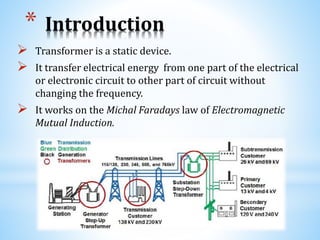
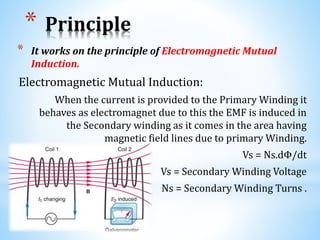
The document provides an overview of transformers, including their need, introduction, history, working principles, construction, types, and applications. Transformers are essential for adjusting voltages in power systems and come in various types such as step-up, step-down, and auto transformers. Key features include electromagnetic mutual induction, core constructions, cooling methods, and numerous applications in everyday electrical systems.