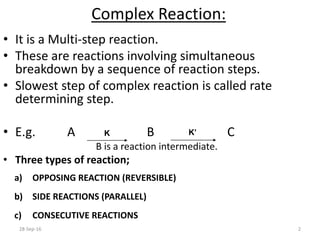
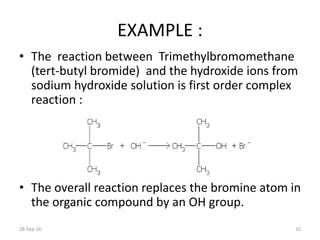
This document discusses first order complex reactions. It defines a complex reaction as a multi-step reaction involving reaction intermediates. A first order complex reaction is one where the overall reaction rate depends on the concentration of a single reactant. Determining the order of a complex reaction requires experimental analysis, as the reaction orders may not equal the stoichiometric coefficients. An example of a first order complex reaction provided is the hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide, which proceeds through a tert-butyl radical intermediate and has an overall first order dependence on the organic reactant concentration.



![Order of Reaction:
• This is the number of concentration terms that
determine the rate.
• Consider the reaction:
A + B C + D
• The overall equation is,
Rate = k [A]x [B]y
• The overall order of reaction is x+y
28-Sep-16 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stordercomplexreaction14ch42-190930090650/85/1st-order-complex-reaction-5-320.jpg)




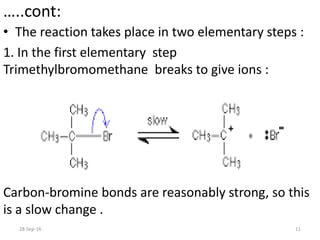
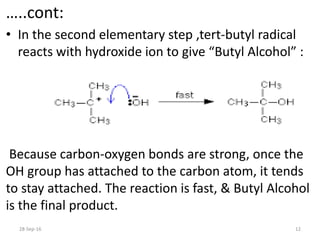
![…..cont:
• The tert-butyl radical is the reaction
intermediate.
• The slow step of a reaction is known as
the rate determining step. SO,
rate = k [C4H9Br]
• The reaction is first order with respect to the
organic compound.
28-Sep-16 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1stordercomplexreaction14ch42-190930090650/85/1st-order-complex-reaction-13-320.jpg)

