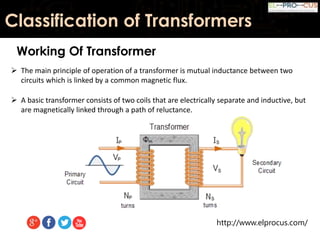
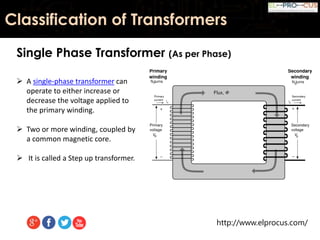
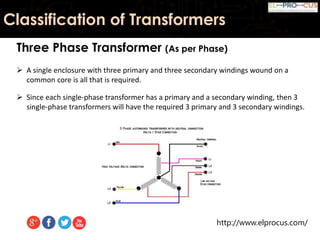
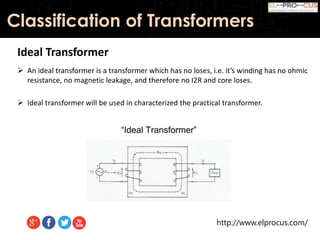
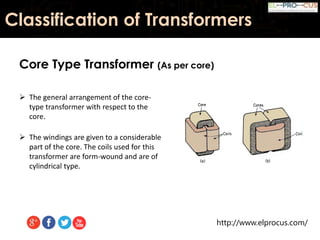
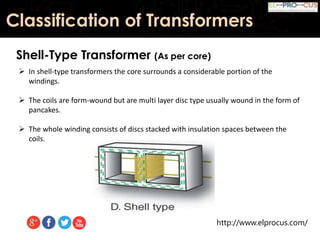
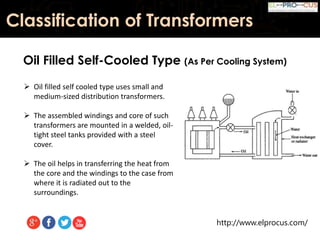
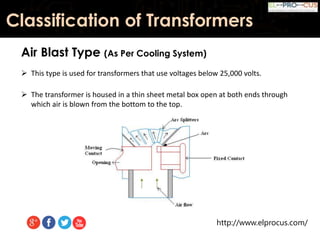
This document provides an overview of transformers, detailing their function as static devices that change AC electrical power from one voltage level to another through mutual inductance. It classifies transformers based on phase (single-phase and three-phase), core type (core type and shell type), and cooling systems (oil-filled, air-cooled). Additionally, it highlights advantages and disadvantages, concluding that transformers are essential in electrical applications for adjusting voltage and current levels.