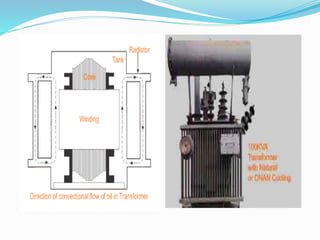
A transformer transfers electric power from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils with a common magnetic core that allows power in one coil to induce a magnetic field that generates power in the other coil. Transformers operate by mutual inductance between the two coils and can raise or lower voltage levels while proportionally changing current. Commercial transformers have laminated steel cores to reduce eddy currents and losses, and use different cooling methods like air or water to dissipate heat from transformer components under load.