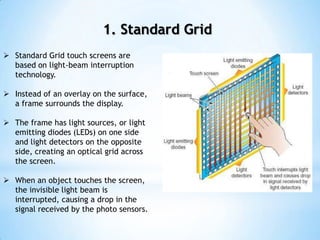
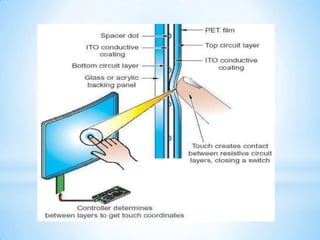
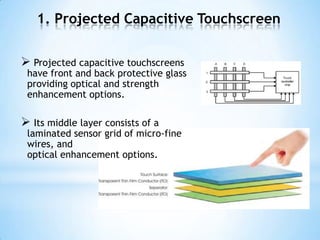
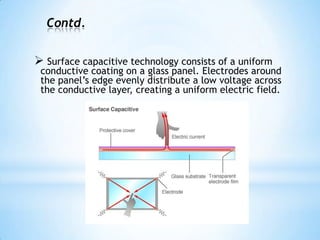
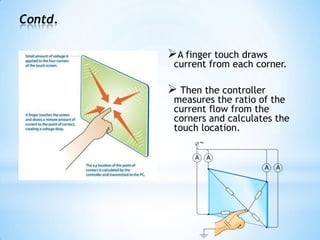
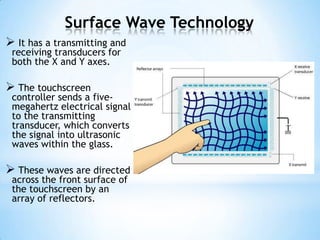
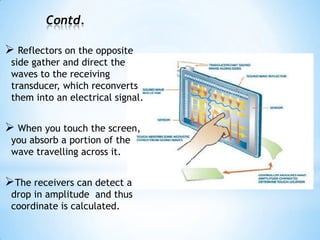
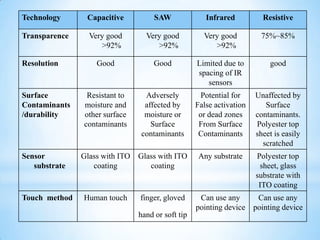
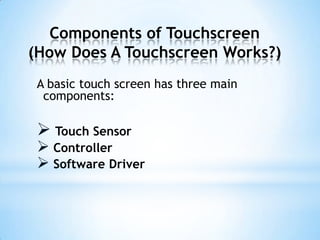
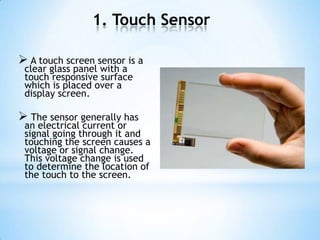
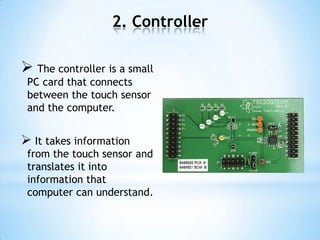
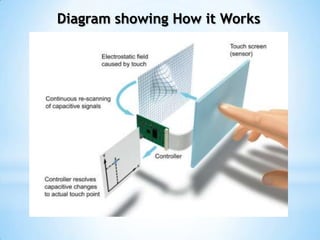
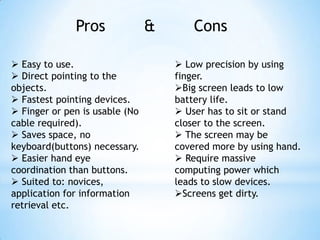
The document provides an overview of touch screen technologies, including their history, functions, various types, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. It details the evolution from the first touch sensor developed in 1971 to modern technologies like capacitive and surface acoustic wave touch screens, highlighting how they work and their components. Additionally, it discusses future developments and the potential for replacing traditional input methods like keyboards and mice.