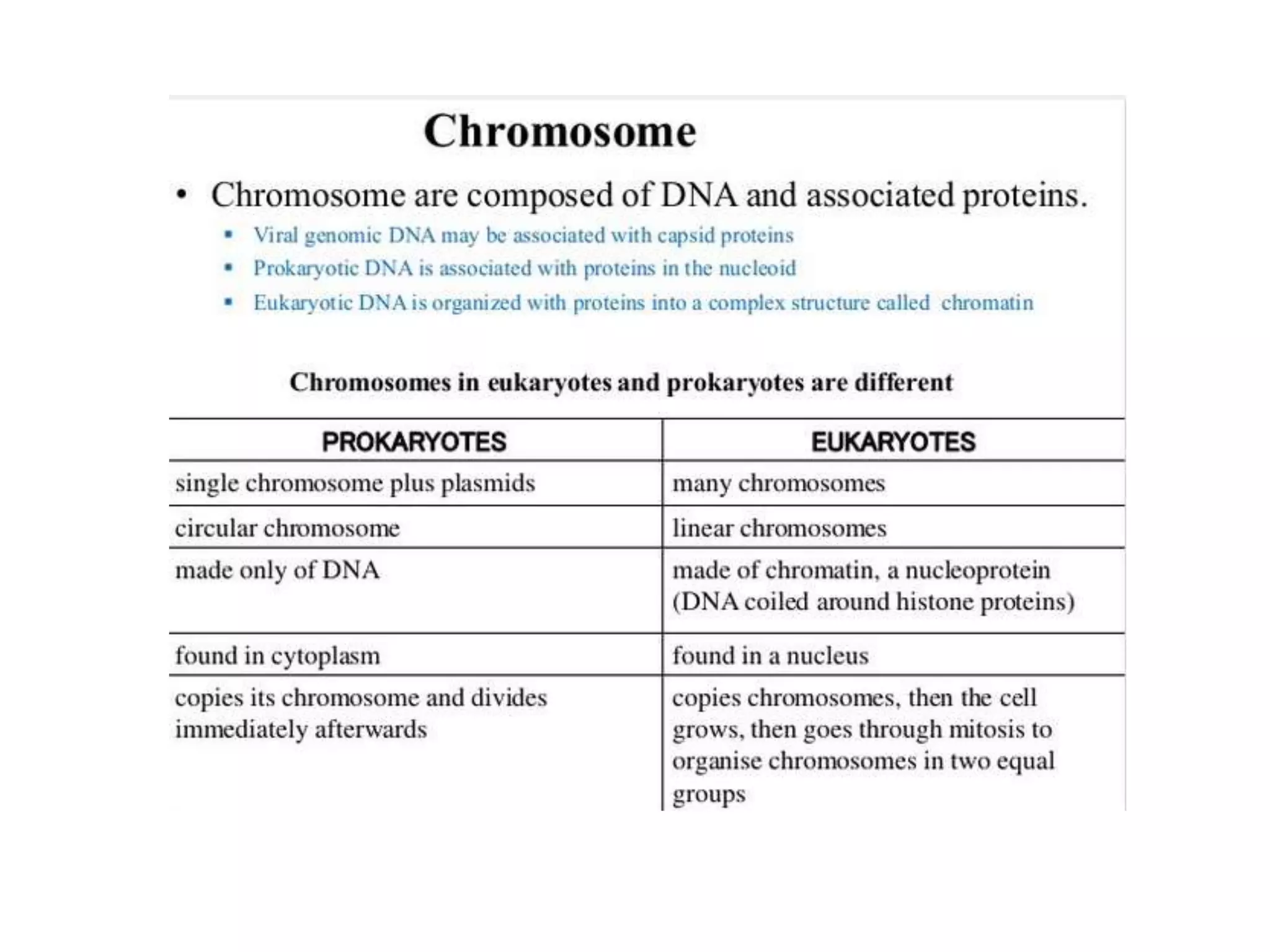
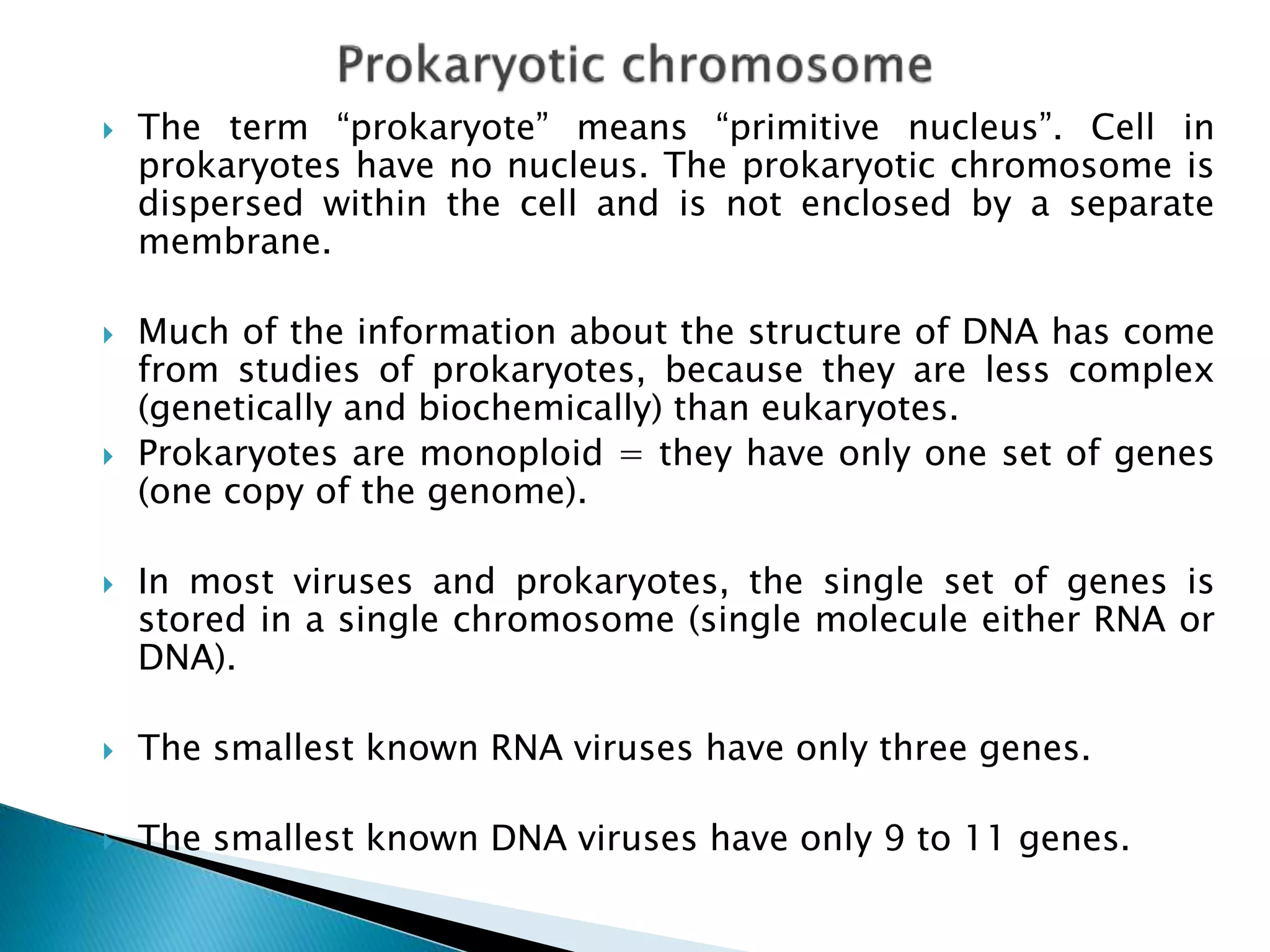
1) Prokaryotic chromosomes are not enclosed in a nucleus, and their DNA is dispersed within the cell. Much of what is known about DNA structure comes from studying prokaryotes.
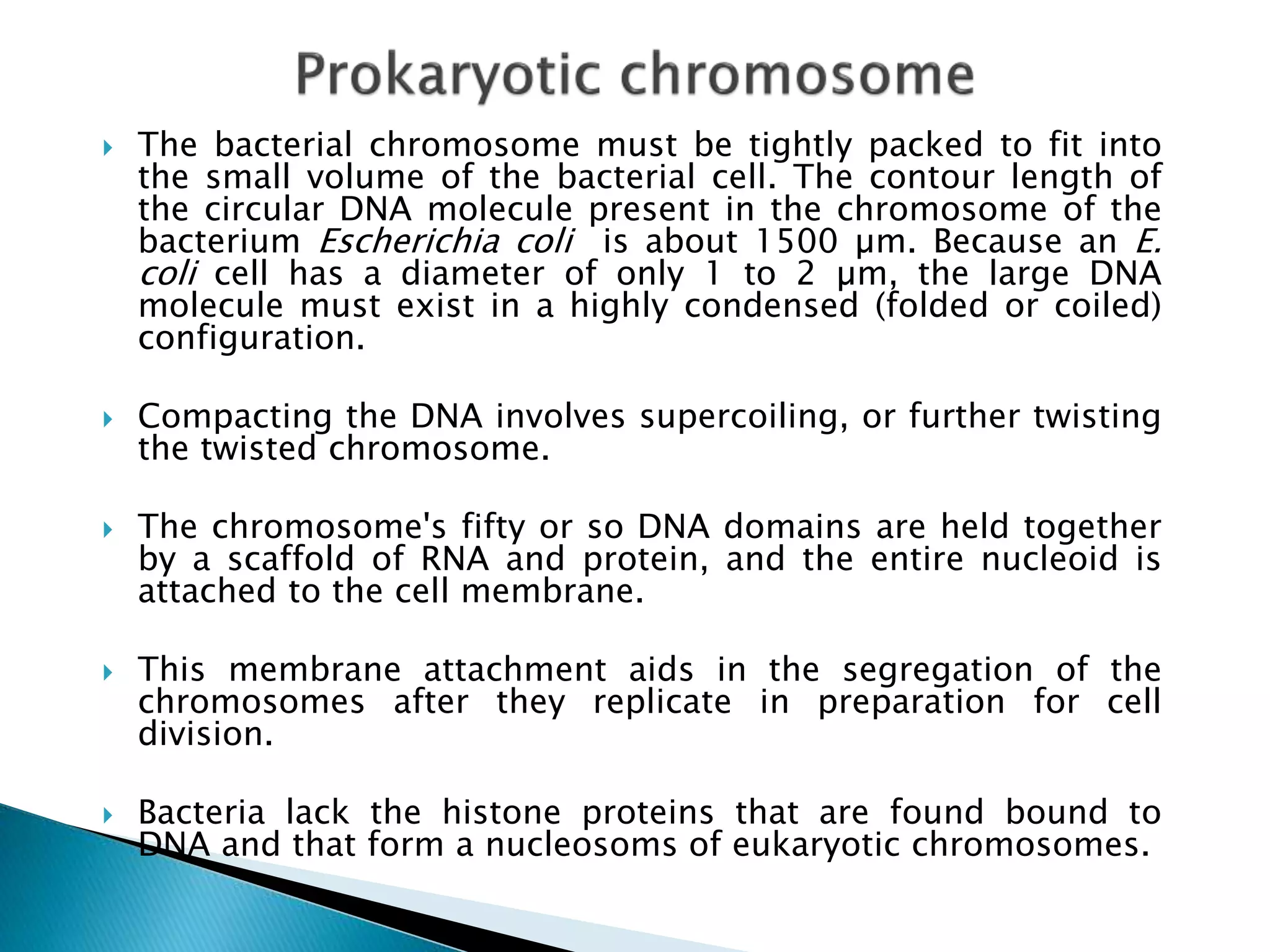
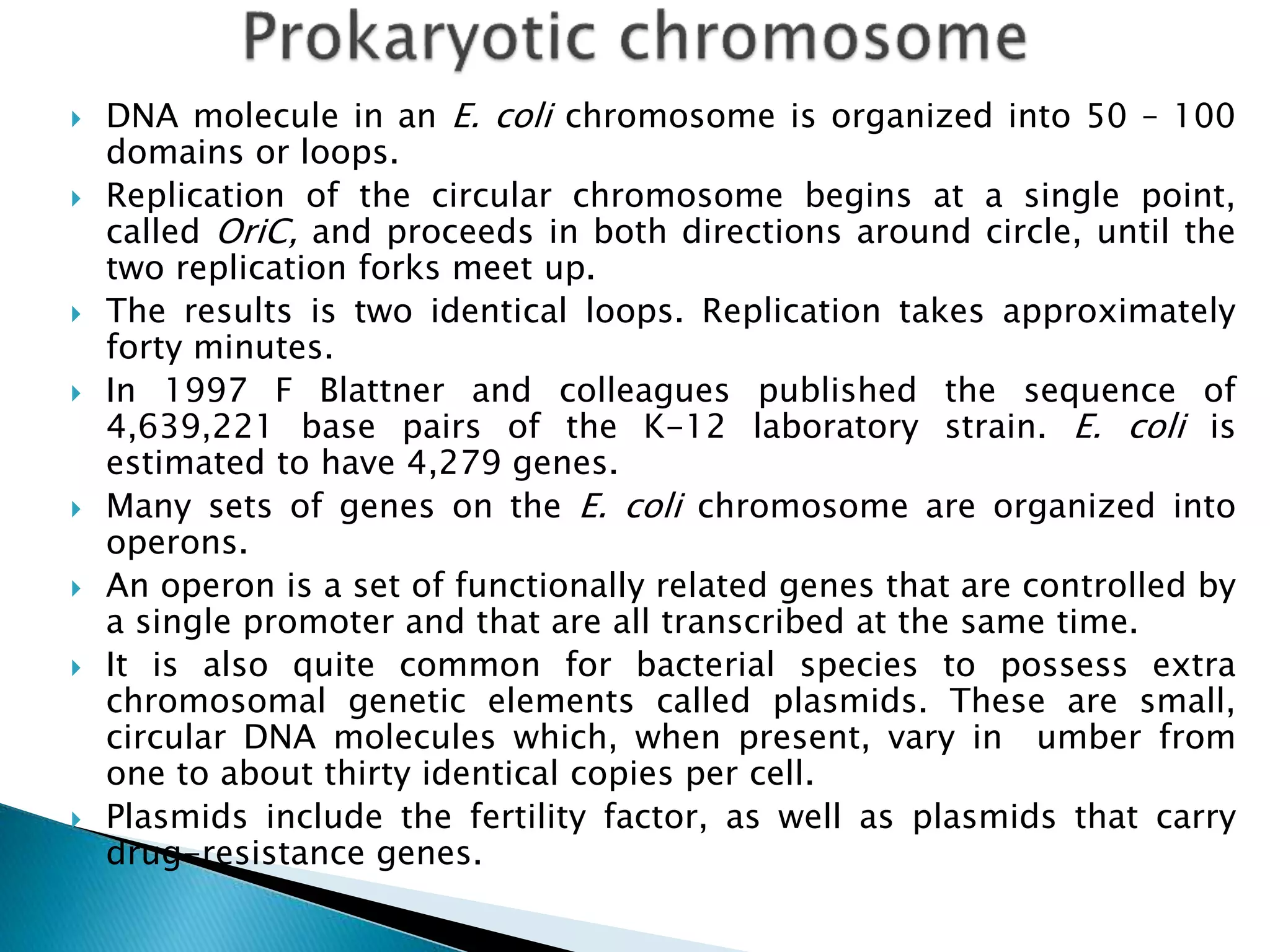
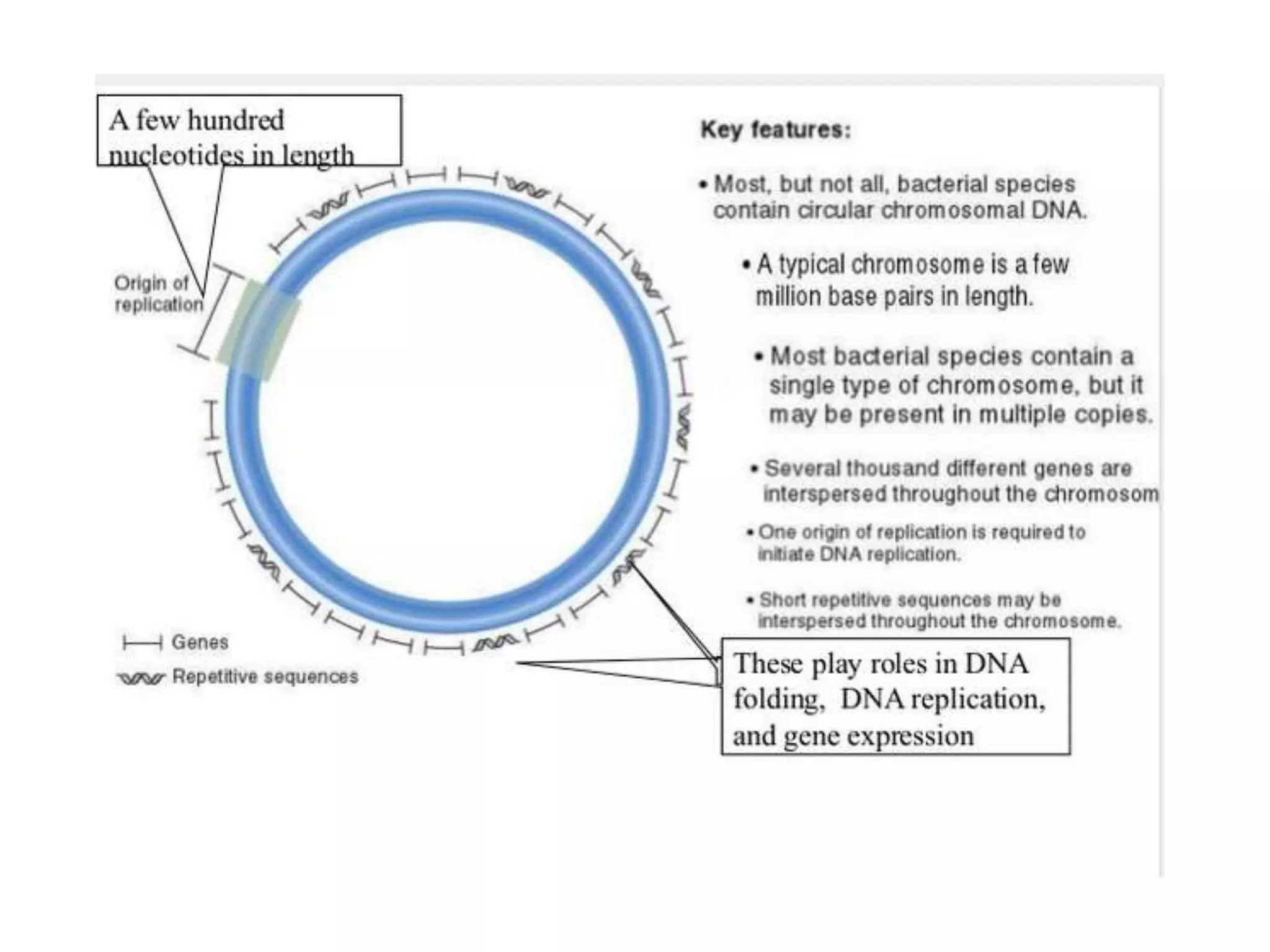
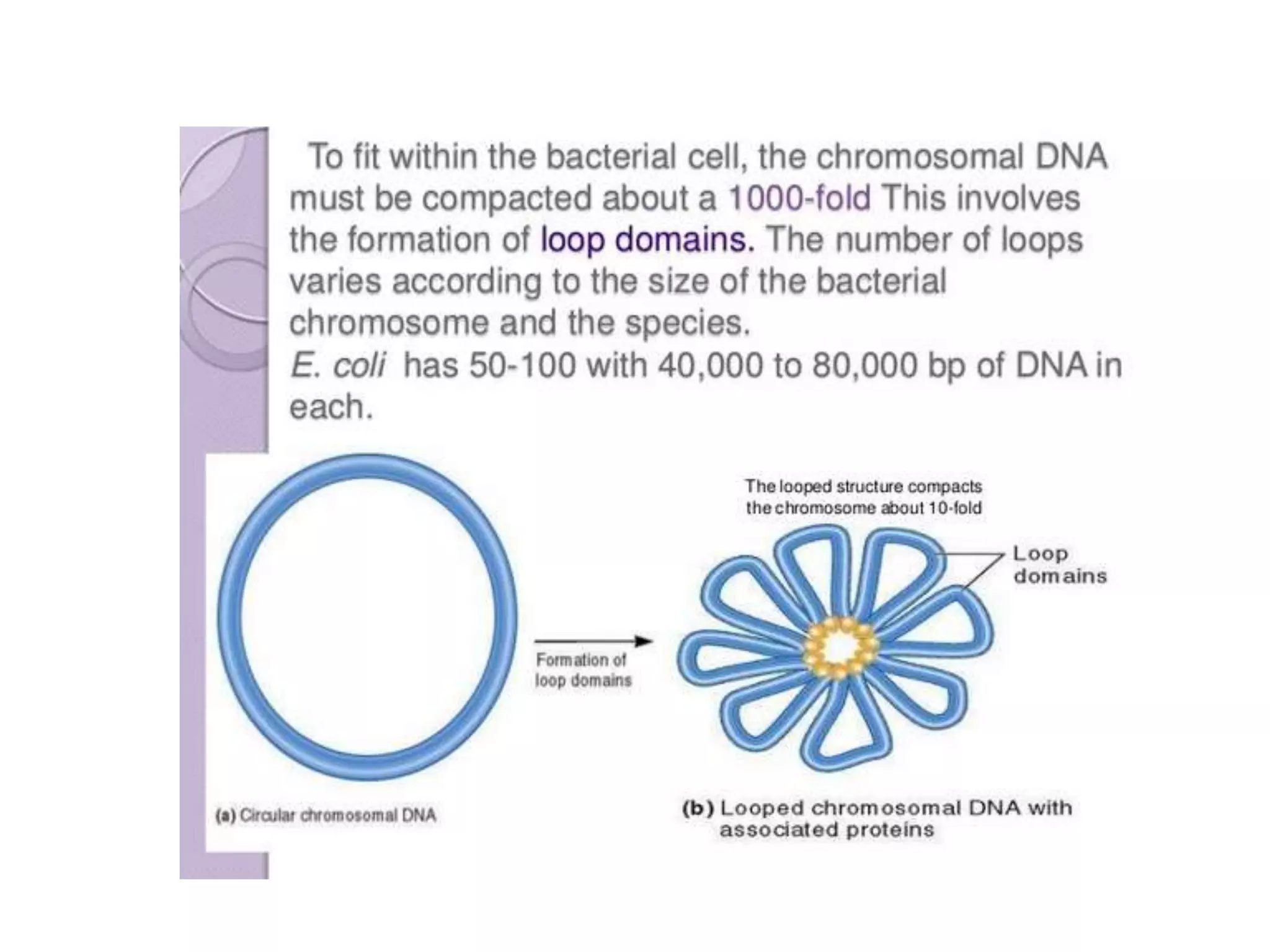
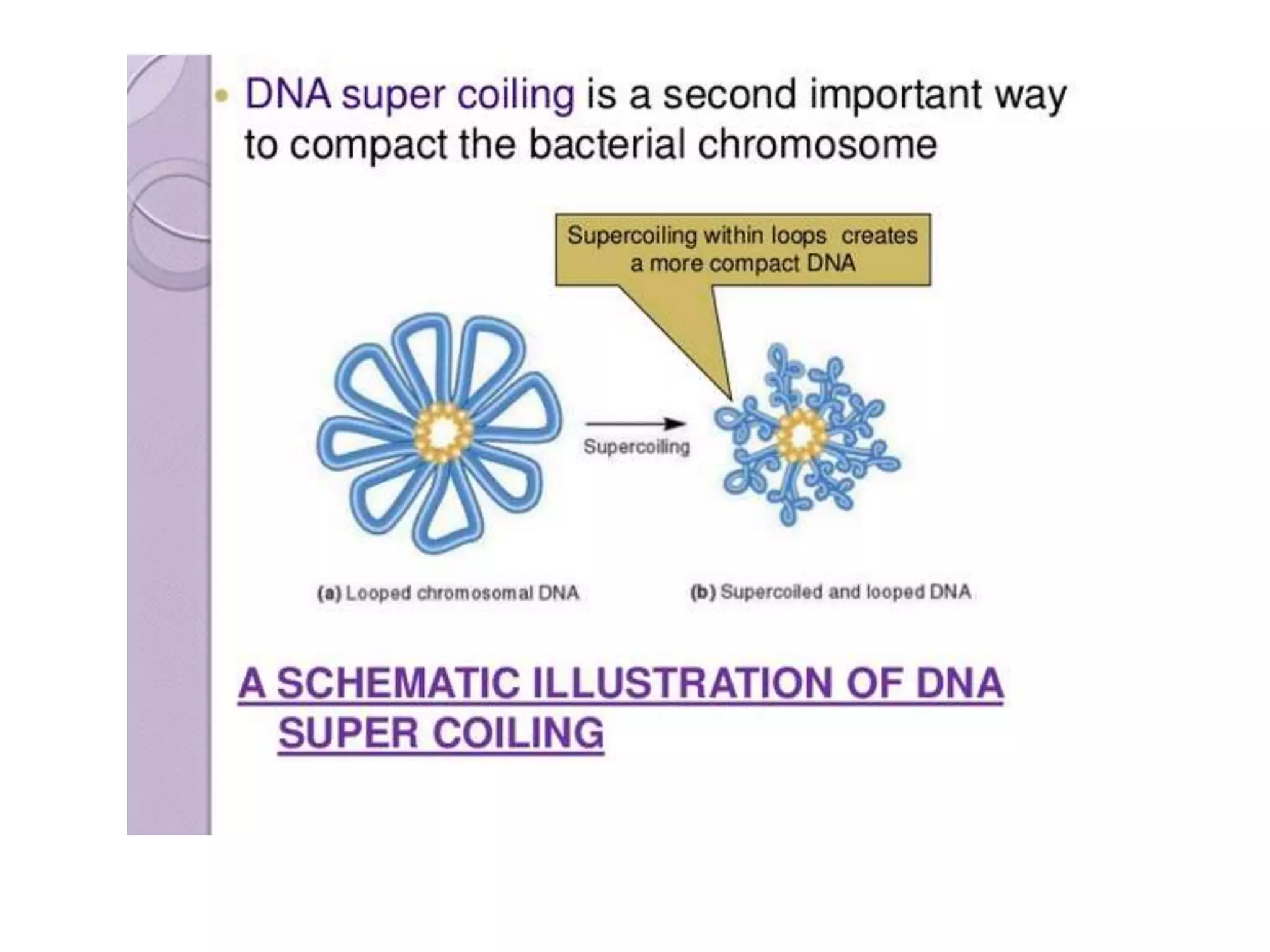
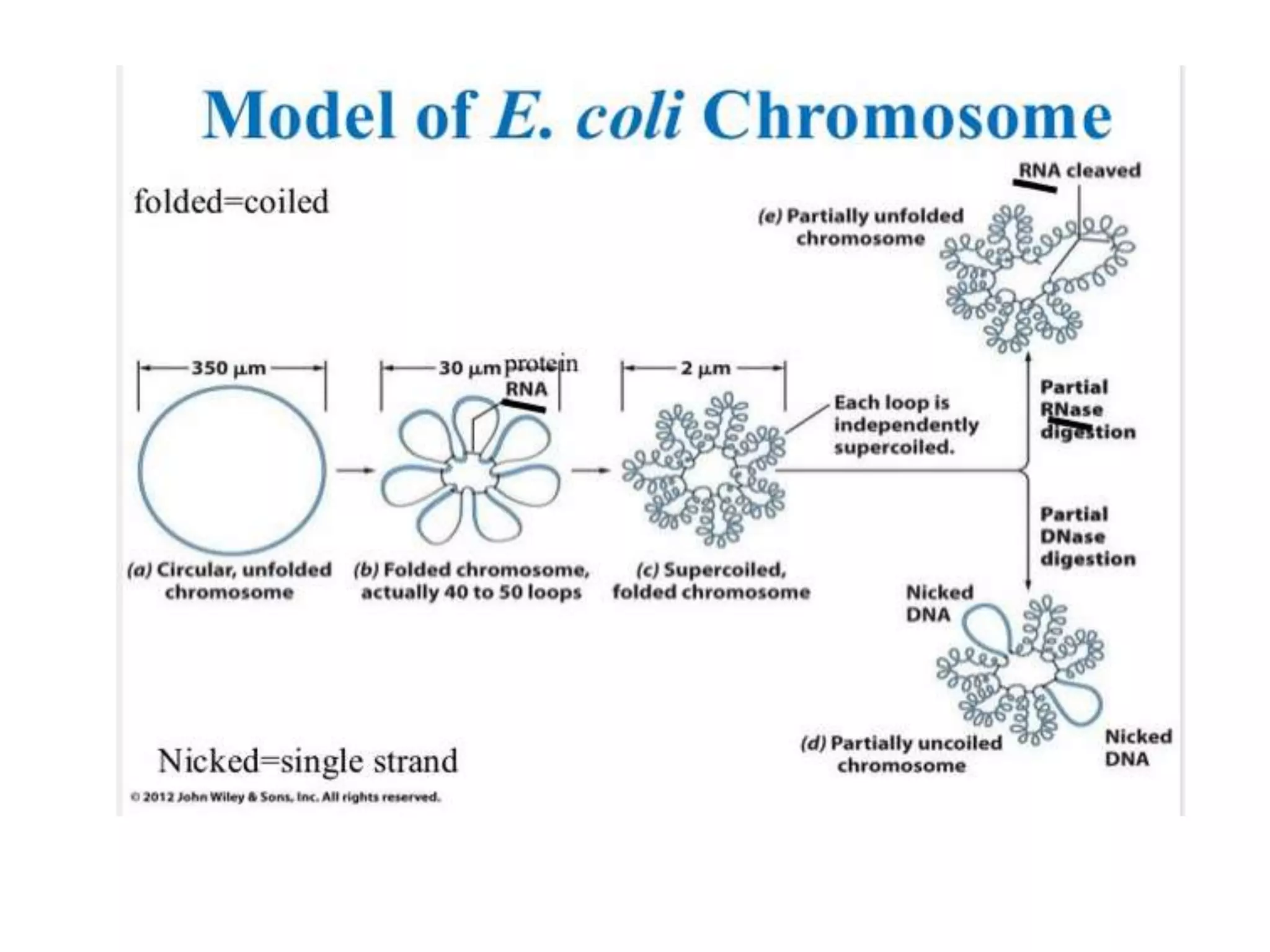
2) Prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome that must be tightly packed to fit in the cell. In E. coli, its chromosome is condensed through supercoiling and organized into loops attached to the cell membrane.
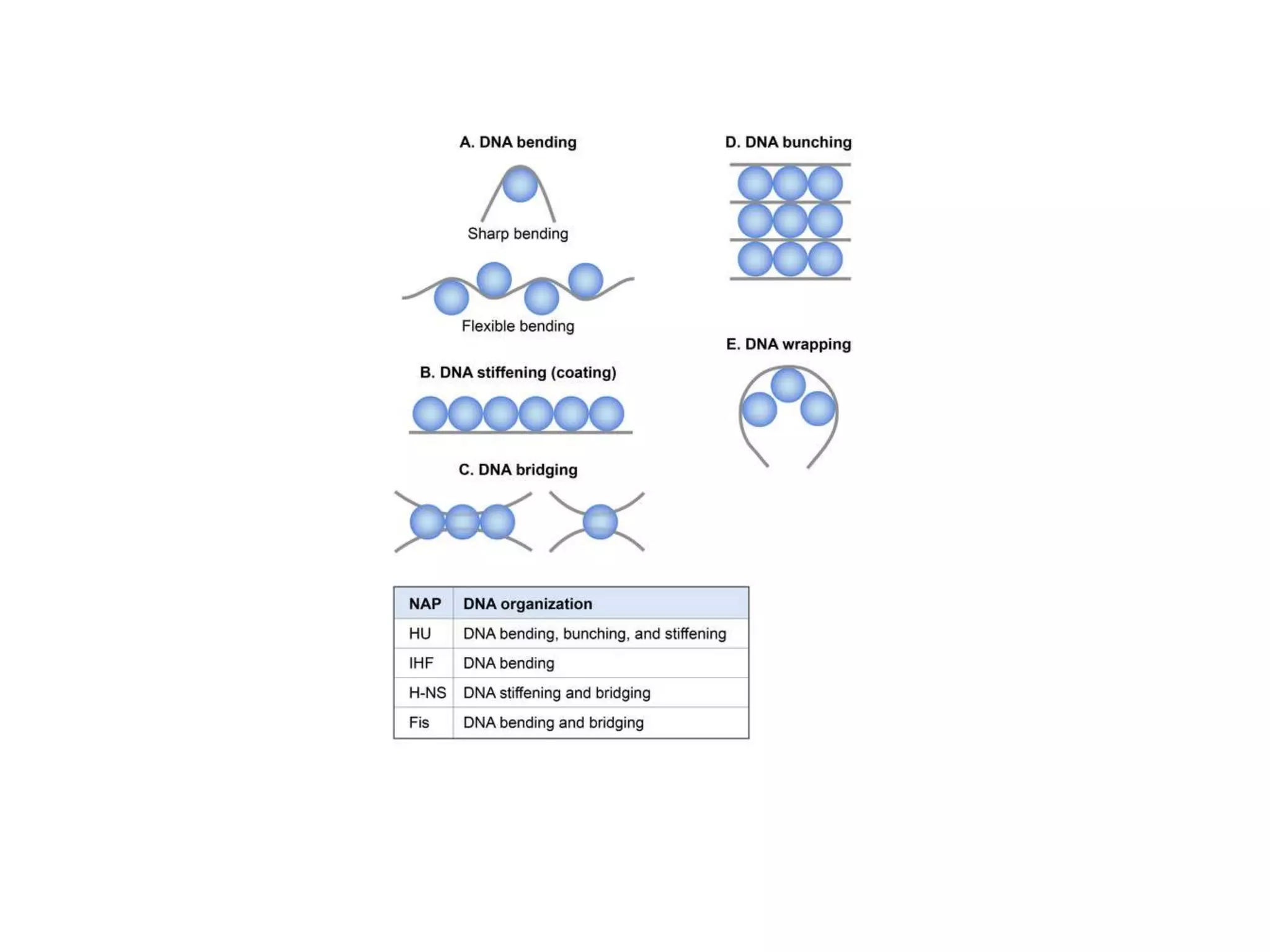
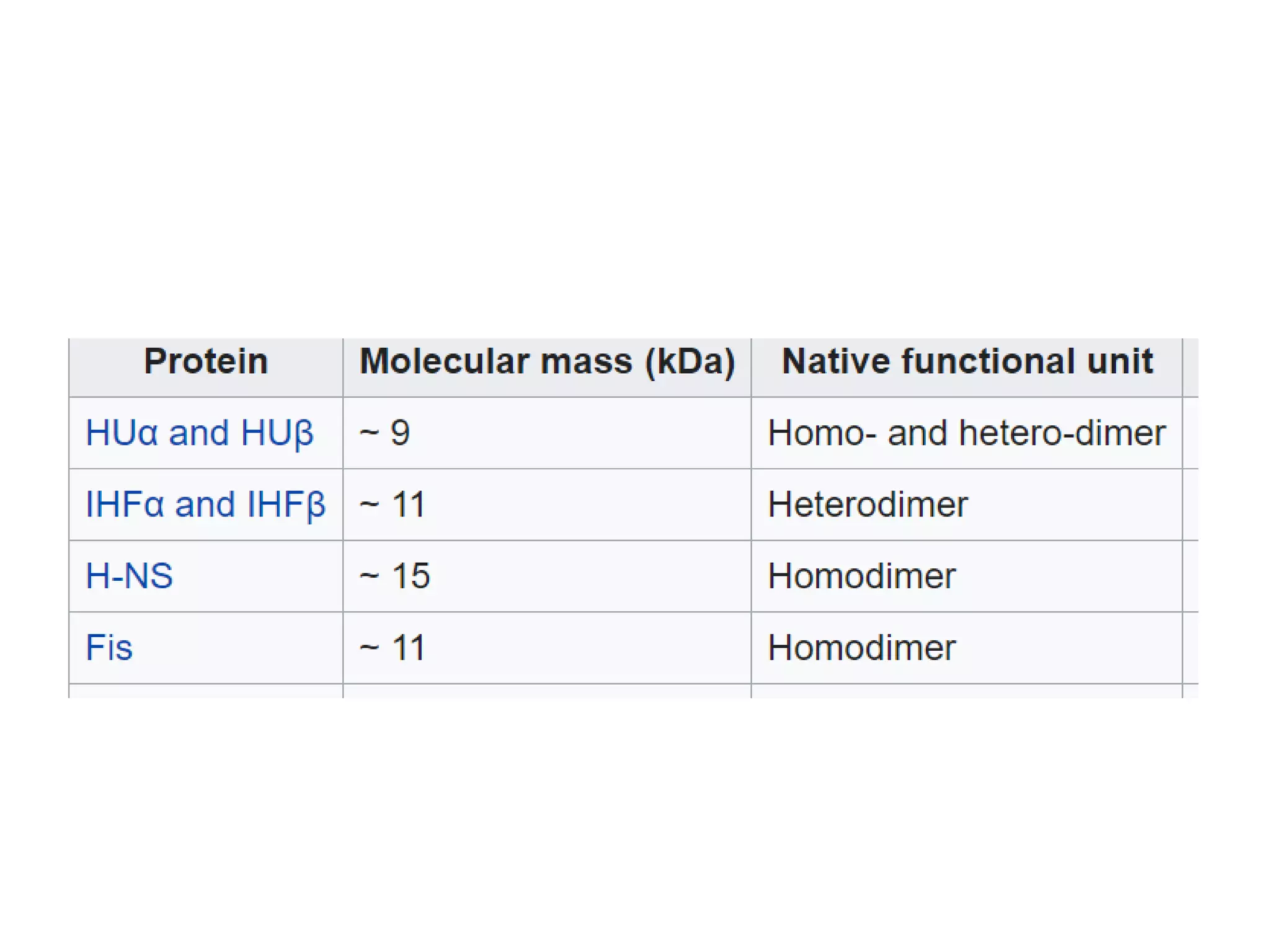
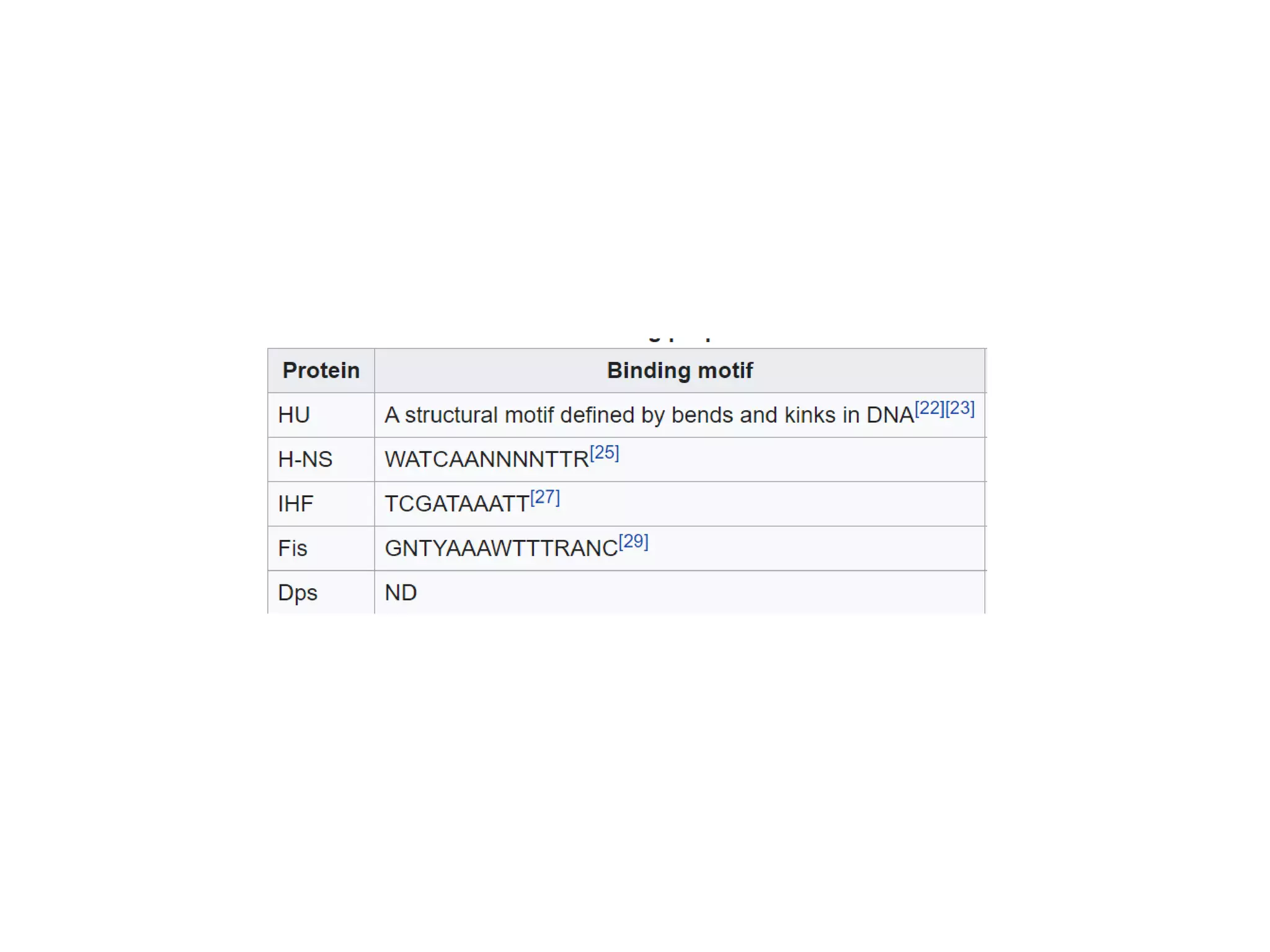
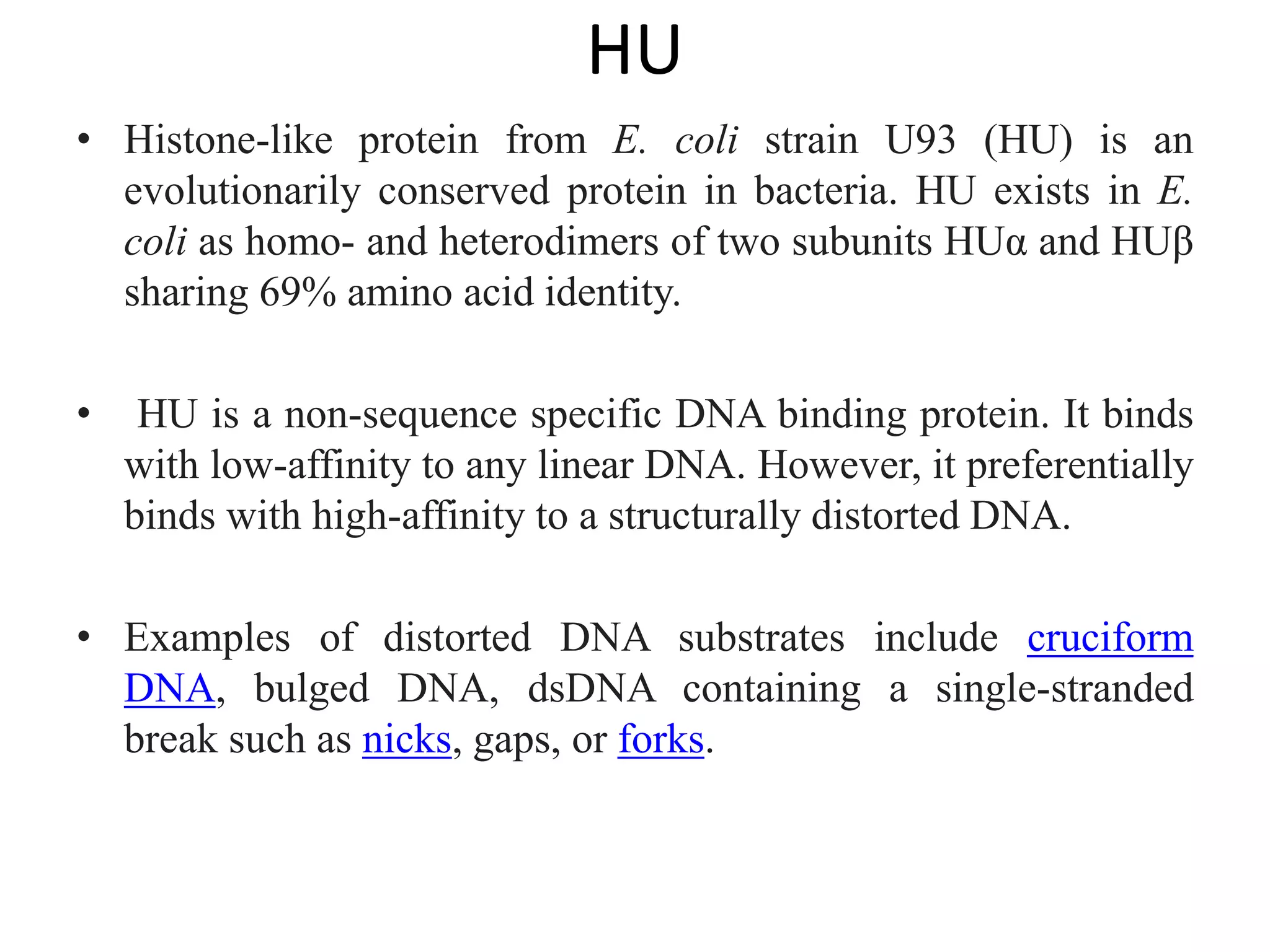
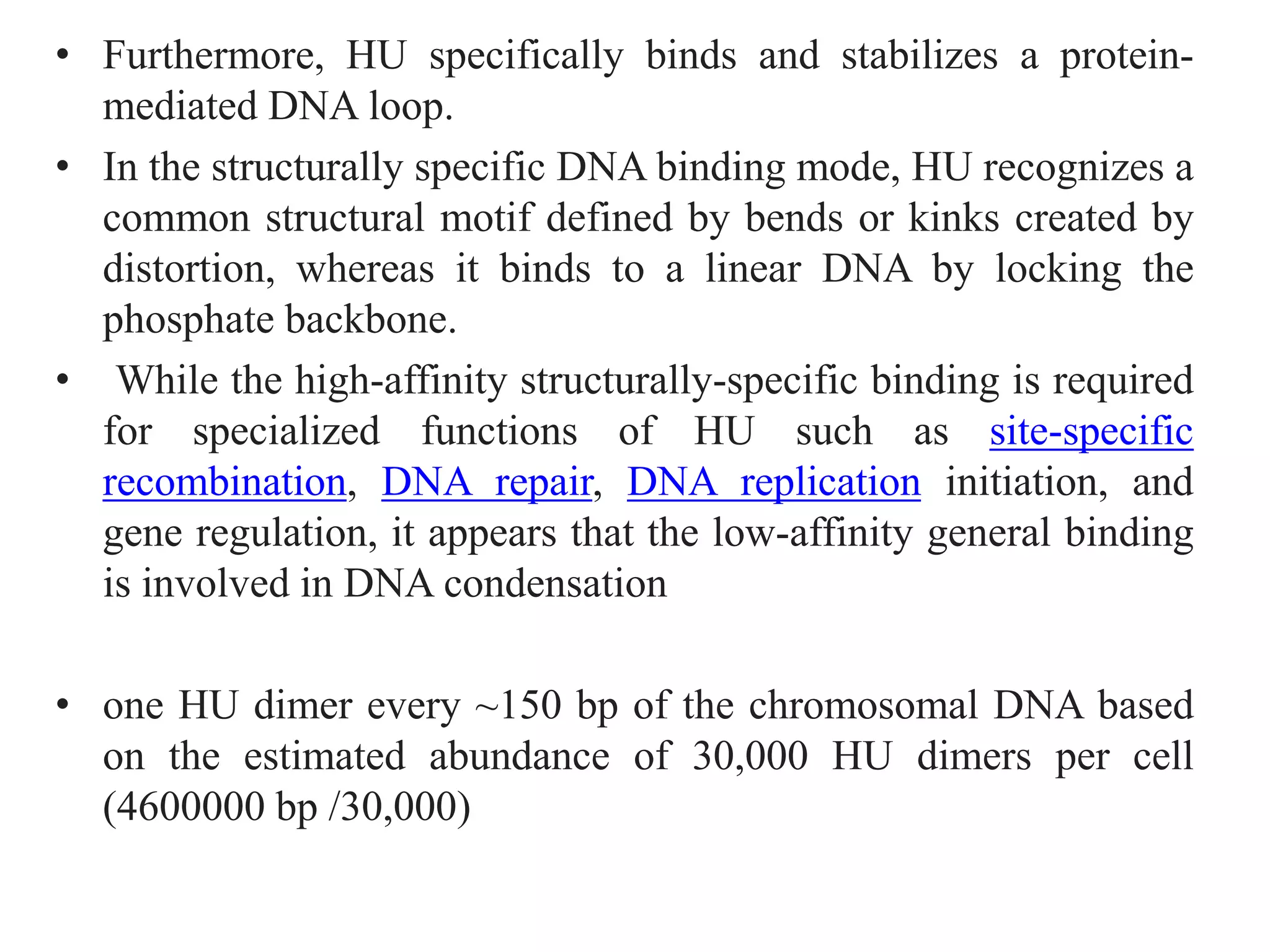
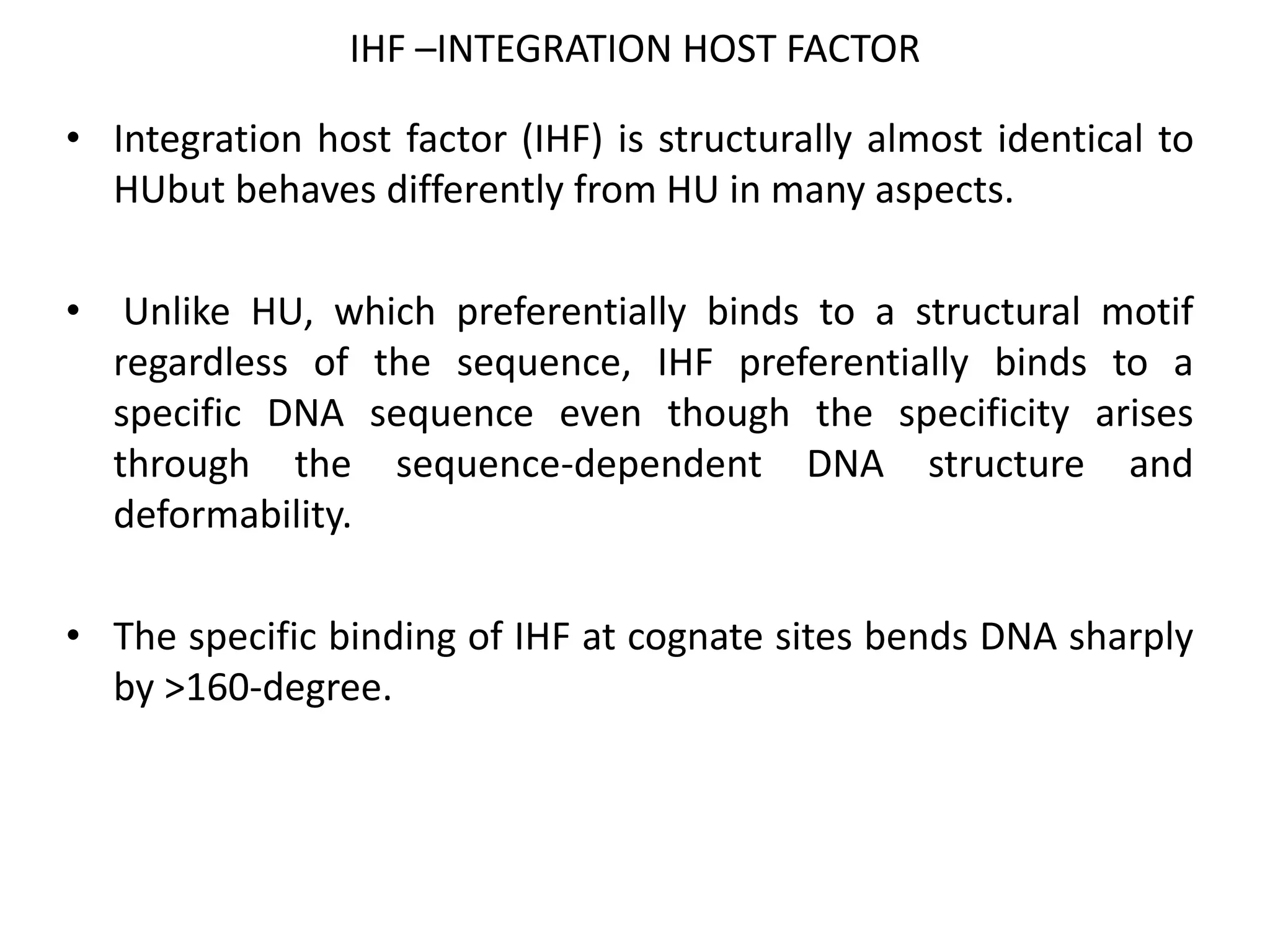
3) Nucleoid-associated proteins are important for condensing and organizing the bacterial chromosome through bridging, wrapping and constraining DNA supercoils. The most extensively studied in E. coli are HU, IHF, H-NS, and Fis.