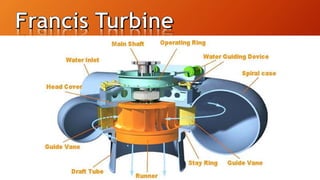
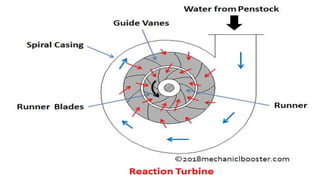
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Francis turbines, including their types, main parts, advantages, disadvantages, efficiencies, and applications such as in the Itaipu Dam. It highlights the design and operational characteristics of Francis turbines, their historical development, and recent advancements to enhance efficiency and reduce complexity. Overall, the Francis turbine is identified as a widely used and highly efficient type of water turbine suitable for hydroelectric power generation.