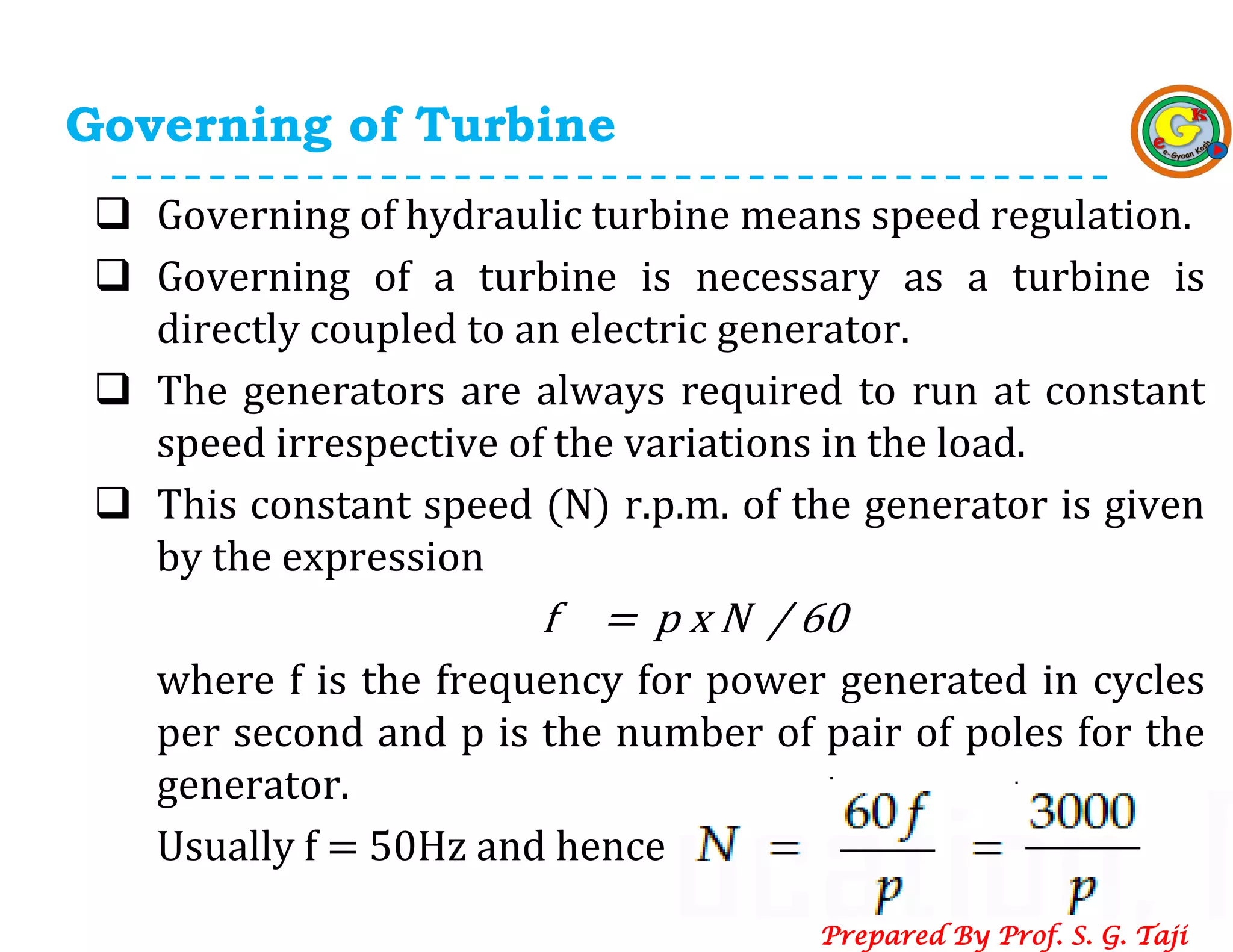
The document discusses the governing of hydraulic turbines, focusing on maintaining constant speed for electric generators connected to them. It explains the importance of speed regulation and different methods for impulse and reaction turbines, including spear and deflector regulations. Additionally, it outlines the components involved in the governing process, such as servomotors and regulating rings.