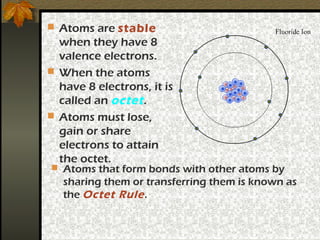
1) Atoms form chemical bonds in order to attain a stable electron configuration with 8 valence electrons, known as an octet.
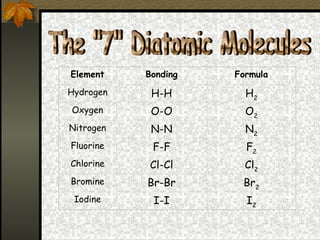
2) There are three main types of bonds: ionic bonds form when atoms transfer electrons to become ions, covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons, and metallic bonds involve delocalized electrons distributed among positively charged metal ions.
3) Whether a bond is ionic or covalent depends on the electronegativity of the atoms involved - ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds form between two nonmetals.