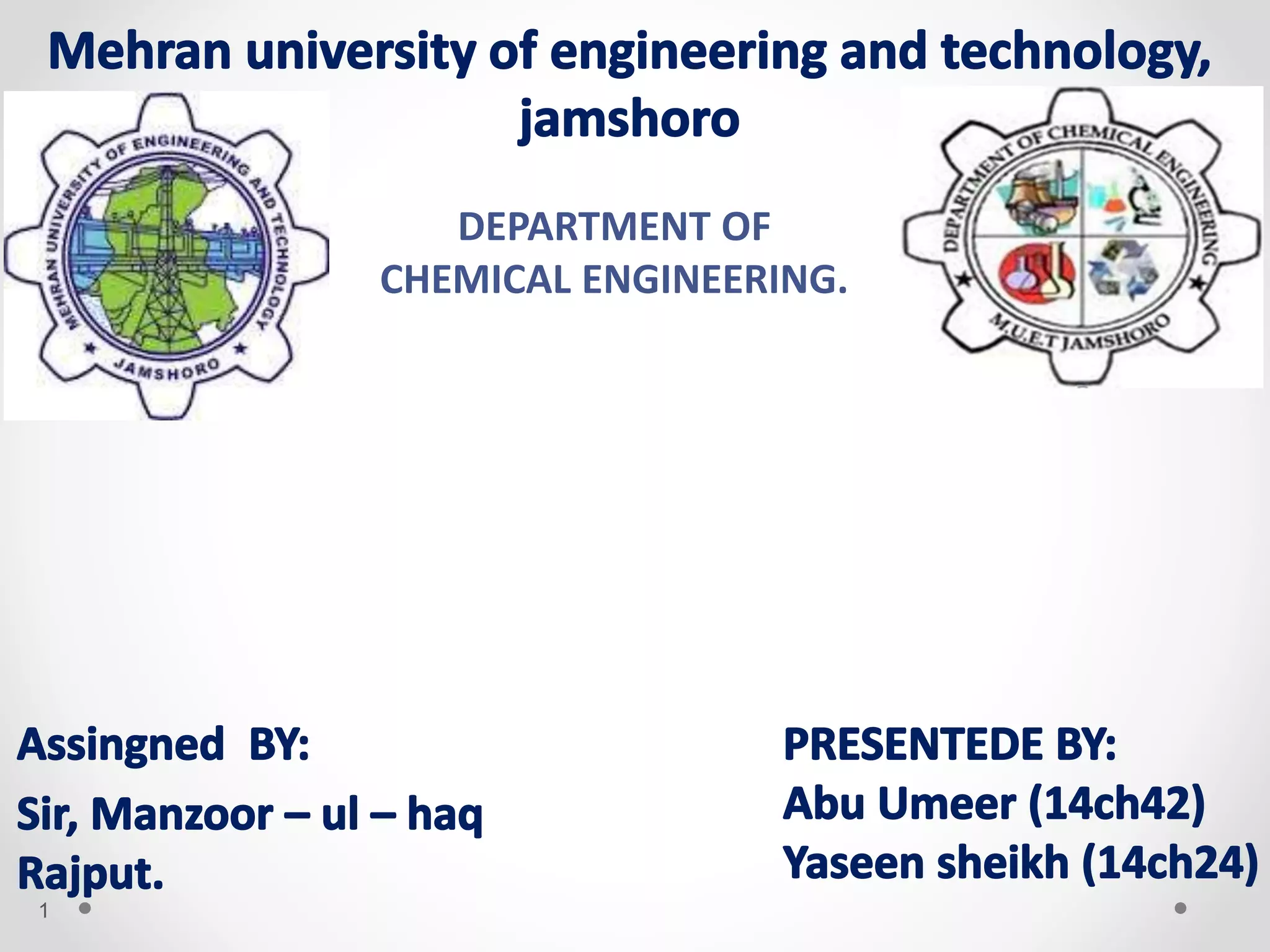
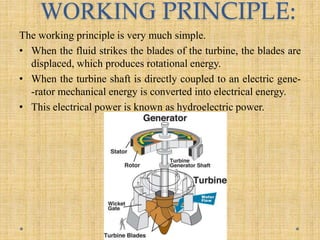
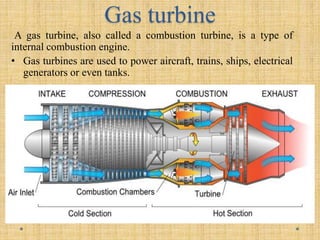
Turbines work by converting the kinetic energy of a moving fluid like water, steam, gas or wind into mechanical rotational energy. There are different types of turbines that are designed based on how the fluid interacts with the turbine blades including impulse turbines where the fluid hits the blades at high speed, and reaction turbines where the pressure of the fluid changes as it passes through the rotor blades. Common types of turbines include water turbines like the Pelton, Francis and Kaplan turbines, steam turbines used in power plants, gas turbines that power aircraft and generators, and wind turbines that convert wind energy into electricity.