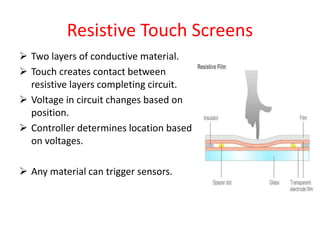
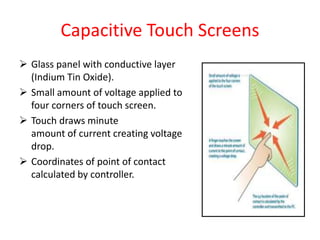
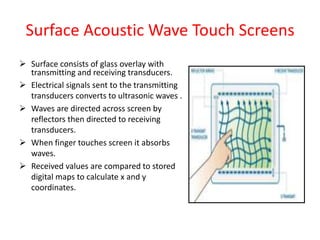
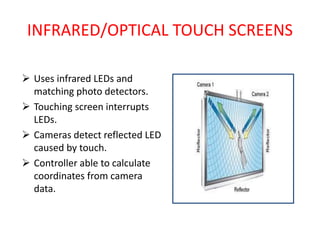
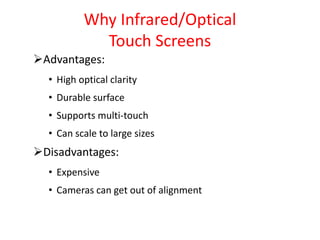
Touch screens can detect the presence and location of touch within the display area. There are four main touch screen technologies: resistive, capacitive, surface acoustic wave, and infrared/optical. Resistive screens use two conductive layers that create a circuit when touched. Capacitive screens use glass with a conductive layer and detect minute currents from a touch. Surface acoustic wave screens use ultrasonic waves disrupted by touch. Infrared/optical screens use LEDs and cameras to detect touches interrupting the LEDs. Touch screens enable direct interaction with displays and are found in devices like phones, games, and kiosks.