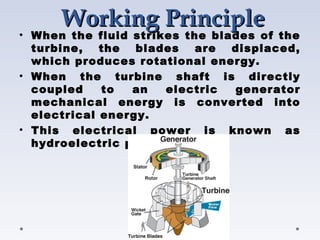
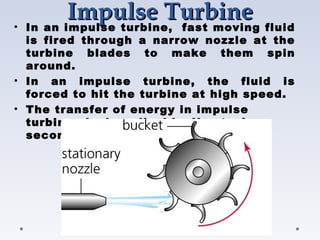
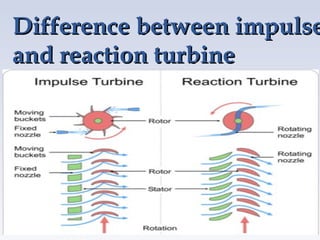
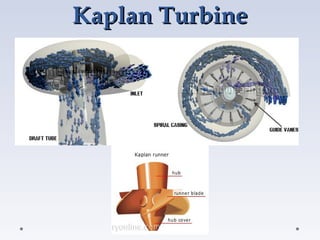
A turbine is a machine that converts kinetic energy from a moving fluid like water, steam or gas into rotational motion. There are two main types of water turbines - impulse turbines which use the velocity of a fluid jet to turn blades, and reaction turbines where the fluid's pressure changes as it passes through the turbine. Common impulse turbines are Pelton and cross-flow turbines, while Francis and Kaplan turbines are examples of reaction turbines. Turbines extract energy from fluids and convert it to electrical energy through a generator, and are widely used in hydroelectric power plants depending on factors like head and flow.