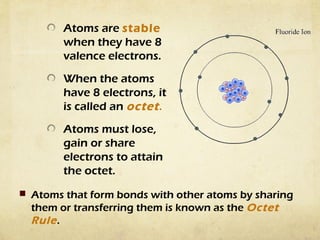
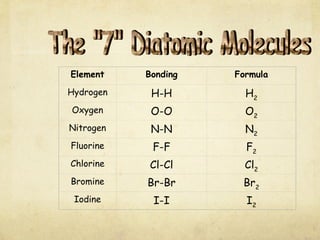
Atoms form bonds by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons to attain a stable electron configuration with 8 valence electrons, known as an octet. Ionic bonds form when atoms transfer electrons to become ions with opposite charges that are attracted to each other. Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to attain a full outer shell. Common diatomic molecules that form through covalent bonding include hydrogen (H2), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), fluorine (F2), chlorine (Cl2), bromine (Br2), and iodine (I2). Ionic bonds typically form between metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds form between two nonmetals.