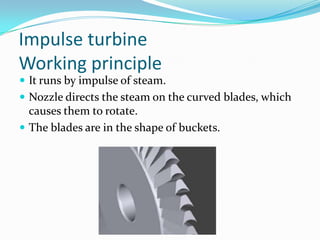
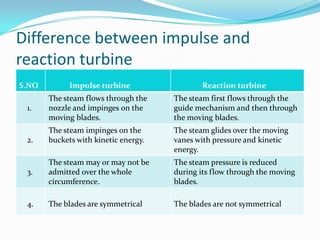
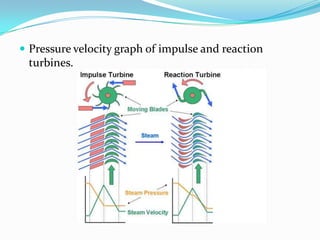
There are two basic types of turbines: impulse and reaction turbines. Impulse turbines use nozzles to direct steam onto curved blades, deriving energy from the steam's kinetic energy. Reaction turbines have fixed and moving blades, with the steam's pressure and kinetic energy driving the moving blades. Most steam turbines use a mixture of impulse and reaction stages to maximize efficiency. Turbines are used widely in power plants, ships, aircraft engines and other applications to convert fluid energy into useful rotational work.