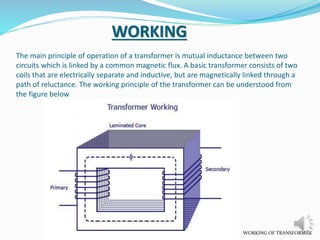
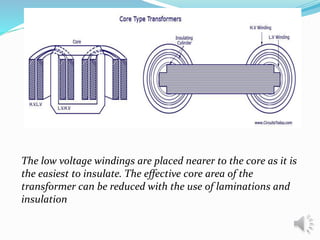
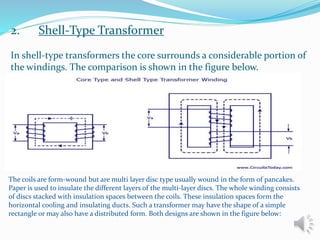
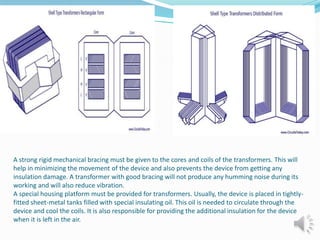
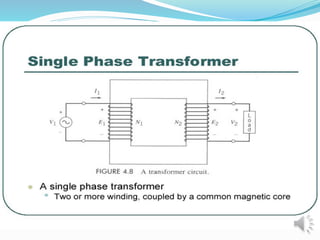
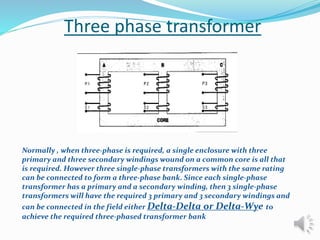
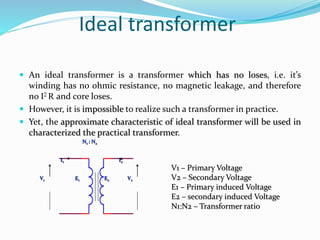
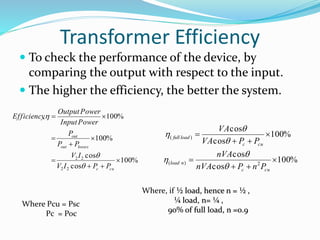
A transformer is a static device that changes alternating current (AC) at one voltage level to AC at another voltage level through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils, the primary and secondary windings, wrapped around a laminated iron core. When an alternating current is applied to the primary winding, it produces an alternating magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. This allows the transformer to step up or step down voltages without changing the frequency. The transformer transfers power between its two coils through electromagnetic coupling between the coils wound around the iron core.