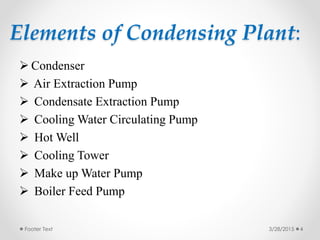
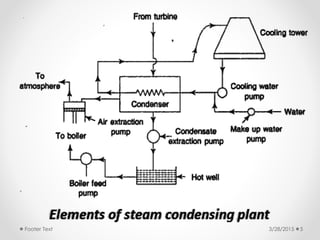
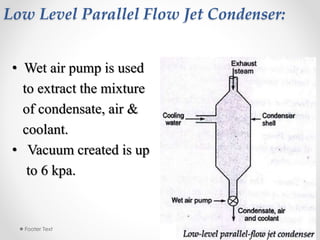
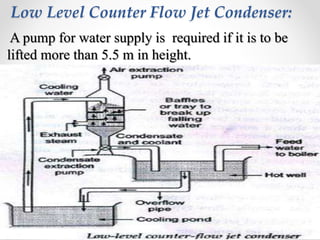
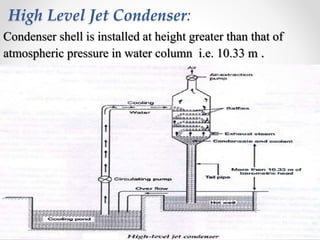
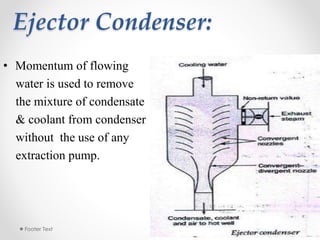
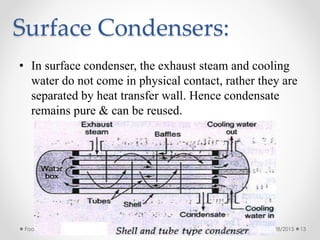
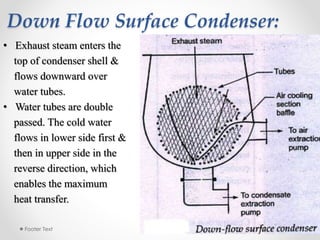
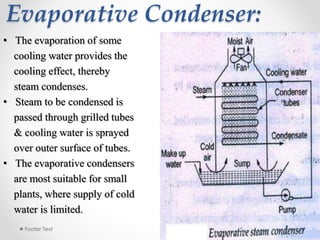
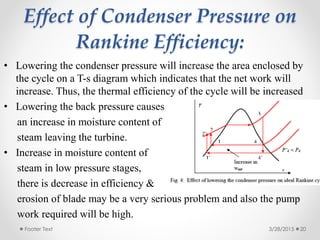
Steam condensers condense steam into water by removing heat using circulating cooling water. This reduces pressure in the turbine exhaust and increases efficiency. There are two main types: jet condensers where steam and water directly mix, and surface condensers where they are separated by a heat transfer wall, allowing pure condensate reuse. Lower condenser pressures increase thermal efficiency by allowing more expansion through the turbine, though very low pressures risk moisture issues. Vacuum is created from specific volume changes when steam condenses.