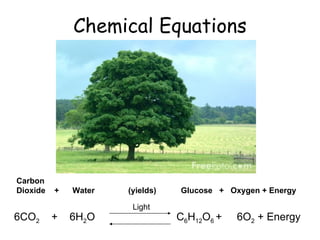
The document discusses chemical equations and balancing reactions. It provides examples of chemical equations showing the formation of glucose from carbon dioxide and water during photosynthesis, the formation of carbon dioxide from carbon and oxygen, and the formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen. It also discusses the law of conservation of mass, which states that the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products in a chemical reaction.